Install the IBM z/OS Connect Server zosConnect-3.0 feature image to a Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform
How to build and deploy an IBM® z/OS Connect
zosConnect-3.0 API by using a zosConnect-3.0 API project and the z/OS Connect Server image to install
z/OS Connect to an OCI-compliant container platform in an online environment.
About this task
zosConnect-3.0 Applies to zosConnect-3.0.
Containers Applies to z/OS Connect container deployments.
Throughout this topic, Docker is used as an example for image build technology and Red Hat® OpenShift® Container Platform is used as an example for the container deployment. Note, Red Hat OpenShift 4.9 is supported on Linux/s390x and amd64.
The z/OS Connect Server and IBM z/OS Connect Designer images are supported by Open Container Initiative (OCI) compliant runtimes and other OCI-compliant container runtimes and container registries can be used.
- To install and deploy the z/OS Connect API image in an online environment, complete the installation steps in Table 1 in sequence.
- To install and deploy the z/OS Connect API image in an offline environment, see Install the IBM z/OS Connect Server zosConnect-3.0 feature image to an offline Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform.
- The z/OS Connect documentation is available in the IBM Document offline tool, should you require an
offline
copy. For more information, seeIBM z/OS Connect offline documentation.
The following topic describes the steps that are required to build and deploy the IBM z/OS Connect Server API image with Red Hat OpenShift. For information on how-to build and deploy the z/OS Connect API images with Podman, see Installing and uninstalling an IBM z/OS Connect Server image with Podman.
| z/OS Connect installation steps |
|---|
| Download the z/OS Connect Server image. |
| Verify the z/OS Connect Server image (Optional). |
| Build the z/OS Connect API image. |
| Install the IBM Operator Catalog. |
| Install the IBM z/OS Connect Operator. |
| Configure an image pull secret. |
| Configure environment variables. (Optional) |
| Configure Transport Layer Security (TLS networking capability) (Optional). |
Create a ZosConnect Custom Resource instance. |
| Invoke z/OS Connect API. |
The following tasks must be completed.
- Access to an OCI-compliant container platform.
In this procedure, the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform is used as an example.
- For detailed steps about how to install Red Hat OpenShift, see
Installing Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform.
- Ensure that you have a supported version of Red Hat OpenShift installed. For more information about
Red Hat OpenShift compatibility, see
Supported OpenShift and Kubernetes versions
- For detailed steps about how to install Red Hat OpenShift, see
- Access to an OCI-compliant container runtime.
The example commands in the following procedure use docker. If you are using Podman as your container platform, use podman instead of docker in the example commands. For more information about installing Docker, see
Download and Install Docker Desktop.
- Create a z/OS Connect API project.zosConnect-3.0 artifacts (WAR files) can be deployed in a z/OS Connect Server container that is at the same release level or later than the release level of the z/OS Connect Designer that was used to generate the artifacts. For more information, see Developing API provider with zosConnect-3.0 and z/OS Connect artifact compatibility.Restriction: WAR files should not be deployed in a z/OS Connect Server container that is an older release level than the release level of the z/OS Connect Designer.
- Configure the Container Platform cluster with Role Based Access-Control (RBAC) ready for the
deployment of z/OS Connect APIs. For more information
about how to configure
cloud adminandapplication developerroles for z/OS Connect on Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform, seeAuthorizing users for z/OS Connect by using role-based access control (RBAC). For more information about RBAC, see
RBAC overview.
Important: RBAC must be configured on the cluster before starting the installation procedure. - Optional: Verify that the z/OS Connect Server image signature is an optional step. If you need to verify the z/OS Connect signed images, you need to install the following
command-line tools:
Gnu Privacy Guard
OpenSSL
skopeo
Note: These command-line tools can usually be installed on Linux by using the package manager.
- Optional: If using z/OS Connect policies to adjust how an API request is processed in z/OS Connect, see Configuring IBM z/OS Connect policies. When building the WAR file in Build a z/OS Connect API image as part of this procedure, you must include the policy configuration and rules file within the image.
Download a z/OS Connect Server zosConnect-3.0 feature image
Before you begin
The following tasks must be completed.
-
Download and install an OCI-compliant container runtime.
Note: Docker is used as an example container tool. Docker 19.0.3 or higher is supported.Other OCI-compliant container tools, such as Podman are also supported.
- To get access to the z/OS Connect Server image, you must have an IBM entitlement registry key to pull the images from the IBM Cloud Container Registry
icr.io. Refer to your license document for specific instructions on obtaining
the entitlement key.Note: If you don't have the license document with the entitlement key, place a new order for the product in
ShopZ where the additional documentation contains the entitlement key. As an existing customer, if you already have a license for IBM z/OS Connect Unlimited, no charge is incurred when the new order is placed.
Procedure
Results
docker image ls
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
icr.io/zosconnectunlimited/ibm-zcon-server 3.0.100 6d2af17d10bd 1 days ago 979MBWhat to do next
-
Optional: z/OS Connect images are signed. You must have downloaded an z/OS Connect Server image to continue the installation procedure. For more information on verifying image signatures, see Verify a z/OS Connect image signature (Optional).
If you don't need to verify your image signatures, build your z/OS Connect API image by using a z/OS Connect API project and the z/OS Connect Server image that is downloaded in this step. For more information, see Build a z/OS Connect API image.
Verify a z/OS Connect image signature (Optional)
Digital signatures provide a way to ensure that an image is both authentic (it originated from the expected source) and has integrity (it is what is expected). z/OS Connect images are signed and this topic describes how to verify the signatures on those images.
Before you begin
The following tasks must be completed.
-
The z/OS Connect public keys must exist on the same machine as the command-line tools.
Copy the following text block exactly as shown into a text editor, and save it in a file namedPRD0012028key.pub.asc:-----BEGIN PGP PUBLIC KEY BLOCK----- mQINBGQU0cUBEACqSHOnQ2HyQRdr0dkcYpehWGz/OSXLpOiKpmgqcvLEm2ZIGpZu pzN5wc57XOxhz5YNodODFysewjqKntgQg1EbQ85g8BmV14iZJZ/8oVMCQGe6yt2G efpD1+qY/QxK+JBB45Y5E6TEudNPzhhNY/9BsImPvHLSD95ikMYHVs2jCIquTXdT UC1fyaXKU5T1qQZd1XxTX+HEaFGIInRHRWvjw2z92LNM35Ul6vJU5R8f8yVZIRAG Y+J8/4qBRd2w23uUupNWQw6QYdW3Q3K6LVZc3K9ykJ8/zNaYBLT/dUXd3L2UYPO7 glWmO3oJynGc0kQczq/ohtCiUtKkXigYZ1feFC0nrFsVa7+Edzao5LOCYNhd9ASM KZBL11VYvQ9pdjeWa4yd/VuTtG6l3GwN1AHXY+dLYdG3lrB0UmTNfyHZoJtIJ+yd cmTZHhfvQ5djjCDwuNxN6NLuAKkzBzUNK3CMi7swKwym7agidMtf4G/WUAy981+P 502RGEtEDO98egA7yEXjGNB0vh7wuqyUKtugsCpGYQhuto42L8nEUogM69JK8Z9J d2xs9PM/N8DEFdOXc73MMYnZejstoZ71t79MyEKw/3flKMADJE3x1xebnOMIj4CI 32Mnc0YHnmeADuYRtbk8omEOQAlWJrCFRUMr8+uSfvUb8QChuhKZDURRKQARAQAB tEBJQk0gei9PUyBDb25uZWN0IEVudGVycHJpc2UgRWRpdGlvbiBVbmxpbWl0ZWQg PHBzaXJ0QHVzLmlibS5jb20+iQI6BBMBCAAkBQJkFNHFAhsPBQsJCAcCBhUKCQgL AgQWAgMBAh4BBQkAAAAAAAoJELBRtMIty7kNhqwP/1YQPQECXMUqno1z0OfQK+Wn +eVQlS8cwvgarpKMv/a3tjFwggJvTaB6TRzdEcBHMSaXqY0+ljnHn7pHWtIQA3uR FZszNWWzsRG9ahlne2NqjIwzCrvIN0BNKL3LSsJWOOptSTSjCxqeg9UmThdtXBu4 8DBCjHSsvtNa0hnSJG2tC5HQ3bnoduU1D7v9jZIP2SEg/lL6iZkKAz1HLxT9oqLL KMpoUAVwRFN/wTFpQy83loxkU+xqXHgcq0htZWWspeqRrTSGkhtqEDcO8Bt3jSQ0 p9U7Bq9chpmEwngN5WwtvxXcrMMerlbaVJ6jLbNnJwERv+Q5N36Wl1hoNffV6Itw LOYp4rfqO6eV5yFmC2gYLq6xMEHHM4q8nUQ1KhmwoARzwXJuRxocDl62kjq2YBOR 6H8WLZmHuE0ba0dp4JR+Wg99no2Sud4dT6Rs/ZylezyJGaFEEK7NNrl+G1JYVbms Ynq6McZVz+Hcqow5k7PsZ4KviFb+F/DlP/lNCDlabFy+IC0gD4gjoKYbyOed+rKc ZUd4DDxLl2KqEUiItn3aIU3epLAf9MtrGd+tugwMQPaq0v2Gep8zntuWew2TWEoy c7C0udUwdjw1q4SwyJzYwiapwz6LCu+dlu7sf2Kxds5USYBWsrTxVzga3/BtRghK V7Pi5/oMEPjk9O7eoOnL =2ZDV -----END PGP PUBLIC KEY BLOCK----
About this task
z/OS Connect images are signed. If you need to verify the image signatures, complete the following procedure.
Enabling signature verification when container images are pulled to a host system can be
automated. For information on automating image signature verification, see
Verifying image signing for Red
Hat Container Registry.
Some of the steps in this procedure use gpg. GPG2 is the extended version of GPG
and gpg2 can be used instead of gpg.
Procedure
Results
Build a z/OS Connect API image
About this task
To build a z/OS Connect API image from your API
project, you must use the container platform tool of your choice to build an image
FROM the z/OS Connect Server image.
To prepare your z/OS Connect API project image for a container environment, you must use the z/OS Connect Server image. For more information, see Download a z/OS Connect Server zosConnect-3.0 feature image.
Procedure
Results
The container runtime, for example Docker, validates a successful push. The z/OS Connect API image is now hosted in the private Container Registry registry to access externally with valid login credentials.
Log in to your private Container Registry to verify the successful push of the z/OS Connect API image.
Install the IBM Operator Catalog in Red Hat OpenShift
Before you begin
- You must be logged in to Red Hat OpenShift Web
Console with your Administrator user role. If you do not have a cluster-admin
role, see
Authorizing users for z/OS Connect by using role-based access control (RBAC).
About this task
Create and apply the ibm-operator-catalog CatalogSource resource to the cluster
to enable the IBM Operator Catalog to include all
IBM Operators, such as the IBM z/OS Connect Operator.
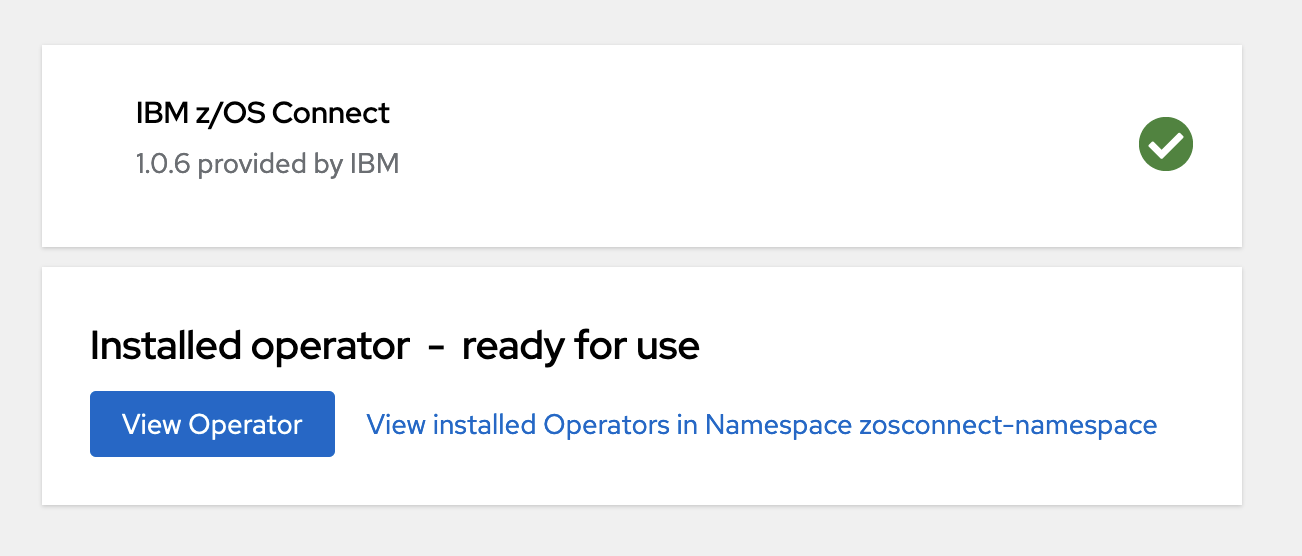
After you complete this task, the IBM z/OS Connect Operator is available in the OperatorHub section of the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform.
Procedure
Results
CatalogSource is successfully applied and the z/OS Connect tile that is used in the next task is available
in the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform
OperatorHub.Install the IBM z/OS Connect Operator
Install the IBM z/OS Connect Operator to deploy z/OS Connect APIs in a Container Platform.
About this task
The IBM z/OS Connect Operator is an application that
is deployed to the Red Hat OpenShift Container
Platform, by using Red Hat OpenShift Web Console
OperatorHub. Once installed, the ZosConnect Custom Resource (CR) is available on
the cluster, where the z/OS Connect API deployment
details are defined. The IBM z/OS Connect Operator
watches for the ZosConnect CR, and uses it to create the resources needed for the
deployment of a z/OS Connect API in Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform.
- Default - The
AllNamespacesinstallation mode supports a single IBM z/OS Connect Operator to be installed in the cluster, which watches forZosConnectCR instances that are created in any namespace. - The
OwnNamespaceinstallation mode supports multiple IBM z/OS Connect Operators to be installed in the cluster, however it only watches forZosConnectCR instances that are created in its own namespace.
ZosConnect CR, therefore multiple z/OS Connect API deployments.Procedure
Configure an image pull secret in the Container Platform
About this task
In this task, an image pull secret is created in Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform that contains the
Container Registry location and credentials for the z/OS Connect API built in Build a z/OS Connect API image. For more information, see
Using image pull secrets.
Procedure
Results
What to do next
If your API project requires environment variables for the connection and credential details, go to Configure environment variables (Optional).
If you need to configure TLS, see Configure Transport Layer Security (TLS) in a Container Platform (Optional). For more
information about TLS, see
Self-Serviced End-to-end Encryption Approaches for Applications
Deployed in OpenShift
If you use volumes in a container platform to mount keystores for your z/OS Connect API image to use, see Configure volumes (Optional).
Otherwise, you have completed the preparation steps and are ready to deploy your z/OS Connect API image. For more information, see Create a ZosConnect Custom Resource (CR).
Configure environment variables (Optional)
Use ConfigMap and Secret Objects in a Container
Platform to store the connection and credential configuration values for your z/OS Connect API image to use.
About this task
If the z/OS Connect API image built in Build a z/OS Connect API image contains a z/OS Connect API project with connection and credential
environment variables, you must use a ConfigMap, and optionally a
Secret in the Red Hat OpenShift
Container Platform.
The ConfigMap and Secret Objects store the connection and
credential configuration values in the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform. These are then
mapped to your z/OS Connect API image in the Create a ZosConnect Custom Resource (CR) instance.
The z/OS Connect API project connection and credential configurations are in the ../liberty/config directory.
-
A
ConfigMapis used to store connection information. For example, a ../liberty/config/db2.xml with
To create a<zosconnect_db2Connection id="db2Conn" host="${DB2_HOST}" port="${DB2_PORT}" credentialRef="commonCredentials" />ConfigMap, follow theConfigMapsteps in the following procedure. -
A
Secretis used to store credential information. For example, ../liberty/config/db2.xml with
To create a<zosconnect_credential user="${DB2_USERNAME}" password="${DB2_PASSWORD}" id="commonCredentials" />Secret, follow theSecretsteps in the following procedure.
ConfigMap and
Secret in Red Hat OpenShift.If you require environment variables, complete the procedure in order.
Procedure
What to do next
If you need to configure TLS (secure networking configuration options), see Configure Transport Layer Security (TLS) in a Container Platform (Optional). For more information, see
Self-Serviced End-to-end Encryption Approaches for Applications
Deployed in OpenShift.
If you use volumes in a container platform to mount keystores for your z/OS Connect API image to use, see Configure volumes (Optional).
Otherwise, the preparation steps are complete and you are ready to deploy your z/OS Connect API image. For more information, see Create a ZosConnect Custom Resource (CR) instance .
Configure Transport Layer Security (TLS) in a Container Platform (Optional)
Configuring TLS (secure networking configuration options) for a z/OS Connect API deployed to a Container Platform with the IBM z/OS Connect Operator.
Before you begin
This page outlines the secure networking (TLS) configuration options for a z/OS Connect API deployed to a Container Platform with the IBM z/OS Connect Operator.
If your z/OS Connect API requires environment variable configuration for connection and credential details, you must complete the configuration preparation steps before starting this section. For more information, see Configure environment variables (Optional).
About this task
At the end of this topic, you will understand the methods of configuring TLS for a z/OS Connect API deployed to a Container Platform. You will have completed the preparation steps required for the next topic, Create a ZosConnect Custom Resource (CR) instance.
If the platform is Red Hat OpenShift, you will know about the TLS termination types that are offered by Red Hat OpenShift Routes, and might or might not have created a certificateSecret object containing TLS certificates, in preparation for creating a secured Route in the next topic.
If the platform is native Kubernetes, you will know about the TLS configuration method that is offered by Kubernetes Ingress, and will have created a certificateSecret object containing TLS certificates, in preparation for creating a secured Ingress in the next page.
The procedure as part of this page outlines how to create the certificateSecret Secret object for Red Hat OpenShift Routes and native Kubernetes Ingress, if this is required for your chosen configuration.
- Routes
-
In Red Hat OpenShift, a router is deployed to the cluster that functions as the Ingress endpoint for external network traffic. This route exposes the service for an application so that any external device can access it. It can be either secure or unsecured, depending on the network security configuration of your application. The focus of this section is on secured routes as these require additional steps in storing TLS keys and/or certificates.
There are three types of security routes, each defined by the TLS termination type:Edge, which requires an insecure z/OS Connect Server.Passthrough, which requires a secure z/OS Connect Server. For more information, see Securing IBM z/OS Connect resources for zosConnect-3.0.Re-encrypt, which requires a secure z/OS Connect Server. For more information, see Securing IBM z/OS Connect resources for zosConnect-3.0.
Note: Where application is referenced, this is thePodresource on the Container Platform containing the z/OS Connect API.- Edge
With Edge termination, a TLS connection is established between the client and the router, and then terminated at the router. The connection between the router and the application is unencrypted. This is shown by
TLSandclearin the diagram.TheTLSconnection is created with a certificate/key pair in PEM-encoded format, where the certificate is valid for the route host. Also, a separate CA certificate in a PEM-encoded format can be used to complete the certificate chain. In Red Hat OpenShift, the router provides its own certificate/key pair and CA certificate defaults in PEM-encoded format. To provide your own values, seeReplacing the default ingress certificate and add tls.key, tls.crt and optionally ca.crt from Table 2 to the certificateSecret in the procedure. If not specified, the router defaults are used.
As the TLS connection terminates at the router, there is no method of providing trust between the router and the application with Edge. Therefore, the z/OS Connect Server must not have TLS enabled. However, the
Re-encrypttermination type provides this functionality, see Re-encrypt.
Table 2. Edge key/value pairs for certificateSecret Key Value Note Required tls.key TLS key in PEM-encoded format as part of certificate/key pairing.
If not specified, the Red Hat OpenShift router defaults are used. Optional tls.crt TLS certificate in PEM-encoded format as part of certificate/key pairing.
If not specified, the Red Hat OpenShift router defaults are used. Optional ca.crt TLS CA certificate in PEM-encoded format that completes the certificate chain.
If not specified, the Red Hat OpenShift router defaults are used. Optional If you are not using the router default values for tls.key, tls.crt and optionally ca.crt, follow the steps in the procedure to configure the certificateSecret forEdgewith the key/values in the Table 2. This certificateSecret is referenced in thecertificateSecretReffield in step 6.f when creating the z/OS Connect Custom Resource instance. This is where theEdgeroute is created by the IBM z/OS Connect Operator for z/OS Connect API deployment.
- Pass-through
With
Passthroughtermination, encrypted traffic is sent straight to the destination without the router providing TLS termination. Therefore, no key or certificate is required on the route. The application is responsible for serving certificates for the traffic at the endpoint, therefore TLS must be enabled on the z/OS Connect Server. This is currently the only method that can support requiring client certificates, also known as two-way authentication.
There are no additional configuration steps that are required for TLS when implementing pass-through. You have completed the preparation steps and are ready to for z/OS Connect API deployment. For more information, see Create a ZosConnect Custom Resource (CR) instance.
- Re-encrypt
With
Re-encrypttermination, a TLS connection is established between the client and the router, and then terminated at the router. The TLS connection is then re-encrypted, establishing a new TLS connection between the router and the application. This is shown byTLS1andTLS2in the diagram respectively.TLS1is created with a certificate/key pair in PEM-encoded format, where the certificate is valid for the route host. Also, a separate CA certificate in a PEM-encoded format can be used to complete the certificate chain. In Red Hat OpenShift, the router provides its own certificate/key pair and CA certificate defaults in PEM-encoded format. To provide your own values, see Replacing the default ingress certificate and add tls.key, tls.crt and optionally ca.crt in the Table 3 to the certificateSecret in the procedure. If not specified, the router defaults are used.TLS2is created with a separate destination CA certificate in PEM-encoded format. This certificate belongs to the application, therefore the z/OS Connect Server must have TLS enabled. Because the router re-encrypts the connection, it acts as an internal consumer and it trusts the internal certificate by the application. To provide this certificate, add destCA.crt the certificateSecret in the procedure.
Table 3. Re-encrypt key/value pairs for certificateSecretRef Key Value Note Required tls.key TLS key in PEM-encoded format as part of certificate/key pairing.
If not specified, the Red Hat OpenShift router defaults are used. Optional tls.crt TLS certificate in PEM-encoded format as part of certificate/key pairing.
If not specified, the Red Hat OpenShift router defaults are used. Optional ca.crt TLS CA certificate in PEM-encoded format that completes the certificate chain.
If not specified, the Red Hat OpenShift router defaults are used. Optional destCA.crt TLS CA certificate of the application in PEM-encoded format.
This certificate is inside the z/OS Connect Server and configured in Config TLS PKCS12. Yes Follow the steps in the procedure to configure the certificateSecret forRe-encryptwith the key/values in Table 3. This certificateSecret is referenced in thecertificateSecretReffield in step 6.f when creating the z/OS Connect Custom Resource instance. This is where theRe-encryptroute is created by the IBM z/OS Connect Operator for z/OS Connect API deployment.
- Ingress
-
Note: The IBM z/OS Connect Operator does not support Ingress on Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform.
Ingress resources are Kubernetes-native resources that play the same role as Red Hat OpenShift Routes. The Kubernetes Ingress definition only currently supports a single TLS port
443, and assumesEdgeTLS termination. The TLS connection is created with a certificate/key pair in PEM-encoded format, where the certificate is valid for the ingress host.Table 4. Ingress key/value pairs for certificateSecretRef Key Value Note Required tls.key TLS key in PEM-encoded format as part of certificate/key pairing.
If not specified, the Red Hat OpenShift router defaults are used. Yes tls.crt TLS certificate in PEM-encoded format as part of certificate/key pairing.
If not specified, the Red Hat OpenShift router defaults are used. Yes Follow the steps in the procedure to configure the certificateSecret forIngresswith the key/values in Table 4 certificateSecretRef. This certificateSecret is referenced in thecertificateSecretReffield in step 6.f when creating the z/OS Connect Custom Resource instance. This is where theIngressis created by the IBM z/OS Connect Operator for z/OS Connect API deployment.
Procedure
Results
What to do next
If you use volumes in a container platform to mount keystores for your z/OS Connect API image to use, see Configure volumes (Optional).
If you don't use volumes in a container platform, you are ready to deploy your z/OS Connect API. For more information, see Create a ZosConnect Custom Resource (CR) instance.
Configure volumes (Optional)
Use volumes in a container platform to mount keystores for your z/OS Connect API image to use. Volumes are mounted file systems available to pods and their containers.
About this task
In this task, all artifacts that are required for SSL configuration in a z/OS Connect Server are stored in Secret objects in Red Hat OpenShift. This includes keystores, truststores, and certificate passwords. These are mounted to the z/OS Connect API pod through volumes in the Create a ZosConnect Custom Resource (CR) instance section.
The following example shows a configuration file with SSL within a
z/OS Connect Server and keystore elements configured. In
the procedure, CERTIFICATE_PASSWORD, clientKey.p12 and
clientTrust.p12 are stored as Secret Objects in Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform.
<ssl id="sslCertificates" keyStoreRef="clientKeyStore" trustStoreRef="clientTrustStore"/>
<keyStore id="clientKeyStore" password="${CERTIFICATE_PASSWORD}" location="${server.config.dir}/resources/security/clientKey.p12" type="PKCS12"/>
<keyStore id="clientTrustStore" password="${CERTIFICATE_PASSWORD}" location="${server.config.dir}/resources/security/clientTrust.p12" type="PKCS12"/>- clientKey.p12 and clientTrust.p12 are example PKCS12
certificate files that were preconfigured in the procedure How to configure a TLS connection with PKCS12 keystores. The
.p12format is used here for illustration purposes; other certificate formats are also supported. - CERTIFICATE_PASSWORD is the password for the clientKey.p12 and clientTrust.p12 certificates.
Procedure
- Log
in as
zcon-userto the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform web console. Make sure that you are in the Developer perspective by using the navigation. - Click Secrets in the navigation.
- Select a Project to view the list of Secrets or Create a
Project. If a Project does not exist, you must Create a Project.
- Click Create on the Secrets panel and select Key/value secret.
- Enter a
Secretname.For example,keystore-secret. - Enter the keystore key in the Key field. For example,
clientKey.p12. - Enter the
keystorecontents in the Value field.For example, theclientKey.p12certificate in plain text. - Click Create.
- Click Secrets in the navigation.
- Click Create on the Secrets panel and select Key/value secret.
- Enter a Secret name for the truststore certificate. For example,
truststore-secret - Enter the truststore key in the Key field. For example,
clientTrust.p12 - Enter the
truststorecontents in the Value field.For example,clientTrust.p12certificate in plain text. - Click Create.
To create the CERTIFICATE_PASSWORD, complete the following
steps:
- Click Secrets in the navigation.
- Click Create on the Secrets panel and select Key/value secret.
- Enter a Secret name for the certificate password. For example,
certificate-password. - Enter the certificate key in the Key field. For example,
CERTIFICATE_PASSWORD. - Enter the certificate credential in the Value
field. For example, the
CERTIFICATE_PASSWORDin plain text.
Results
Check the Secrets panel to view the Secret you created.
What to do next
You are ready to deploy your z/OS Connect API. For more information, see Create a ZosConnect Custom Resource (CR) instance.
If you have configured volumes in the container platform, you must also complete the Optional - Volume steps that are part of the Create a ZosConnect Custom Resource (CR) instance steps. These steps ensure that:
- The
CERTIFICATE_PASSWORDis mapped to the z/OS Connect API pod as an environment variable. - The
clientKey.p12andclientTrust.p12files are mounted to the z/OS Connect API pod as volumes at the defined location.
Complete the Create a ZosConnect Custom Resource (CR) instance steps, including the Optional - Volume steps when you reach them in the following procedure.
Create a ZosConnect Custom Resource (CR) instance
Creating a ZosConnect Custom Resource (CR) instance to enable deployment
of your z/OS Connect API project.
About this task
In this section, a z/OS Connect API is deployed to the
Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform. This is done
by creating an instance of the ZosConnect Custom Resource (CR) that is enabled on
the Red Hat OpenShift Cluster by the IBM z/OS Connect Operator.
To create an instance of the ZosConnect CR, you must specify the configuration
details for the z/OS Connect API to be deployed.
The IBM z/OS Connect Operator automatically creates
the necessary resources for the z/OS Connect API to run
as specified in the ZosConnect CR.
ZosConnect CR, therefore multiple z/OS Connect API deployments. Procedure
Results
When the ZosConnect Custom Resource is created, the IBM z/OS Connect Operator creates the resources that are
required for your chosen configuration based on the fields that are completed in this procedure. To
view these resources, open the Topology page where the
ZosConnect instance is created.
In the example shown in Figure 3, the name of the ZosConnect Custom Resource is
zosconnect-sample. Click inside the dotted area of the
zosconnect-sample Custom Resource to view the resources that are associated with
the created ZosConnect Custom Resource.

The Pod containing the z/OS Connect API is created by
the zosconnect-sample-deployment deployment. To view the Pod, click
zosconnect-sample-deployment in the Resources tab to
open the Deployment > Deployment details page. Navigate to the
Pods tab to view the Pod.
In this example, the Pod Status is Running and
1/1 replicas are Ready. Only 1
Deployment>Replicas was specified for the ZosConnect Custom
Resource.
- The Pods might take a few seconds to become ready.
- The Pods that are created by the IBM z/OS Connect Operator are annotated with
productName,productID, andproductMetricto allow the IBM License Service to recognize the z/OS Connect Pods should IBM License Service be required by other IBM products that are installed into the same cluster.
Invoke z/OS Connect APIs
About this task
In this task, the z/OS Connect API is deployed to the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform by using a Red Hat OpenShift Route configured earlier in the procedure.
expose
flag in the ZosConnect Custom Resource.Procedure
-
Log in as
zcon-userto the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform web console. Make sure that you are using the Developer perspective by using the left navigation. -
From the navigation, click Topology.
Select the project where your
ZosConnectinstance is created.For example,zosconnect-sample-deployment. -
Click inside the dotted line around the
ZosConnectinstance.From the panel that opened to the side of the screen, make sure that you are viewing the Resources tab.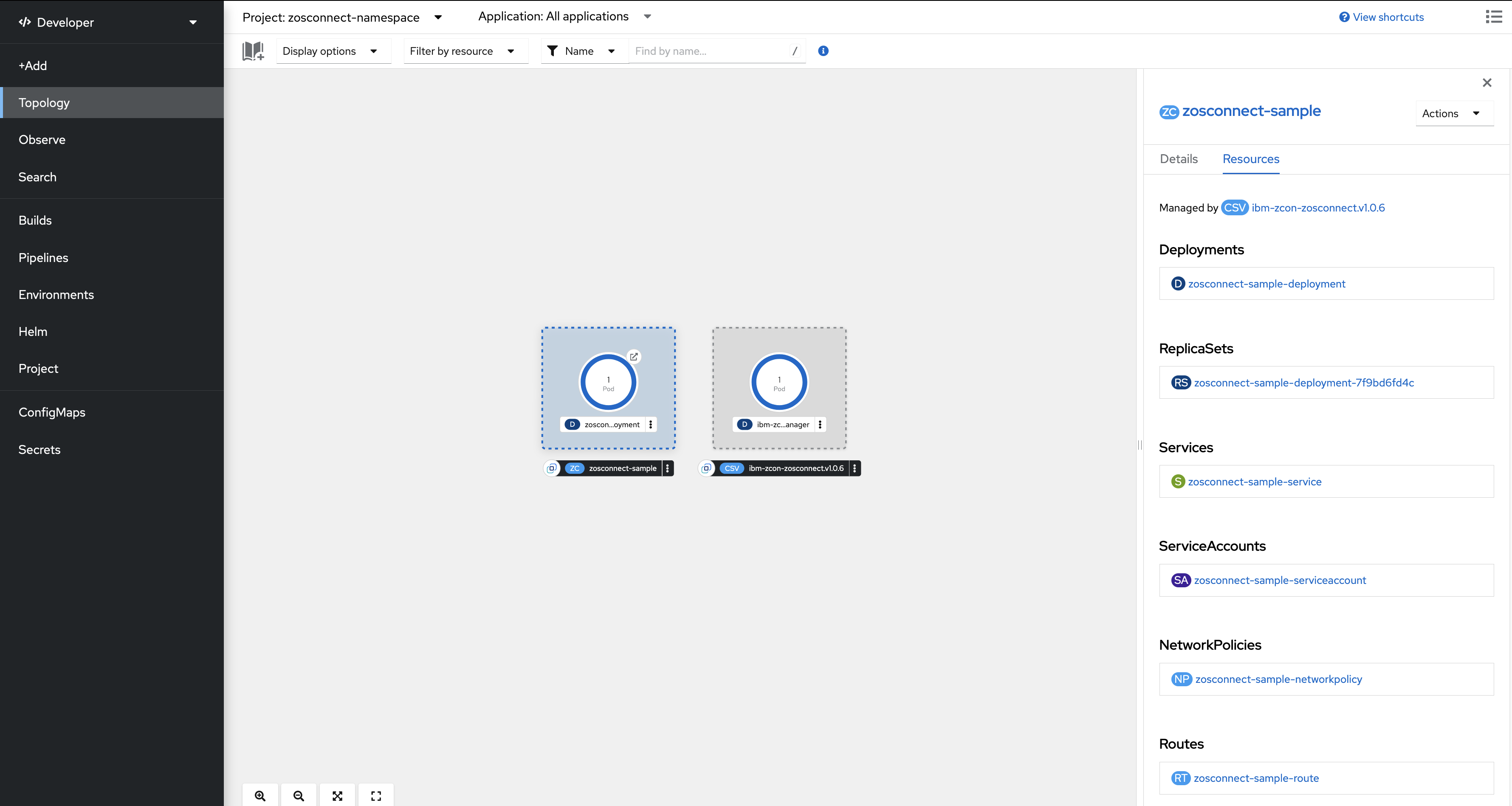
- Click Red Hat OpenShift Route listed in the Resources tab to navigate to the Route > Route details page.
-
Click the link in the Location field to invoke the z/OS Connect API that uses the Red Hat OpenShift Route. The Location value is the external URL path to the Pod. This is expected to return a 404 response. The z/OS Connect API operation URI values need to be appended to this value to invoke the API operations.
- Optional: Append a valid URI for the deployed z/OS Connect API onto the provided Route Location value to invoke the z/OS Connect API operation.
- The Red Hat OpenShift Route returns successfully.
 to open the
to open the