Monitoring Java Management Extensions (JMX) MBeans
With the JMX data provider you can collect data from JMX MBeans. Each JMX data source you define must identify either a single MBean (single instance) or a certain type of MBean (multiple instances). You must know the Object Name of the MBean or an Object Name pattern for a type of MBean that contains the data you want to collect. Use an Object Name pattern to only identify a set of similar MBeans. The set of MBeans that match the pattern must all provide the data that you want to see in the monitoring table. A typical Object Name pattern looks like *:j2eeType=Servlet,*. This Object Name Pattern matches all MBeans that have a j2eeType of Servlet. You can expect any MBean matching that pattern to have a similar set of exposed attributes and operations that can be added to your data source. A data source that uses that pattern collects data from each MBean matching that pattern. The attributes that you define for this data source must be available for any MBean matching the Object Name pattern you defined for the data source.
Use the following steps to add a JMX data source to collect data from Java Management Extension (JMX) MBeans:
- On the Agent Initial Data Source page (Figure 103) or the Data Source Location page, click Data from a server in the Monitoring Data Categories area.
- In the Data Sources area, click JMX
- Click Next.
- On the JMX Information page (Figure 104), click Browse to see all of the JMX MBeans on the MBean
server.
After you have defined the data source, you can use the browse function to pre-populate your attribute list. You can then add to, remove from, or modify the attributes that the browser inserted. The names for these attributes can be long and difficult to type correctly. Using the Browse option is an easy way to input the correct name.
Note:You can manually create JMX data sources by specifying an Object Name and clicking Next without using the browser. Manually creating JMX data sources creates two data sources. An event data source containing predefined attributes for JMX notifications is created. Also, a collection data source is defined containing one attribute that you must specify in the wizard.- MBean pattern
- Displays the MBean pattern.
- Global JMX Options
- Displays the level of support (Figure 105).
Support is provided for the following JMX servers:
- Java 5 operating system MBean Server. Connection is made using the JSR-160 connector. Notifications and monitors are supported.
- WebSphere® Application Server, version 6 and later. Connectors are provided for both SOAP and RMI protocols. JMX Monitors are not supported because MBeans cannot be created by a remote agent.
- WebSphere Community Edition and other Apache Geronimo-based application servers. Connection is made through standard JSR-160 connectors. JMX notifications and monitors are supported in versions 1.1 and later.
- JBoss Application Server, version 4.0 and later. See the following link to an item in the Troubleshooting appendix if you need support for JMX Monitors.
- WebLogic Server, version 9 and newer. Connector is provided for T3 protocol.
- The first time you run the JMX browser, there are no items in
the Connection Name scroll down menu. To add
connections, click the plus (+) icon. You can also use the plus (+)
icon to modify or delete connections you have already defined. The
connection definitions are stored in the workspace, so that, when
you create a connection, it is remembered. Complete the following
steps to create a connection. If you already have a connection, skip
to the next step.
- To create a new connection to an MBean Server, click the plus (+) icon to add a new connection or to edit an existing connection. The following window (Figure 106) is displayed when no connections have been defined:
- After clicking the plus (+) icon to add a connection, the JMX Connection Selection page (Figure 107) is displayed:
- Use the MBean Server Connection Wizard to connect to an MBean server. The new connections listed on the page are selections you can make to create a new connection. You can use the list of existing connections to reconfigure an existing connection. Select one of the new connection types and click Next to begin creating a new connection.
- After selecting a connection type, you might be asked to select
a more specific type of connection. On the page above, two templates
based on the "Standard JMX Connections (JSR-160)" connection type
are shown. Select the template that is most appropriate for your
MBean server and click Next.
The Connection Properties page (Figure 109) contains the details on how to connect to an MBean server. This page needs to be completed with details about your MBean server.
(Optional) Select Set as agent configuration defaults if you want the defaults for JMX to be copied from these properties. For example, the default JBoss base paths is C:\jboss-4.0.2.
After you have specified the properties needed to connect, click Test Connection to ensure that the connection can be established. If the connection is not successful, correct the necessary properties.
When the connection is successful, click Finish to return to the browser that will begin using the connection you just configured.
The Java class path information in the Connection Properties page contains three fields that should be completed as necessary to connect to an MBean server that requires java classes that are not included in the Java 5 runtime environment. Normally, the MBean server you need to connect to should be installed on the same system as the Agent Builder. In this case, specify the directory where the application containing the MBean server was installed as the Base Paths field. The Jar Directories field should then list the directories relative to the Base Paths directory that contain the jar files needed to connect to the MBean server. The Class Path field can be used to include specific jar files. The jar files listed in the Jar Directories field do not need to be listed separately in the Class Path field.
Any of the fields can contain more than one reference; just separate the entries by a semicolon. These values are the same values that are needed when configuring the agent. See JMX configuration for additional information about these fields.
- After you have selected a connection, the JMX Browser downloads
information about the MBeans from the JMX server. This information
is displayed in the following four areas of the JMX Browser window
(Figure 110):
- MBean Key Properties area (upper left) - This is collection of every unique Object Name key found from all the MBeans on the server. The [Domain] entry is special because it is not really a key, but it is treatedt as an implied key for the value of the MBean's domain. When you select an item from this list, the JMX Browser finds all of the MBeans that contain that key property and displays the list of values of that key property in the list on the right. When you check a key property, it is included in the Object Name pattern for the data source.
- Selected Key Property Values area (upper right) - Shows the values of the currently-selected MBean Key Property from all MBeans. Selecting one of these values will check the MBean key property and update the Object Name Pattern that is displayed in the text field below with the MBean key property name and value.
- A table listing all MBeans matching the Object Name Pattern (center)
- As you select Key Properties and Values from the MBean Key Properties
and Selected Key Property Values lists, you will see the Object Name
Pattern update and the list of MBeans in this table will change to
reflect the list of MBeans that match the pattern you have currently
selected. If you have a pattern that is not matching any MBeans,
you can clear entries in the MBean Key Properties list by clicking
the check box next to a key being used by your pattern and removing
the check mark. Also, you can manually edit the pattern to find the
MBeans you are looking for. The pattern *:* selects all MBeans.
You can use this table to browse the MBeans from the server and decide which ones contain the data you want to monitor. To help browse a potentially large number of MBeans, you can sort by any key attribute (from the context menu or by clicking on a column header). You can also show any key attribute in any column by selecting "Show Key Property" from the context menu. When you see a key property value in the table that identifies MBeans you want to monitor, right-click on that value and choose Select only MBeans with Key Property from the context menu.
- A table containing details for a selected MBean - The JMX Browser shows you information about a single MBean. To see details for an MBean, you select the MBean from the table showing the list of MBeans matching the current filter. The key information about the MBean is the list of Attributes, Operations, and Notifications it defines.
To create a data source from the JMX Browser, use the four panels described above to build an Object Name Pattern that matches a set of MBeans that each contains the monitoring data you want to collect. For example, if you wanted to monitor data from all of the ThreadPool MBeans, you would do the following:
- Select type from the MBean Key Properties panel. Selecting type causes the values in the Selected Key Properties Values to be updated to list all unique values from the type key of any MBean.
- Select ThreadPool from the list of values for the type key. After selecting ThreadPool, the type key property name is checked in the MBean Key Properties panel and the Object Name Pattern is updated to "*:type=ThreadPool,*". The list of MBeans is also updated to show only the MBeans that match this pattern.
- Select one of the MBeans from the MBean list to see the attributes, operations and notifications available for the MBean. If your MBean list contains more MBeans than you want to monitor, you must continue this procedure of selecting key properties and values until you have the Object Name Pattern that identifies the set of MBeans you want to monitor. You can also display a context menu in the MBean list to update the Object Pattern with key property values shown in the table.
- When the object name pattern is correct, select an MBean from the table. All attributes of the selected MBean will be the initial attributes in the new JMX data source. Some attributes might not contain data. After the JMX data source is created review the attributes and remove any that are not significant. If the selected MBean has no attributes, you will be warned that the data source will be created with no attributes. If the selected MBean contains notifications, an "Event" data source will also be created to receive notifications from the MBeans.
- Click Finish in the filled on JMX Information page. Data sources are created based on the MBean that was selected in the previous step. If no MBean was selected, an attribute group with no attributes is created and a warning is displayed, giving you a chance to select an MBean if you want to. The notification data source has the word, Event, at the beginning of the data source name to distinguish it from the data source that shows attributes.
- To change other JMX options for the agent, click Global
JMX Options. These options allow you to do the following:
- Select whether JMX monitors are supported by this agent. See the next section for a description of JMX monitors. If you want JMX monitor attribute groups and Take Action commands to be created, check Include JMX monitor attribute groups and take actions.
- Select the types of MBean servers your agent will connect to when it is deployed. There are several vendor-specific types of servers listed, along with a generic JSR-160-Compliant Server for standards-based servers. You can select as many as needed, but you should only select server types that support the MBeans that are being monitored. You must select at least one. If you select more than one, at agent configuration time you are prompted to specify which type of server you want to connect to.
- Click OK after you have selected the desired option.
- Click Next.
- On the Select key attributes page, select key attributes or indicate that this data source produces only one data row. See Selecting key attributes for more information.
- Click Next.
The JMX Agent-Wide Options window shows the types of application servers that the Agent Builder supports. If you previously selected Set as agent configuration defaults on the Connection Properties page, the type of application server that you browsed to is automatically selected.
- In the JMX Agent-Wide Options window (Figure 112), select any other types of application servers to which you want your agent to be able to connect.
- Do one of the following steps:
- If you are using the New Agent Wizard, click Next.
--OR--
- Click Finish to save the data source and open the Agent Editor.
- If you are using the New Agent Wizard, click Next.
- If you want to change the types of application servers to which you can connect after the agent has been created, click Global JMX Options in the JMX Data Source Information area (Figure 113).
- In the JMX Agent-Wide Options window (Figure 114), change any selections that you want.
- Click OK.
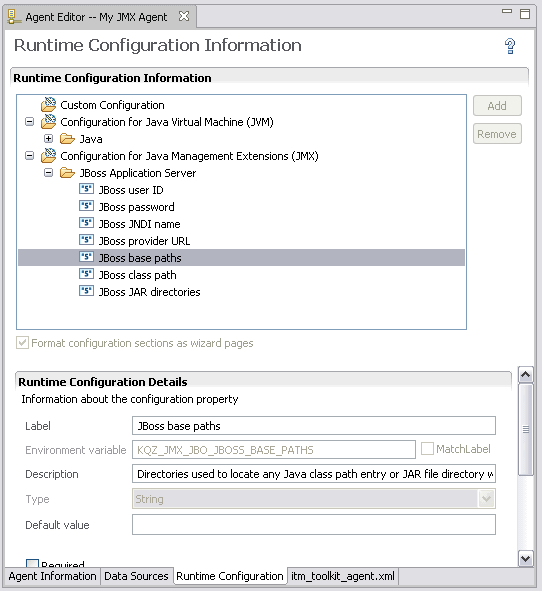
- To view the configuration sections and properties
that were automatically generated, click the Runtime Configuration tab of the Agent Editor (Figure 115).
The default value of the property, JBoss base paths, has the same value that was entered in the JMX browser in Step Figure 110.
For more information about the attribute groups for JMX events, see (JMX Event attribute groups),