IBM OpenPages GRC REST API V2
Use this version of the IBM OpenPages GRC REST API for new implementations.
The IBM OpenPages GRC REST API provides access to IBM OpenPages® data and metadata. This data-centric API is specified in terms of resources, their URIs, and actions that can be performed on these URIs.
For information about how to use the IBM OpenPages GRC REST API V2, see the reference documentation.
Prerequisites
- IBM OpenPages
- Web services such as ASDL and REST
- HTML and the JavaScript scripting language JSON
- Programming languages and integrated development environments (IDEs), such as the Java™ programming language and the Eclipse IDE, or the C# programming language and the Microsoft Visual Studio IDE.
SCIM 2.0 support
IBM OpenPages GRC REST API V2 conforms to the SCIM 2.0 specification for user provisioning and management.
For more information, see System for Cross-domain Identity Management.
Performance
You can add indexes to improve the performance of running a query.
For more information, see Reporting Schema folder settings.
Security and authentication
Authentication is delegated to the IBM® WebSphere® Application Server, so each entry point doesn't need to verify the authentication token.
Use basic authentication, client certificate authentication, and OAuth 2.0 authentication with IBM OpenPages on premises or IBM OpenPages on Cloud.
Use token-based authentication with IBM OpenPages for IBM Cloud Pak for Data.
Basic authentication
Basic authentication is configured by default through your OpenPages application server. The basic authorization scheme follows the RFC 2617
specification. The client implements the basic authorization scheme by sending an HTTP request
header. Basic authorization contains the text Basic followed by the username,
colon (:), and password. The text must be encoded in Base64. For example, to send the username
Aladdin and password open sesame, use the following HTTP header
field:
Authorization: Basic QWxhZGRpbjpvcGVuIHNlc2FtZQ==The OpenPages GRC REST API adheres to the RESTful systems principle of statelessness, so each request made must provide the credentials of the user. Basic authentication is considered secure if it is used with some external secure system such as SSL. For the greatest security, ensure that clients send only unencrypted credentials and that requests are sent over HTTPS.
Client certificate authentication
OpenPages offers client certificate authentication with WebSphere Liberty Profile (WLP).
Client certificate authentication is a mutual certificate-based authentication method, where the client provides its client certificate to the server to prove its identity. The server allows requests only after it authenticates the client. The client must provide a public key certificate that identifies who the client is. For the client to be authenticated, the server must trust the certificate. WLP can be configured to trust any client certificate by adding it manually to their trust keystore. WLP can also trust the client certificate if another trusted certificate digitally signs the client certificate. For example, WLP can trust the client certificate if a well-known SSL Certificate Authority, such as DigiCert, issues a certificate that signs the client certificate for ibm.com® .
This traffic is over SSL (HTTPS), which ensures the security of the connection and encryption. Also, the control at the API level provides an option to configure your security model to allow only certain pre-approved clients to make requests to the REST API. To allow the IBM OpenPages GRC REST API to use client authentication rather than basic authentication, you must configure IBM WebSphere Liberty. For information about configuring an application in IBM WebSphere Liberty to use client certificate authentication, see How to Set up Liberty to Use Certificate-Based Authentication.
OpenPages integration with IBM WebSphere Liberty security requires configuration changes. For more information, see Integrating OpenPages with IBM WebSphere Liberty security.
Token authentication
Token authentication is configured by default through your OpenPages application server under IBM
OpenPages for IBM Cloud Pak for Data. The token is a Microprofile JSON Web
Token (MP-JWT) as described in Eclipse MicroProfile Interoperable JWT RBAC. The client sends
an HTTP request Authorization header that starts with the text Bearer followed by a
valid MP-JWT token such as Authorization: Bearer <Valid MP-JWT
Token> .
To get a valid token, use one of the authentication APIs described in Generating an authorization token or API key on the server where OpenPages is installed.
The IBM OpenPages GRC REST API adheres to the RESTful systems principle of statelessness, so each request made must provide the credentials of the user. All communications under IBM OpenPages for IBM Cloud Pak for Data enforce SSL by default.
Configuring OAuth 2.0 authentication
OAuth 2.0 allows users to keep their usernames, passwords, and other information private when they share specific data with an application. You can configure OAuth2.0 authentication for IBM OpenPages REST API V1 and V2 on IBM OpenPages on premises or IBM OpenPages on Cloud.
In this configuration, OpenPages performs the role of resource server in OAuth 2.0 authentication flows. You can use an OAuth 2.0 authorization server or an OpenID Connect (OIDC) provider as the Identity Provider (IdP).
Before you begin
Your environment must meet the following criteria:
- An OAuth 2.0 authorization server or OIDC provider is set up and running.
- Register a client account to be used by the OpenPages server to perform introspection or validate identity. This account must be created in the OAuth 2.0 or OIDC provider. OpenPages uses the client ID and client secret for validation of tokens with the authorization server only.
- Each external client that uses the OpenPages REST APIs must either be assigned a service account user ID in the OAuth 2.0 authorization server, or have a user identity in the OIDC Provider. The username of the service account or functional ID that is mapped to each client must match a user in the OpenPages system.
- If needed, create a user in OpenPages with
the username
service-accountand required permissions for the flow of client credentials to work correctly. Theclient_idcomes from the OIDC provider. - OpenPages 9.0 or later is installed and the OpenPages servers are running.
- You can log in to the OpenPages application from your browser.
About this task
In this task, you configure an IBM WebSphere Liberty server to act as an OpenID Connect Client. For more information, see OpenID Connect Client (openidConnectClient).
You can use any provider that supports OAuth 2.0 or OpenID Connect protocols.
Procedure
What to do next
To use the OAuth 2.0 protocol for IBM OpenPages GRC REST API public authentication, use JSON Web Token (JWT) Bearer Tokens that are issued by the Authorization Server or OpenID Provider.
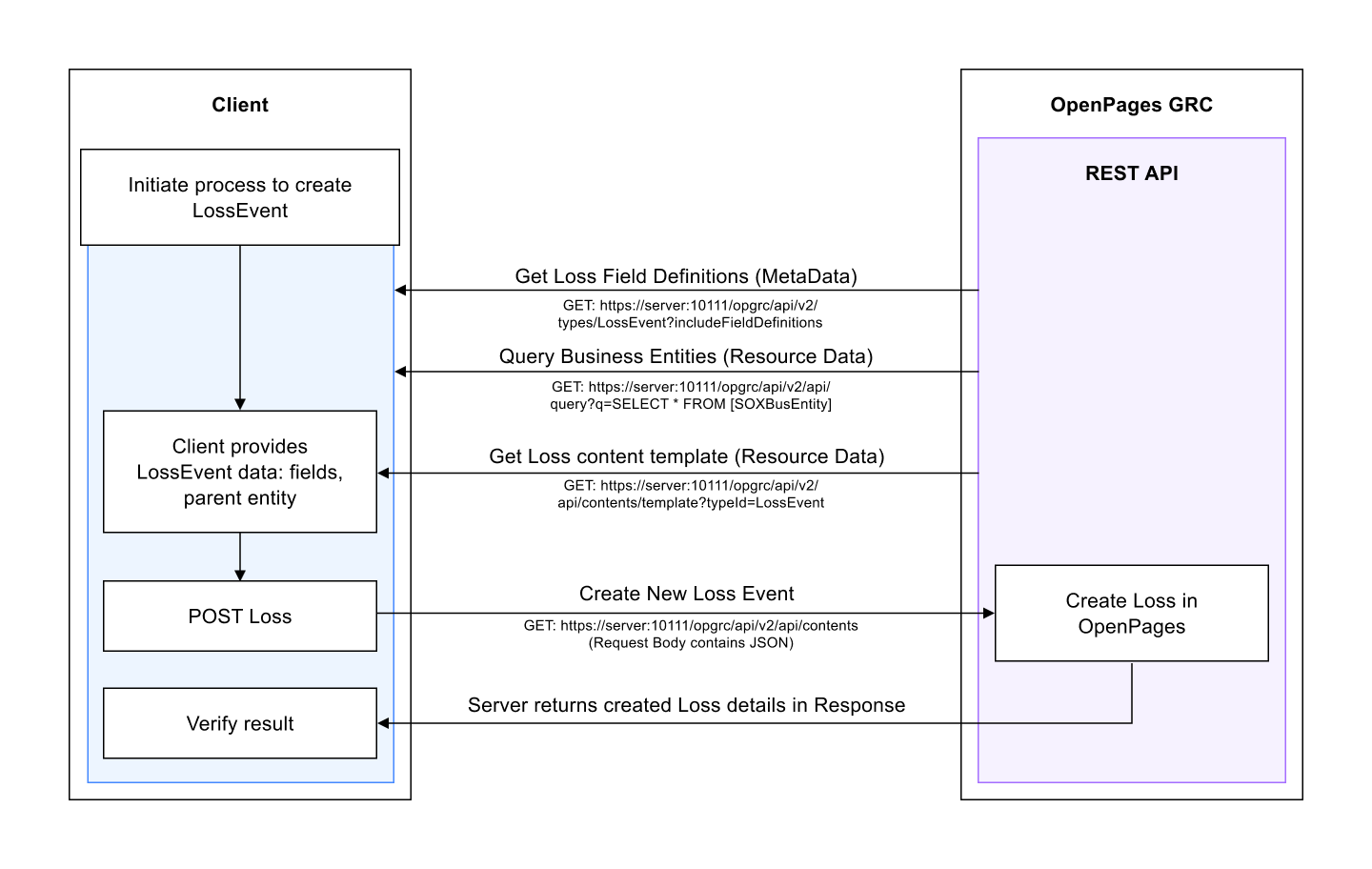
Client/server interactions
Client interaction with the IBM OpenPages GRC REST API, including the sequence of events, depends on the design of the client and the interaction objectives. An interaction retrieves Metadata and Configuration information, and then it sends further requests to the server to gather more data or perform updates.
Integrating OpenPages with IBM WebSphere Liberty security
Before you begin
- You must have access to the OpenPages application server and permission to modify the server configuration.
- You must have an x509 public key certificate that represents your client. This certificate
requires a Subject that identifies the user in OpenPages that this client is authenticating as. For
example, a subject might be
/CN=OpenPagesAdministratorfor a userOpenPagesAdministrator, or/C=US/O=IBM/OU=WFSS/CN=brianlfor another user with the namebrianl. These usernames must exist as user accounts within OpenPages.
About this task
This task shows you how to configure a newly installed environment to allow client certificate authentication for the REST API. If you modified the Global Security configuration or GRC Security Domains (for instance for using SSO), you might need to adjust these steps for your environment.
Procedure
What to do next
You can test how the client certificate authentication works by using a REST client that has support for this authentication method. For example, the UNIX-style cURL command supports this method.
For example, if the client certificate is in client1.pem and the server is
my-op-server, use the following cURL command:
curl --tlsv1.2
--no-alpn --verbose --cert /path-to-/client1.pem
https://my-op-server:10111/opgrc/api/v2/types- All output that is related to the SSL handshake because of the inclusion of the
--verboseoption. - A response body that contains the JSON that describes the OpenPages metadata schema because the request specifies that all types are to be returned.
If your server is not using a valid SSL certificate, you can add the --insecure
option to the command for testing purposes. The --no-alpn option was introduced in
cURL version 7.36.0. If your cURL version is earlier than 7.36.0, remove the
--no-alpn option.
You can use this method to test other IBM OpenPages GRC REST API endpoints.
Mapping Regulatory Events to Mandates, Sub-Mandates, and Requirements
About this task
To make the association, use a IBM OpenPages GRC REST API call. The examples in this task illustrate the use case where you have one Regulatory Event that needs to be associated to an existing Mandate and Sub-Mandate.