Preventive Service Planning
Abstract
The two port 16 Gbps adapter in the 2145-DH8 node has fewer ports than the four port 8Gbps adapter. Therefore, additional host, SAN and storage configuration changes are needed, when upgrading an 8Gbps node to a 16Gbps node.
Content
This note describes the methods for replacing 8Gbps HBAs with two port 16Gbps HBAs; either when migrating from older nodes using the 8 Gbps HBAs to 2145-DH8 node with the two port 16 Gbps HBAs, or when replacing the 8Gbps HBAs within a DH8 node.
Note: The information below does not apply when replacing 8Gbps HBAs with the four port 16Gbps HBA. Because these HBAs have the same number of ports, the new 16Gbps ports will have the same WWPNs as the ports they are replacing, so SAN rezoning is not required.
WWPN Modes
In this document we make reference to a 2145-DH8 node in "Standard Mode" and in "Legacy Mode".
- Standard Mode is where the 2145-DH8 node is using the WWNN that was assigned to it (or another 2145-DH8 node) in the factory.
- Legacy Mode is where the 2145-DH8 node is using the WWNN that had previously been assigned to an earlier generation SVC node (for example a 2145-CG8 node).
How to understand the images below
SVC WWPNs for the 2145-CG8 nodes and older are in the Legacy Mode format
50:05:07:68:01:XY:zz:zz
The zz:zz is a unique number assigned to the node by the manufacturing team.
The XY is generated by the SVC software for each port. For example legacy port allocation for a 4 port 8Gbps HBA in slot 1 would have the port numbering of 40, 30, 10 and 20.
2145-DH8 nodes in Standard Mode have WWPNs in the following format
50:05:07:68:0c:VW:zz:zz
The zz:zz is a unique number assigned to the node by the manufacturing team.
The V is the HBA slot number and the W is the port number of that adapter. For example port allocation for a 4 port 8Gbps HBA in slot 1 would have the port numbering of 11, 12, 13 and 14.
In the diagrams below, the number in the blue boxes represent the value of XY for Legacy Mode and older nodes, or VW for Standard mode.
The vast majority of SVC nodes will be using values of zz:zz that result in the Y being either 0 or 8 as shown in the images below. However a small number of 2145-CG8 nodes were shipped in 2014 where the values of Y were 1 and 9 instead of 0 and 8.
See the appendix below for more details about WWPNs configurations on the 2145-DH8.
Problem Statement
When moving from the 4 port 8Gbps HBA to the 2 port 16Gbps HBA the port allocation will change, and therefore consideration should be taken on the upgrade approach. Diagram 1 illustrates the legacy mode port allocation between CG8 and DH8 nodes. Diagram 2 illustrates the 16Gbps HBA port allocation in legacy and Standard mode on the DH8 nodes.
For the duration of this document we will be focussing on the non-disruptive hardware replacement procedure, however the same set of problems will also apply to removing a 4 port 8 Gbps HBA and replacing it with a 2 port 16 Gbps HBA.
The existing documentation for non disruptive hardware replacement indicate that the fibre channel cables should be removed from the old HBA and plugged into the same port on the new HBA, as shown in the Diagram 1. This procedure means that the node hardware can be completely replaced and the SAN zoning and host configuration does not need to be changed in any way to allow the host to talk to the new hardware.
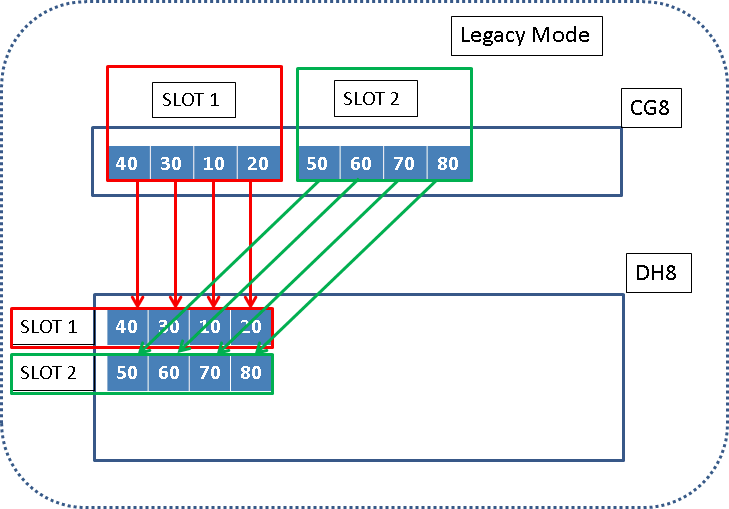
Diagram 1. CG8 to DH8 with 8 Gbps cards and Legacy Mode port allocation.
However the 16 Gbps cards have half the number of ports per HBA, so the WWPN allocation does not allow for each of the WWPNs used by the 4 port card to be configured in the 2 port HBAs, as shown in Diagram 2

Diagram 2. CG8 to DH8 directly to 16Gbps with Standard Mode port allocation.
Because the WWPNs are not all preserved, any zoning, backend storage subsystems and hosts which were communicating with the WWPNs 10, 20 ,70 or 80 will have to be re-configured.
Options for Enabling 16Gbps Technology
Two options are available; the first option is based on a non-disruptive upgrade to a DH8 SVC node with 8Gbps HBA in legacy mode, and the second option is based on upgrading directly to DH8 nodes with 16Gbps HBAs.
Option One
- use 16 Gbps for additional ports only
This process includes upgrading non-disruptively from the older SVC nodes with 8Gbps HBAs to DH8 SVC nodes with a mixed configuration of 8Gbps HBAs and 16Gbps HBAs. The below points describe the process for option one:-
- Implement a new DH8 node with 8Gbps HBAs as per the older SVC node 8Gbps HBA configuration; add additional 16Gbps HBAs to the DH8 node as per the customer’s requirements.
- Remove the older SVC node from the IO Group and cable the new DH8 node with 8Gbps HBA as per the port allocation in diagram 3.
- Power up the DH8 node and confirm that the node is running in legacy mode, and that it logs into the SAN fabric and joins the SVC cluster. Next, verify the node has started servicing host I/O before repeating this process on the remainder of the older SVC nodes in the cluster.
- At this point, the DH8 nodes will be running in legacy mode and all zoning and access to the storage will remain intact with the same WWPN conventions as used previously.
- The final step is to cable and zone the 16Gbps ports into the SAN fabric and migrate hosts and storage onto the 16Gbps ports as needed, eventually phasing out the 8Gbps host connectivity and replacing with 16Gbps HBAs.
*Note:- If the SVC cluster is already utilising DH8 nodes with 8Gbps HBAs, the 16Gbps HBAs could be installed as required and later zoned into the fabric, which will require a reboot of the node. If an 8Gbps HBA is removed from a DH8 node and replaced with a 16Gbps HBA there would be an element of re-zoning required (ref Diagram 5) or refer to option 2.
The advantages of this approach for the customer would allow transition to DH8 nodes with 16Gbps capabilities without requiring zoning changes. Additionally, host I/O would remain on the same WWPNs to the nodes.

Diagram 3. Illustration of a CG8 node with two 8Gbps HBAs migrating to a DH8 node with multiple 8Gbps HBAs and multiple 16Gbps HBAs.

Diagram 4. Illustration of a CG8 with single 8Gbps HBA migrating to DH8 with single 8Gbps HBA and multiple 16Gbps HBAs.
Option Two
- use only 16Gbps ports
The second option is based on upgrading to a DH8 node with 16Gbps HBAs; includes a larger amount of planning (zoning and host access) as this would remove the older SVC nodes with 4 port 8Gbps HBAs, and introduce the new DH8 nodes with 2 port 16Gbps HBAs. The below points describe the process for option two:-
Please note that the benefit of legacy mode in this scenario is very limited, so it will often be appropriate to use the new Standard mode WWPNs.
- Select and remove the older SVC node from an IOgroup.
- Install a DH8 node with 16Gbps HBAs.
- Re-cable the DH8 node according to the mode selected* (reference diagram 5 and 6 for Legacy Mode or diagram 7 and 8 for Standard Mode).
- SAN zoning changes for DH8 node depending on the mode adopted:-
- (Standard Mode) Rezone the new 16Gbps WWPNs; include into the node zone, storage zone and host zones – hosts to re-scan for new paths.
- (Legacy Mode) 2 legacy WWPNs will not be available (as described in Problem Statement), and therefore re-zoning is required to allow hosts and storage to talk to the available WWPNs in the new configuration.
- LUN Mapping in the backend storage subsystems will also need to be re-configured for the allow any new WWPNs to access the storage as necessary.
- All the new WWPNs changes will require the host to rescan and change previous persistent reservations – confirm host IO access through new node before continuing.
- Verify the new DH8 16Gbps node joins the IO Group and has paths to storage, nodes and hosts.
- Check the SVC event log and verify all the hosts, controllers and other SVC nodes have established paths to the new node.
- Continue the process for the partner node within the IO group, followed by the remainder of the IO Groups within the cluster.
* Each SAN fabric will require a level of planning when considering using Legacy Mode or Standard Mode with 16Gbps HBAs. When using Legacy Mode, 2 of the legacy WWPNs will be removed and will require re-zoning (ref. to diagram 5 and 6). When using Standard Mode, all the 16Gbps WWPNs will be new and require full re-zoning (ref. to diagram 7 and 8).
The advantages of this approach would provide the customer with immediate 16Gbps capabilities without the need for the 8Gbps intermediate step, or further zoning changes after the 16Gbps upgrade has been completed.

Diagram 5. CG8 to DH8 directly to 16Gbps with Legacy Mode port allocation.

Diagram 6. DH8 to DH8 directly to 16Gbps with Legacy Mode port allocation.

Diagram 7. CG8 to DH8 directly to 16Gbps with Standard Mode port allocation.

Diagram 8. DH8 to DH8 directly to 16Gbps with Standard Mode port allocation.
Port Masking
For environments which have implemented SVC fibre channel port masking, there will be a reduction of FC ports when upgrading to the 16Gbps 2 port HBAs. Therefore any port masking configured for FC ports which are not available after the 16Gbps HBA upgrade, will require further changes to allow the appropriate traffic to communicate through the correct FC ports.
The important point to understand is that the bits in the port masking view relate to the number of configured ports, regardless of their slot therefore the WWPNs of the bit positions may change between older nodes with 8Gbps HBAs and DH8 with 16Gbps HBAs. The port numbers (bit positions) are counted from left to right (viewed from the rear) in each slot and in ascending order of slot number.
Please Note: prior to making changes to the HBA configuration where there is Port Masking enabled; there should be multiple ports setup for the inter-node communication in case ports are removed when upgrading to 16Gbps HBAs. There is a limitation with updating the port masks when a node is offline.
Therefore we follow a best practice of having at least two inter-node links between nodes in a SVC cluster. In the case a single port for the inter-node communication breaks, there would be no solution at present as the port masking is unable to be changed whilst the node is offline. To avoid this, the port mask bits could be set (1) for every unused port to allow inter-node communication through the unused ports.
In addition, the port mask is static; for example the port mask is not remapped when ports are re-numbered due to HBA changes. The inter-node communication could accidentally be masked out when HBAs are changed, and nodes would be unable to re-join the SVC cluster. To overcome this the port mask bits should be mapped to the WWPN of the ports prior to the HBA upgrade.
Appendix: DH8 WWPN Allocation

Diagram 9. Legacy and Standard Mode port allocation for 8Gbps HBAs on DH8 node.
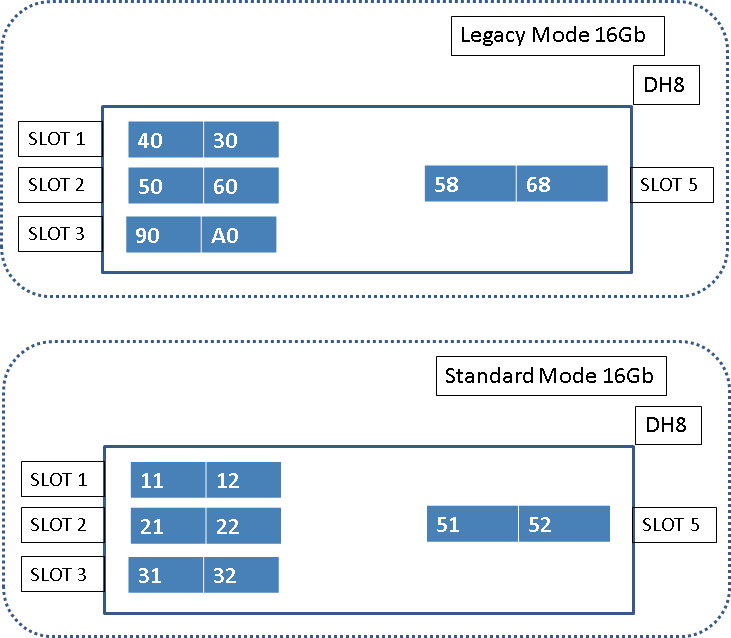
Diagram 10. Illustration of DH8 nodes when configured with 16Gbps HBA in both Legacy and Standard Modes.
Was this topic helpful?
Document Information
Modified date:
17 June 2018
UID
ssg1S1004999