Question & Answer
Question
How can I use role-based access control (RBAC) with the special user []guest[]?
Answer
When RBAC is active, an application client program must supply a user name and password to interact with the application. To illustrate this, this technote uses an adapter as an example of an application client program.
To set up a WebSphere® InterChange Server environment, you need application accounts for all Internet Inter-ORB Protocol (IIOP) and WebSphere MQ adapters that you want to run. By default, these adapters have an application account with the user name guest and the password guest. If RBAC is inactive, the login accounts for all adapters are unused. Authentication is supported only for IIOP and MQ adapters; other types of adapters do not require login verification, regardless of the RBAC status.
When you configure an adapter, you must specify the application account name and password as values for the standard connector properties ApplicationUserName and ApplicationPassword.
The Adapter Access Control feature is enabled only when the value of DeliveryTransport is IDL. By default, the adapter logs in with the guest identity. If the Use guest identity box is cleared in the connector configuration, the Adapter Identity and Adapter Password fields are enabled when RBAC is turned on. That is, if the Adapter Access Control section of the Security tab is set up as in this screen capture, the connectors use the guest account.
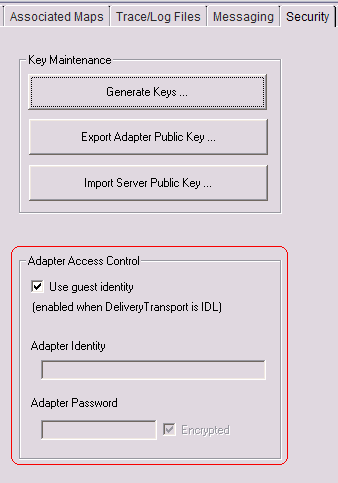
Note: The guest user is defined by the system, so the passwords for that user cannot be changed.
For each operation that must be secured, the administrator defines roles that are allowed to perform the operation. Only users that are members of the permitted roles are allowed to perform the operation. When permissions are assigned to roles, the permissions are referred to as the security policy for the role. Users can be assigned to multiple roles.
Important note: An operation or an action is not secure if no roles are assigned to it, and every authenticated user (including guest) can perform any action on it. Users are allowed to perform an action that is secure only if the user has been assigned to a role that has been granted access to the action. See the section "Role-based access control" in the topic Securing InterChange Server (http://publib.boulder.ibm.com/infocenter/wbihelp/v6rxmx/index.jsp?topic=/com.ibm.wics_general.doc/doc/tech_intro/techmst24.htm) for information about RBAC for InterChange Server.
Example
- Activate RBAC (RBAC ON) and create the user admin with administrative access.
- Start InterChange Server.
At this point, user guest or any authenticated user has access to the server and can perform all operations on the components.
- Create the new role component_role and give access to connectors and collaborations. That is, secure the connectors and collaborations and assign them to a new user component_user.
The user component_user can now manage the collaborations, the connectors, and the map. The map has not been assigned, so it is not secure.
- Log in as user guest. You can access only the map, which is not secure, but you cannot access the secured collaborations and connectors.
- The user admin however will be able to administer all the components.
RBAC is designed to secure at the component level. After all of the components are secure, only users with assigned components can manage their components, so the user guest cannot manage any of the secure components. Refer the RBAC ACL Security in the related Information section below for more information on RBAC ACL security policy and automated role assignments.
Related Information
Was this topic helpful?
Document Information
Modified date:
15 June 2018
UID
swg21315759