Published: 2 December 2023
Contributors: Amanda McGrath, Alexandra Jonker
Supply chain risk management (SCRM) is the process of finding and addressing potential vulnerabilities in a company’s supply chain. SCRM aims to minimize the impact of these risks on a company's operations, reputation and financial performance.
Supply chain management is essential to business operations. But amid globalization, supply chains have become increasingly complex and interconnected. Companies rely on a vast ecosystem of suppliers, manufacturers, distributors and logistics professionals to deliver goods and services to customers around the world.
However, this complexity also means that there are more points at which supply chain disruptions can occur—a lesson learned by many during the global COVID-19 pandemic. Such disruptions can slow operations, lead to shortages of materials or resources, damage brand reputation or hurt profitability.
Implementing a supply chain risk management strategy is a way for companies to build the resilience to navigate uncertainty and ensure business continuity. With proactive preparedness, companies can avoid or minimize disruptions, reduce costs, improve quality and enhance customer satisfaction. SCRM also helps companies comply with regulations, protect their brand reputation and foster sustainability.
With ESG disclosures starting as early as 2025 for some companies, make sure that you're prepared with our guide.
Register for the ebook on ESG reporting frameworks
Internal and external supply chain risks can come from various sources, including natural disasters, geopolitical events, supplier bankruptcy, quality issues and cyberattacks.
Natural disasters such as earthquakes, hurricanes or floods can upend supply chains. So can political and economic developments, including war and geopolitical instability, trade disputes, strikes and fluctuations in everything from currency valuation to fuel prices. Risk management processes put contingency plans in place that can limit the impact of such events.
Healthy supply chains rely on healthy supplier partnerships. Weaknesses in a provider’s financial stability, capacity constraints or other issues could create instability. If a supplier’s reliability is in question, companies that rely on it may decide to diversify their sources or investigate backup options to ensure a steady flow of materials or components.
Digital systems and communication technologies are often employed to manage orders, inventory and distribution, leaving supply chains increasingly vulnerable to cyberattacks. Ransomware attacks and malware can halt production, delay distribution and prove costly. Breaches of sensitive supply chain data can expose proprietary information or customer data, leading to reputational damage and legal consequences.
Cyberattacks may also be used to disrupt transportation and logistics, damage critical infrastructure, steal intellectual property, create counterfeit products or perpetuate financial fraud. SCRM assesses vulnerabilities in digital systems and data privacy, helping organizations develop security and response plans.
Consumer demand is changing faster (and more unpredictably) than ever, as needs, preferences and options evolve. Accurately predicting demand can have a major impact on profitability, so risk mitigation might include optimizing inventory levels and enabling flexibility in production schedules and distribution channels to meet varying demand.
Visibility into the supply chain is essential to identifying unethical practices related to human rights, labor violations and environmental impact. When a supplier’s behaviors are out of line with international regulatory standards, or a company’s values, it can have consequences for all. Risk management in this area requires due diligence in assessments of practices throughout the supply chain and thorough evaluations of alternatives.
- Identify: Companies will want to spot potential problems or weaknesses that may affect the strength of their entire supply chain. Risk identification can be done by conducting a risk assessment that considers internal and external factors, such as suppliers' location, transportation routes, political stability and weather patterns.
- Assess: Once potential vulnerabilities are identified, companies can then determine how likely they are to occur and what their short- and long-term impact on the supply chain might be. Data and research can help with supply chain risk assessment: quantitative and qualitative methodologies, such as risk scoring, scenario analysis and expert judgment can be useful in comparing historical data and forecasting in light of current metrics and risk factors.
- Mitigate: Once the risks are known and analyzed, companies may decide to come up with strategies to address them, targeting the most significant issues quickly. Risk mitigation strategies can involve diversifying suppliers, improving inventory management, enhancing communication, investing in technology and developing contingency plans.
- Monitor: SCRM is a continuous process, meaning companies may want to keep a close eye on supply chain operations and review policies and SCRM procedures regularly. This approach can involve tracking key performance indicators, conducting audits, building strong supplier relationships and engaging stakeholders. The goal is to limit risk exposure and ensure informed decision-making.
One of the most significant benefits of SCRM is improved resilience. By identifying potential risks and developing contingency plans, companies can prepare for and respond to unexpected events and ensure supply chain security across their operations. This not only helps companies maintain continuity of operations but also ensures they can meet customer demands and maintain their competitive edge.
Effective SCRM may also lead to cost reduction by identifying areas of waste or inefficiency. For example, by optimizing inventory levels, companies can reduce carrying costs and the risk of stockouts. Similarly, by streamlining logistics processes, companies can reduce transportation costs and improve delivery times.
By ensuring that suppliers meet quality standards and regulatory requirements, a company can avoid expensive recalls and legal penalties. This not only protects its reputation but also ensures that retailers and customers receive high-quality products and services.
Identifying and addressing potential problems early can help avoid negative publicity, thereby protecting the company’s brand image and its relationships with stakeholders. More companies are increasingly applying corporate social responsibility practices and seek to achieve environmental, social and government (ESG) goals. SCRM offers a way to support sustainable practices and ensure that all parts of the supply chain are limiting environmental impact.
Implementing SCRM can be challenging for companies due to several factors. Modern global supply chains are deeply complex, making it difficult to track details closely at every step from start to finish.
Furthermore, if a company does not have access to reliable data on its suppliers, it won’t be able to fully and accurately assess risks. Some suppliers may be reluctant to provide data due to privacy concerns or a fear of losing a competitive advantage. And even if they provide enough data to identify risks, they may be unwilling to adopt new practices or alter existing ones.
It also comes with costs: new technologies, training and hands-on monitoring require financial investment that can sometimes prove too much for smaller businesses to accommodate. The more stakeholders involved, the larger the budget required to maintain due diligence across them all.
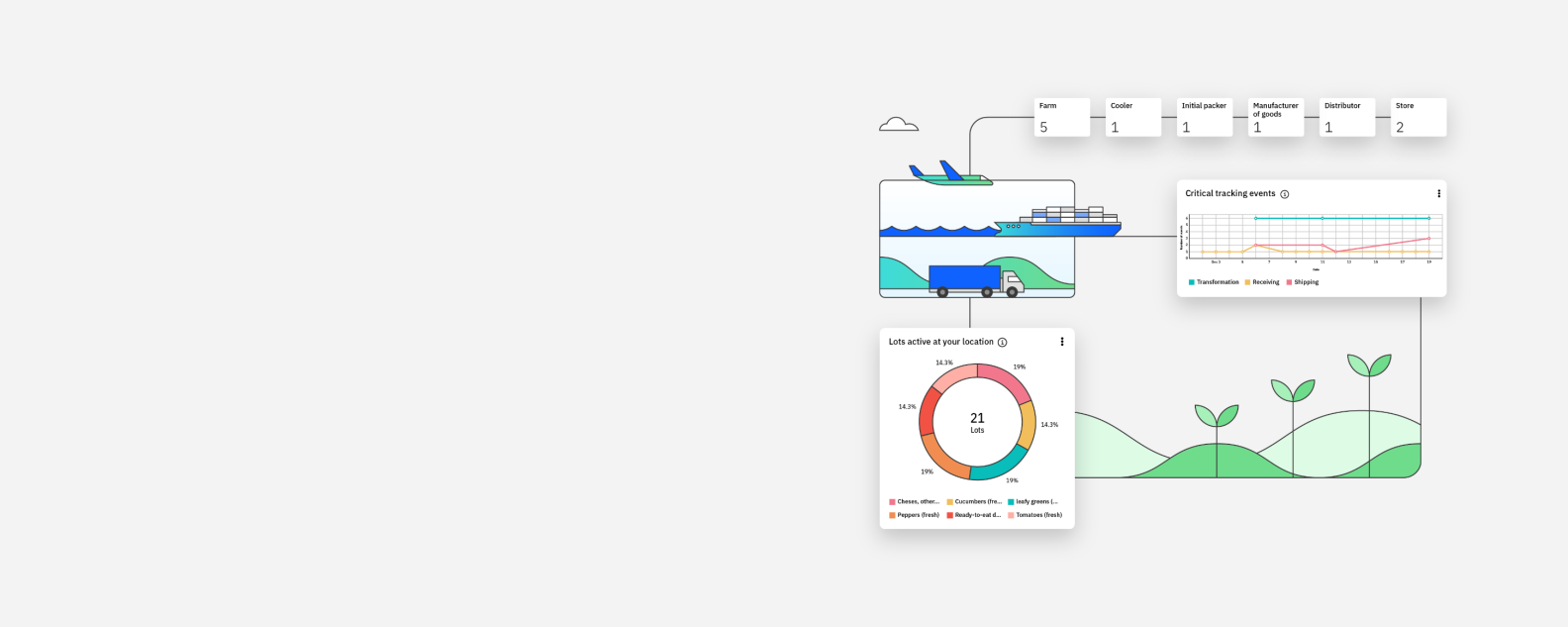
Advanced technologies offer new and powerful ways to work with supply chain analytics and improve supply chain visibility and transparency.
Sensors, GPS and Internet of Things (IoT) devices can provide a wealth of real-time information at every stage of the supply chain. These devices help track each phase of the product lifecycle from raw materials procurement to production to distribution and end use. Supply chain data collected from various points can drive optimization by providing insights into operational efficiencies, potential risks and areas for improvement.
Automation tools and robotics technology can increase efficiency in the supply chain by reducing human error. Automated systems can also operate in hazardous conditions, thereby reducing risk.
As an immutable, accessible ledger, blockchain can enhance transparency and traceability across the supply chain, making it easier to verify the authenticity of products and track the movement of goods.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify the most efficient transportation routes, spotlight potential disruptions or inconsistencies and gain insight into environmental impact. Simulation software can help with modeling potential scenarios to predict risk and develop contingency plans.
Cloud computing can provide scalable solutions for data storage and sharing that make it easier to collaborate and exchange information at every stage of the supply chain.
SCRM involves various roles within an organization. Specific risk management teams may be created to craft and execute the overall strategy for identifying, assessing and mitigating risk events and monitoring supply chain resilience.
In addition, procurement teams are responsible for selecting potential suppliers and managing current ones, ensuring they meet quality and delivery standards. Operations teams manage production, inventory and logistics, making sure they are efficient and resilient. IT teams implement and maintain technology solutions that support SCRM processes.
SCRM is essential to efforts to promote sustainability in business. It helps companies identify and address environmental and social risks in their supply chain, including issues related to environmental impact, waste, energy use and labor practices. For example, implementing technologies that track energy use can lead to significant reductions in carbon emissions.
SCRM can also help companies promote circular economy principles by reducing waste. By fully assessing risk, companies are in a better position to make decisions that align with their goals and values.
Having contingency plans for potential disruptions helps companies prevent situations that create waste and allows them to maintain their pursuit of sustainability goals even amid unexpected changes. A thorough risk management program can bolster a company's reputation for corporate responsibility, which can be critical to its brand image. As a result, supply chain risk management is a key part of a complete sustainability strategy.
Apply the power of artificial intelligence (AI) and the speed of automation to improve supply chain management, resiliency and sustainability.
Use a modular solution built on blockchain to benefit all network participants with a safer, smarter and more sustainable food ecosystem.
Orchestrate your end-to-end supply chain with real-time visibility and actionable workflows powered by artificial intelligence and machine learning.
Build your own blockchain ecosystem with traceability software for better supply chain management.
Empower your team to make informed decisions that help improve margins, increase service levels and minimize unplanned downtime.
Discover how to build your own blockchain-enabled collaboration and data-sharing ecosystem with your supply chain partners.
See how IBM Supply Chain Control Tower allows you to respond faster to changes, enable efficient collaboration and drive operational automation.
Learn how healthcare leaders and CSCOs are adopting key technologies to achieve a step change in their supply chain organizations.
Explore how a supply chain control tower acts as a connected, personalized dashboard of data, key business metrics and events across the supply chain.
Learn how supply chain optimization makes use of technology and resources to maximize efficiency and performance in a supply network.