LINAGE clause
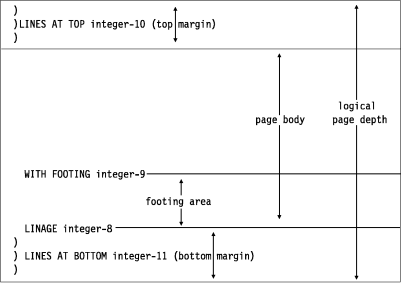
The LINAGE clause specifies the depth of a logical page in number of lines. Optionally, it also specifies the line number at which the footing area begins and the top and bottom margins of the logical page. (The logical page and the physical page cannot be the same size.)
The LINAGE clause is effective for sequential files opened as OUTPUT or EXTEND.
All integers must be unsigned. All data-names must be described as unsigned integer data items.
- data-name-5 , integer-8
- The number of lines that can be written or spaced on this logical page. The area of the page that these lines represent is called the page body. The value must be greater than zero.
- WITH FOOTING AT
- integer-9 or the value of the data item in data-name-6 specifies the first line number of the footing area within the page body. The footing line number must be greater than zero, and not greater than the last line of the page body. The footing area extends between those two lines.
- LINES AT TOP
- integer-10 or the value of the data item in data-name-7 specifies the number of lines in the top margin of the logical page. The value can be zero.
- LINES AT BOTTOM
- integer-11 or the value of the data item in data-name-8 specifies the number of lines in the bottom margin of the logical page. The value can be zero.
The following figure illustrates the use of each phrase of the LINAGE clause.
The logical page size specified in the LINAGE clause is the sum of all values specified in each phrase except the FOOTING phrase. If the LINES AT TOP phrase is omitted, the assumed value for the top margin is zero. Similarly, if the LINES AT BOTTOM phrase is omitted, the assumed value for the bottom margin is zero. Each logical page immediately follows the preceding logical page, with no additional spacing provided.
If the FOOTING phrase is omitted, its assumed value is equal to that of the page body (integer-8 or data-name-5).
At the time an OPEN OUTPUT statement is executed, the values of integer-8, integer-9, integer-10, and integer-11, if specified, are used to determine the page body, first footing line, top margin, and bottom margin of the logical page for this file. (See the figure above.) These values are then used for all logical pages printed for this file during a given execution of the program.
At the time an OPEN statement with the OUTPUT phrase is executed for the file, data-name-5, data-name-6, data-name-7, and data-name-8 determine the page body, first footing line, top margin, and bottom margin for the first logical page only.
At the time a WRITE statement with the ADVANCING PAGE phrase is executed or a page overflow condition occurs, the values of data-name-5, data-name-6, data-name-7, and data-name-8 if specified, are used to determine the page body, first footing line, top margin, and bottom margin for the next logical page.
If an external file connector is associated with this file description entry, all file description entries in the run unit that are associated with this file connector must have:
- A LINAGE clause, if any file description entry has a LINAGE clause
- The same corresponding values for integer-8, integer-9, integer-10, and integer-11, if specified
- The same corresponding external data items referenced by data-name-5, data-name-6, data-name-7, and data-name-8
See ADVANCING phrase for the behavior of carriage control characters in external files.
A LINAGE clause under an SD is syntax checked, but has no effect on the execution of the program.