How aggregate recovery works
To perform aggregate recovery, you must have the control file, data files, and instruction/activity log file created by a previous aggregate backup. To use the simplified ARECOVER command, you must also have an ABARS activity (ABR) record at the recovery site. You can then use the ARECOVER command to recover the data sets from the tape files.
Figure 1 shows the information flow of an aggregate recovery.
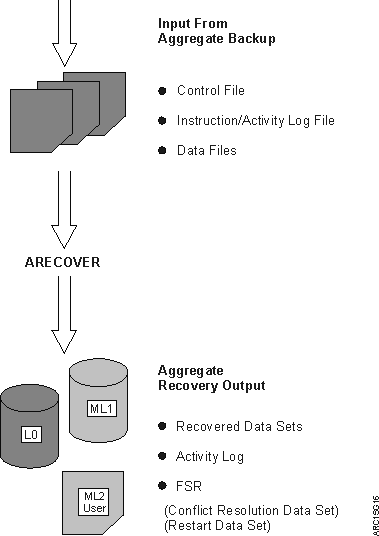
You can choose to prepare the recovery site for the eventual recovery of the aggregate by issuing the ARECOVER command with the PREPARE parameter. You can also choose to verify the aggregate recovery without actually recovering the data sets. Then, when you are ready, you can perform the actual recovery of your data sets.
The control file and data file were created as a result of aggregate backup and are used as input for aggregate recovery.
- The recovered data sets, which are those data sets recovered from the aggregate backup tape data file. Table 1 shows the manner in which aggregate recovery recovers, allocates, and catalogs data sets.
- An activity log, which contains messages written during aggregate recovery processing.
- The FSR, which contains the statistics for aggregate recovery processing. This includes recording the CPU time for processing ARECOVER requests. The FSR can be written as an SMF record if the installation specifies SETSYS SMF(smfid).
- Updates to the ABR record, which shows the CPU time for processing ARECOVER requests. The ABR shows the accumulated CPU time of each restart until the recovery of the aggregate is successful.
- A conflict resolution data set that is used as input to a subsequent
ARECOVER command.
The conflict resolution data set contains names of data sets that the ARECOVER verification process determines to have like-named conflicts that were not resolved by the RECOVERNEWNAME parameters, the DATASETCONFLICT parameter, or the ARCCREXT installation exit. For each such data set encountered, an entry is placed into the conflict resolution data set, with a default action of BYPASS.
You can edit the conflict resolution data set before issuing the next ARECOVER command, and indicate which conflict resolution actions are to be taken by ARECOVER verification processing for each data set entry.
You then issue a subsequent ARECOVER command. The conflict resolution data set is read and used as input to the ARECOVER verification process.
- A restart data set is created when the recovery of data sets does not complete successfully. The restart data set contains the names of all the data sets recovered successfully. When an aggregate recovery is reissued, the restart data set ensures that data sets already processed are not recovered a second time. If you want to start aggregate recovery again from the beginning, delete the restart data set.
- Accounting code records that are written to the ABACKUP control file, FSR, and ABR. You can assign accounting codes to aggregates, which allows you to associate ABARS CPU time to specific aggregates. The codes are written to the ABACKUP control file so they can be propagated at the recovery site.
Related reading
- For more information about creating the ABR record, see How to create the ABR record .
- See EAV considerations for recovery functions.