Aggregate backup and recovery support (ABARS)
Aggregate backup is the command-driven function that backs up a user-defined group (called an aggregate group) of data sets for recovery at another computer site or at the same site. Aggregate recovery is the command-driven function that recovers the data sets that were previously backed up by aggregate backup.
Aggregate backup and recovery support can be used to back up and recover both SMS and non-SMS-managed data.
Figure 1 and Figure 2 show data movement during aggregate backup and recovery and how these functions interact with other products. The DFSMShsm aggregate backup and recovery support function is also referred to as ABARS.
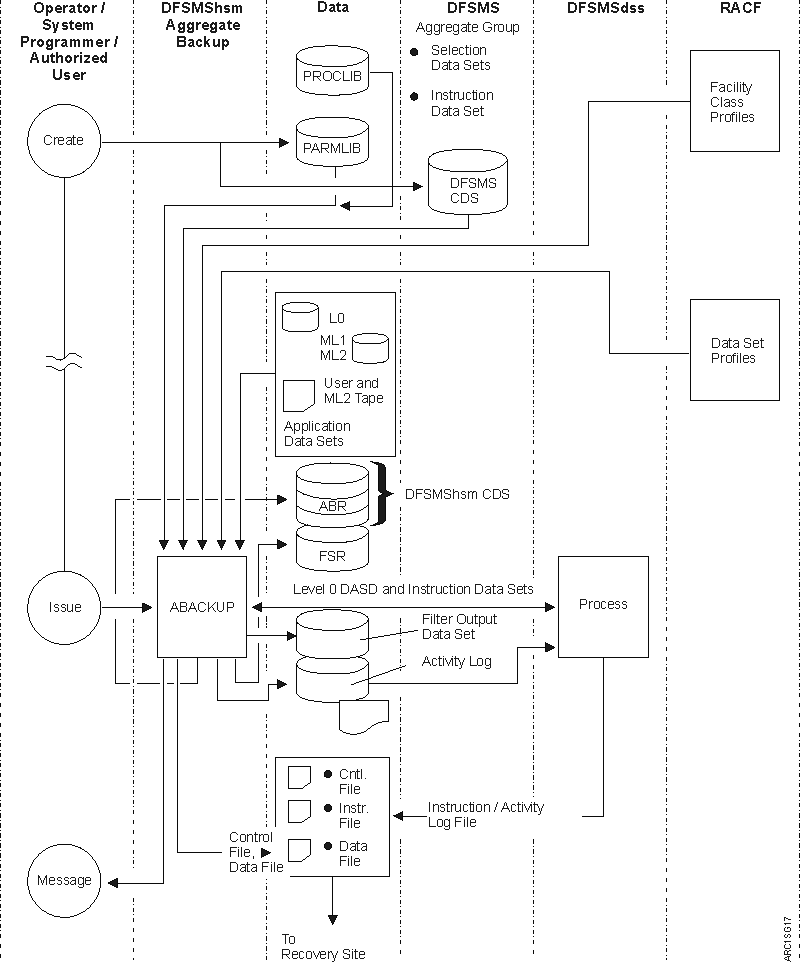

The aggregate group and management class used for aggregate backup are defined to DFSMS through Interactive Storage Management Facility (ISMF) panels.
DFSMSdss is used to move level 0 DASD data sets during aggregate backup and recovery processing.
DFSMShsm can include ML1 and ML2 migration copies of data sets within the aggregate backup. Migration copies that are stored in the cloud (MLC) will not be included and will cause the backup to fail. ABACKUP does not support data sets migrated to the cloud. If the selection criteria results in any of these data sets being selected, then the ABACKUP command fails.
RACF® is used to ensure that RACF-protected data sets that are backed up remain RACF-protected when recovered. When RACF facility class is active and the user has restricted command authority, RACF checking of data sets is performed during aggregate backup. See Checking authorization during aggregate backup for more information.
Although the backup and recovery sites are referred to as two separate data processing centers, you can choose to perform both functions at the same data processing center. This might be useful if you want to divide your data processing center for work load management.