 z/OS Communications Server: SNA Customization
z/OS Communications Server: SNA Customization
 z/OS Communications Server: SNA Customization
z/OS Communications Server: SNA Customization
|
Previous topic |
Next topic |
Contents |
Contact z/OS |
Library |
PDF
Alias selection function z/OS Communications Server: SNA Customization SC27-3666-00 |
|
|
The alias selection function of the session management
exit routine performs various name translation tasks. VTAM® maintains both a real and an alias network-qualified
name for each LU session partner. VTAM can
invoke this function to determine any one of the following four names:
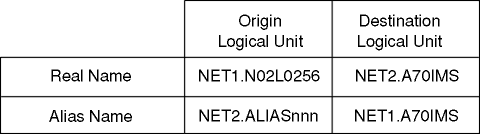
In addition, the alias selection function can map a class-of-service (COS) name for one network to the COS name used in another network. It can also map logon mode entry names or indicate the SSCP owner for a particular resource name. In this sample, the alias function translates the real LU name of a terminal in NET1 into an alias name in NET2. The primary application programs (CICS® and IMS™) in NET2 require the terminal names to be generated in these subsystems. All terminals in NET1 that require access to these application programs must be generated into the subsystems. Because the subsystem maintenance and coordination associated with a large quantity of other-network terminals can be difficult, the alias function translates a real terminal name into an alias terminal name. The alias terminal name is selected from a preassigned pool of alias names. This pool can be pre-generated into the IMS and CICS application programs. When all the names in the pool are allocated to concurrent cross-network sessions, subsequent session requests fail. After a name is freed as a result of a session termination, another cross-network session can be established. Therefore, the preassigned alias name pool needs to contain sufficient entries to accommodate the peak concurrent cross-network session count for CICS and IMS. The session management exit routine must first examine the indicators associated with the LU names to determine what translation is necessary. For example, assume there is a terminal-initiated session from N02L0256 for the application program A70IMS in NET2. There are four network-qualified names associated with this session request, as shown in Figure 1. Figure 1. Real and alias
network-qualified names

|
 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 |