This lesson uses the ASNCLP command-line program to set
up SQL Replication so that changes to the source database are propagated
to the target tables, where they are ready to be consumed by InfoSphere® DataStage®.
In SQL Replication, you register a source
table to prompt the Capture program to read the log for changes to
the table. Capture inserts these changes as rows in a changed-data
table or CD table that is created as part of the
registration process.
You also create source-to-target mappings
between tables called subscription-set members and group
the members into a subscription set to specify that the
Apply program fetch changes to the member tables at the same time.
Because multiple Apply instances can coexist on a system, each has
an Apply qualifier.
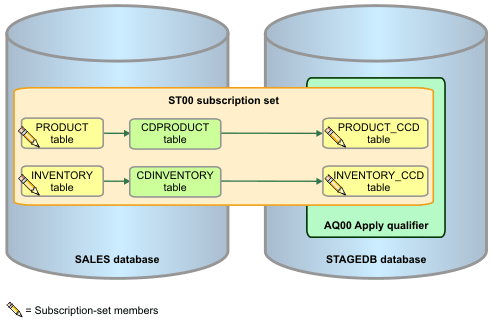
Figure 1. SQL Replication setup
for tutorial
Before you can create these objects, you need to create Capture
control tables and Apply control tables to store
the information.
Note: SQL Replication also has a graphical user
interface, the Replication Center, for creating these objects. For
more detail on using the Replication Center, see the
SQL Replication tutorial.
Procedure
- Locate the crtCtlTablesCaptureServer.asnclp script
file in the sqlrepl-datastage-tutorial/setupSQLRep directory.
In the file, replace <db2-connect-ID> and "<password>" with
your user ID and password for connecting to the SALES database.
- From the DB2® command
window or an operating system command prompt, change directories to
the sqlrepl-datastage-tutorial/setupSQLRep directory
and run the script by issuing the following command:
asnclp –f crtCtlTablesCaptureServer.asnclp
The script prompts the ASNCLP program to connect to
the SALES database, generate an SQL script for creating the Capture
control tables, and then run the script.
- Locate the crtCtlTablesApplyCtlServer.asnclp script
file in the same directory and replace two instances of <db2-connect-ID> and "<password>" with
the user ID and password for connecting to the STAGEDB database.
This script create the Apply control tables.
- From the same command prompt that you used in Step 3, issue
the following command:
asnclp –f crtCtlTablesApplyCtlServer.asnclp
- Locate the crtRegistration.asnclp script
file and replace all instances of <db2-connect-ID> with
the user ID for connecting to the SALES database. Also change "<password>" to
the connection password.
- Issue the following command to run the script that registers
the source tables:
asnclp –f crtRegistration.asnclp
As part of creating the registration, the ASNCLP program
creates two CD tables, CDPRODUCT and CDINVENTORY, to temporarily hold
changes that are captured from the source tables. The CREATE REGISTRATION
command uses the following options:
- DIFFERENTIAL REFRESH
- Tells the Apply program to update the target table only when rows
in the source table change. This method contrasts with full refresh
replication, where the entire target table contents are replaced in
batches. Differential refresh is well suited for dynamic warehousing.
- IMAGE BOTH
- Registers both after-image and before-image columns. When you
select to capture before-image and after-image values, the CD table
contains two columns for each changed value: one for the value in
source column before the change occurred, and one for the value after
the change occurred.
- Find the crtTableSpaceApply.bat file,
open it in a text editor, and replace <stagedb-connect-ID> and <stagedb-password> with
the user ID for connecting to the STAGEDB database. In the DB2 command
window, enter crtTableSpaceApply.bat and run
the file. This batch file creates a new table space
on the STAGEDB database for the two CCD tables that will be created
in the next steps. By default, the ASNCLP program creates target tables
in the default table space for the database, but for this tutorial
you should use a separate table space in case you need to drop and
recreate the tables.
- Locate the crtSubscriptionSetAndAddMembers.asnclp script
file and make the following changes:
- Replace all instances of <sales-connect-ID> and <sales-password> with
the user ID and password for connecting to the SALES database.
- Replace all instances of <stagedb-connect-ID> and <stagedb-password> with
the user ID for connecting to the STAGEDB database.
Next you will run the script to create a subscription set
called ST00 that groups the source and target tables. The script also
creates two subscription-set members that specify the source and target
tables, and creates consistent-change data (CCD) tables in the target
database that will store the changed data, which can then be consumed
by InfoSphere DataStage.
- Issue the following command to run the script to create
the subscription set, subscription-set members, and CCD tables:
asnclp –f crtSubscriptionSetAndAddMembers.asnclp
Options used for creating the subscription
set and two members included the following:
- COMPLETE ON CONDENSED OFF
- The CCD tables are created with the noncondensed, complete attributes:
- Noncondensed
- A noncondensed CCD table holds one row per UPDATE, INSERT, or
DELETE operation so you can keep a history of the operations that
are performed on the source table.
- Complete
- A complete CCD table starts with a full copy of the source table
data.
Only the noncondensed attribute is required for the
replication feature that automatically creates DataStage jobs for reading from the CCD
tables. The complete attribute is used for this tutorial so that you
can see the initial source data in the target CCD table.
- EXTERNAL
- A CCD target table that is also used as a source, in this case
for DataStage.
- LOADX TYPE IMPORT EXPORT
- The Apply program invokes the DB2 export and import utilities
to load the CCD tables with an initial copy of the source table data.
- TIMING CONTINUOUS
- The Apply program processes the set continuously. This option
enables DataStage to update the warehouse in near real time. In some
situations you might want to specify interval-based timing (TIMING
INTERVAL), where Apply periodically processes the set, or
use event-based timing (TIMING EVENT). You need
to coordinate the frequency of subscription cycles with how frequently
the DataStage jobs run. For the tutorial, you specify continuous subscription
cycles because it mimics the real-time data flow of a dynamic warehouse,
and also because it lets you quickly see the results of integrating
SQL Replication and DataStage.
- One last step: Because of a defect in the replication administration
tools, you need to run another batch file to set the TARGET_CAPTURE_SCHEMA
column in the IBMSNAP_SUBS_SET control table to null:
- Find the updateTgtCapSchema.bat file,
open it in a text editor, and replace <stagedb-connect-ID> and <stagedb-password> with
the user ID for connecting to the STAGEDB database.
- In the DB2 command window, enter updateTgtCapSchema.bat and
run the file.
Lesson checkpoint
In this lesson you created
the Capture and Apply control tables to store replication options,
registered the PRODUCT and INVENTORY tables as replication sources,
and created a subscription set with two members. Creating the subscription
set members also created the target CCD tables, which serve as the
interface with InfoSphere DataStage.