White Papers
Abstract
InfoSphere MDM is a Java Enterprise Edition (Java EE) software product. Like any other Java EE software product, installing InfoSphere MDM consists of installing several parts, including:
* a database component
* an application server component
* InfoSphere MDM application content, including WebSphere Application Server applications and bundles
Content
1: Troubleshooting the MDM database component
InfoSphere MDM supports the following database platforms:
- Oracle Database
- IBM DB2
- IBM DB2 for z/OS (partial installation support, for the application server component only)
- Microsoft SQL Server (supported by InfoSphere MDM Standard Edition only)
From InfoSphere MDM Version 11.0 onwards, there is a combined schema for Standard Edition (virtual MDM) and Advanced Edition (physical MDM). The combined InfoSphere MDM database installation creates 953 tables. There are 153 tables to support virtual MDM and the remaining tables support physical MDM. Optionally, the installation also creates a set of database triggers. These triggers are used in Advanced Edition deployments.
The MDM database has the following configuration restrictions:
- Changes to the number of tablespaces for DB2 and Oracle database are not supported.
- Using different schemas for physical MDM data and virtual MDM data is not supported.
Database script overview
All of the Advanced Edition database scripts (for all database platforms) are located in the <MDM_INSTALL_HOME>/database folder, grouped as either Core or Full. The Core subfolder contains only scripts required for core MDM data, while the Full subfolder contains all of the scripts required for core MDM and all of the MDM domain data.
The Advanced Edition tables are grouped into three sets:
- Core tables – These table names are prefixed with CD. These tables are used in all domains.
- Domain tables – These table names match regex [CD*TP]. These tables are used with specific domains, such as insurance or banking.
- Configuration Manager (CM) tables – Used in the configuration of Advanced Edition. See the section below for more details about Configuration Manager tables.
For Standard Edition, the SQL scripts are generated dynamically during installation, so there are no scripts available before installation.
Troubleshooting MDM database creation
All of the InfoSphere MDM database object creation logs are available in the folder <MDM_INSTALL_HOME>/logs/database.

Note: Depending on the details of your installation, you may not have all of the subfolders shown here.
Note: Depending on the details of your installation, you may not have all of the subfolders shown here.
- CMData stores logs that correspond to physical MDM configuration and management object creation.
- CoreData stores logs that correspond to physical MDM core data.
- DomainData stores logs that correspond to physical MDM domain data. The physical MDM domains manage information related to parties, products, and accounts.
- RDMScripts stores logs that correspond to InfoSphere Reference Data Management.
- Virtual stores logs that correspond to virtual MDM data.
If you encounter any problems when creating the database, look for corresponding .err files in the subfolders of <MDM_INSTALL_HOME>/logs/database.
If your implementation of InfoSphere MDM uses the WebSphere Application Server default messaging engine, then there will be nine extra SIB tables, as shown below. These SIB tables are created by WebSphere Application Server when the server that hosts InfoSphere MDM is started.

Tip: If you are using same schema multiple times because of previous failed installations, remember to remove these tables after every installation.
If your installation encounters errors when creating virtual MDM tables, look in the folder <MDM_INSTALL_HOME>/logs/database/Virtual. If the installation has not rolled itself back after a failure, then look for log files at the location <MDM_INSTALL_HOME>/mds/log to find information about why the rollback did not occur.

To recreate the tables, try running the virtual MDM madconfig target. To run the madconfig target:
1. Open a command-line prompt from the <MDM_INSTALL_HOME>/mds/scripts directory.
2. Run the virtual MDM madconfig target:
./madconfig.sh bootstrap_datasource
2: Troubleshooting the application server component
The InfoSphere MDM application server component includes:
- WebSphere Application Server configuration resources that the InfoSphere MDM enterprise applications use to connect to the MDM database, the messaging engine, and so on.
- InfoSphere MDM enterprise applications and business level applications that must be deployed.
WebSphere Application Server configuration resources
Since InfoSphere MDM is a J2EE Application, the application resources configured in its enterprise applications include the following:
JDBC Data Providers – Two JDBC providers are created during the InfoSphere MDM installation: one for physical MDM and another for virtual MDM. A third JDBC provider, called the Derby JDBC Provider, is created when the WebSphere Application Server profile is created. All three providers must exist to successfully complete an InfoSphere MDM installation.

Data sources – The InfoSphere MDM installation creates three data sources: MDM, DWLConfig, and DWLCustomer. Each of these data sources is configured by the installation and should pass a connection test.

JMS Providers – The installation creates two JMS providers: one for WebSphere Application Server default messaging and one for the WebSphere MQ messaging provider.

Queue Connection Factory - The installation creates several queue connection factories. The queue connection factories create connections between various MDM sources and the JMS providers.

Topic Connection Factory - The installation creates three topic connection factories. The topic connection factories create connections to the JMS providers for items such as notifications.

Queues - The installation creates several queues that InfoSphere MDM uses to route messages and transaction information to JMS.

Topics - The installation creates topics that InfoSphere MDM uses to route information to JMS.

Activation Specs - The installation creates JMS activation specifications that are associated with MDM functionality (message-driven beans).

Application server security and role mapping
The installation creates WebSphere Application Server users and groups, and maps the users to the appropriate groups. Based on the user name provided in the Installation Manager panel, the installation created the WebSphere Application Server user.

The InfoSphere MDM security groups are ServiceProvider and ServiceConsumer.

3: Troubleshooting InfoSphere MDM enterprise and business level applications
The InfoSphere MDM enterprise application deployed similarly to the following example graphic.

If the InfoSphere MDM deployment includes user interfaces, then each user interface has a corresponding business level application. In WebSphere Application Server, the business level application and WebSphere enterprise application show the user interfaces as in the following example graphic.
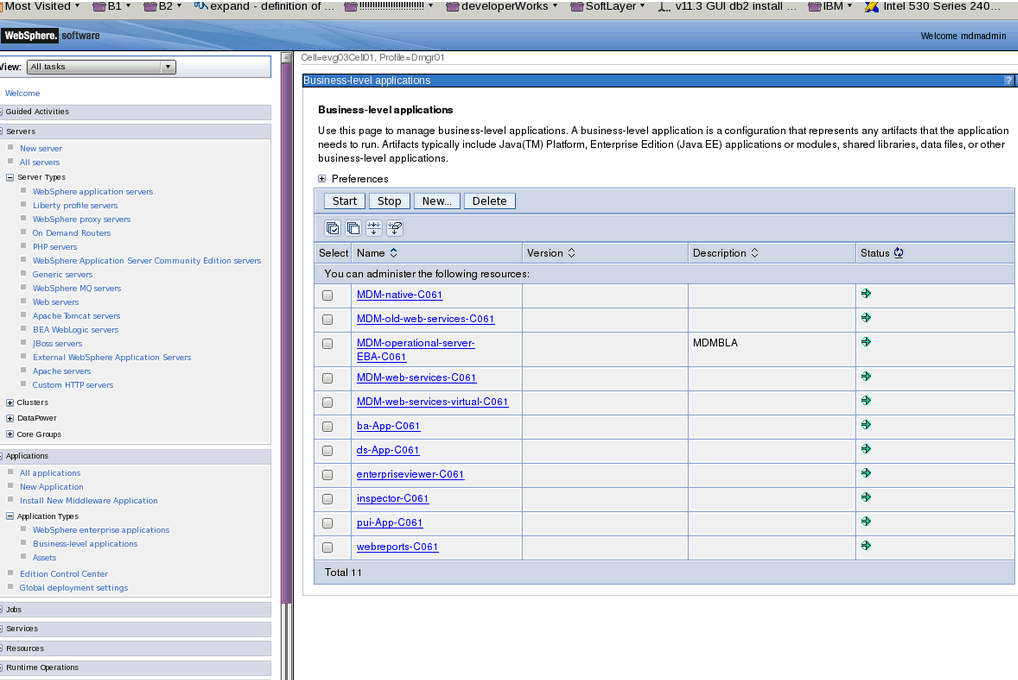
For any successful InfoSphere MDM deployment, all of the installed applications must be in the deployed and running state.
Assets:

Configuration Manager (CM) updates for deployment
Once the Application Server components are deployed, the last step in engine deployment is to enter instance details in the Configuration manager tables. This must be done for the combined Standard and Advanced edition engine, so cannot be ignored. The CM component in Advanced Edition consists of four tables:
1. APPDEPLOYMENT - should have only one row.
2. APPINSTANCE - should be empty unless there is a WebSphere Application Server cluster being used. If a cluster is being used, then there will be one row per node in the cluster.

3. APPSOFTWARE - should contain only one row and the NAME column should be the specified instance value, such as E001.

Tip: If there are multiple instances or a mismatch between installed applications and instances, then you can often resolve it by ensuring that the marked instance name matches the EBA deployed name, as shown in the following example graphic. This can happen if multiple installation attempts are done in the same database without fully uninstalling or cleaning up the database between installation attempts.

a. Use sqldeveloper or its equivalent to create a row with the current instance name, if not there. Delete any other rows from this table.
update APPSOFTWARE set NAME='com.ibm.mdm.hub.server-<instance name>', LAST_UPDATE_DT= CURRENT_TIMESTAMP where NAME='com.ibm.mdm.hub.server-<old_instance_name>';
delete from APPSOFTWARE where NAME='com.ibm.mdm.hub.server';
b. Restart the server and log in.
c. Review the system logs.
4: Troubleshooting installation errors and warnings
Identifying InfoSphere MDM installation problems
InfoSphere MDM installation failures are often identified by an error message that appears during the installation of the application. If you are using IBM Installation Manager to install InfoSphere MDM, then an installation failure will result in a complete rollback to remove the failed installation.

In this case, an Installation Manager popup message appears during the installation of InfoSphere MDM. After the installation user acknowledges the message, Installation Manager will perform a full installation rollback, during which it will uninstall whatever parts of the application were installed before the problem occurred.
Diagnosing installation problems using log files
After you identify that an installation attempt was unsuccessful, it is important to find out the exact reason for the problem. Log files are an important tool to help diagnose these issues. The following log files are created during an InfoSphere MDM installation and can provide critical information in the search for a problem:
- Installation Manager log files
- madconfig command line tool log files
- WebSphere Application Server log files
When an installation fails, the recommended starting point to diagnose the problem is to look at the IBM Installation Manager log files.
Correcting errors and warnings from the Installation Manager log files
The Installation Manager log files are usually located in the $HOME/var/ibm/InstallationManager/logs folder. Installation Manager Logs are stored in a hierarchy with the following file as the entry point: $HOME/var/ibm/InstallationManager/logs/index.xml. Use a browser to view the Installation Manager logs.
1. Copy the $HOME/var/ibm/InstallationManager/logs folder to a local desktop.
2. Open $HOME/var/ibm/InstallationManager/logs/index.xml using a browser.
3. Scroll down in the file until you see blue links. Each link represents a step in the InfoSphere MDM installation process.
In case of a successful install, all of the links have the status INFO. If any of the links in the log file have a status of ERROR or WARNING, this means that the installation may have been unsuccessful, as shown in the following image.

If the InfoSphere MDM installation rolled back with an error that appears in one of the log files, then the approach that you should use to fix the issue is:
1. Find the problem using the logs.
2. Fix the problem and rerun the installation.
To find and then fix an installation problem, you must first figure out the exact reason that the error or warning occurred. Locate and open the native log file linked to the error or warning. For example, consider the following warning message, which is linked to ../native/20140729_1719j.log:

When you open ../native/20140729_1719j.log, you can see the details of the problem:

After you view the details of the problem, then you can try to correct the issue. If you know how to fix the problem, then fix it and rerun the installation. If you do not know how to fix the problem, then you may need to investigate further or contact IBM Support.
Locating other installation logs
Additional sets of installation logs can be found outside the IBM Installation Manager logging system and in a different location under the <MDM_INSTALL_HOME> folder.
- <MDM_INSTALL_HOME>/mds/logs is the location of the virtual MDM data installation logs from the madconfig command line tool.
- <MDM_INSTALL_HOME>logs/database/CoreData and <MDM_INSTALL_HOME>logs/database/DomainData contain logs created during the installation of physical MDM data.
Locating the installation logs corresponding to the key InfoSphere MDM installation steps
The Installation Manager log entries (links) corresponding to the most important InfoSphere MDM installation steps. All of the links shown here are depicted when they implemented successfully, and not showing any ERROR or WARNING statuses. Being aware of these log entries may help you to identify a problem if any of these entries appear in your log files with ERROR or WARNING statuses.
Running an installation using separation mode
A common technique for diagnosing and fixing installation issues is to run the installation in separation mode. This capability enables you to install or modify the product while generating configuration properties files that you can use to configure the product at a later point in time.
Run the installation in separation mode by choosing the Manually run the scripts to configure InfoSphere MDM components after installation option on the final Installation Manager panel before kicking off an installation. Separation mode extracts the configuration options and and enables you to later run a single mad task to configure the product.
For more information, refer to the IBM Knowledge Center: http://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/SSWSR9_11.4.0/com.ibm.swg.im.mdmhs.release.install.doc/Topics/separating-config-and-install.html

5: Troubleshooting failed Installation Verification Tests (IVT)
After Installation Manager finishes installing InfoSphere MDM, it may show an error from the Installation Verification Test (IVT), as in the following example graphic.

Often, an IVT failure can be fixed, especially if the issue is located in the application layer. The first step is to determine exactly what the problem is. Navigate to the application log files at <MDM_INSTALL_HOME>/logs/database and look for .err files under various folders. If there are any database problems, they should be found in this location.
Troubleshooting IVT failures using the WebSphere Application Server logs
Some WebSphere Application Server logs that indicate problems that may not be obvious in the InfoSphere MDM logs. This is true in the cases of the following examples, which can cause IVT failures:
SIB tables missing or created with an older instance
If your installation has missing SIB tables or SIB tables that were created with an older instance, then the WebSphere Application Server logs will have errors such as the following example and will also have BlueprintContainer errors:
[2/7/14 15:51:54:023 PST] 00000058 DWLExceptionU E javax.jms.JMSException: CWSIA0241E: An exception was received during the call to the method JmsManagedConnectionFactoryImpl.createConnection: com.ibm.websphere.sib.exception.SIResourceException: CWSIT0008E: A successful connection was made to the bootstrap server at localhost:7276:BootstrapBasicMessaging but the server returned an error condition: CWSIT0088E: There are currently no messaging engines in bus MDM.SIB.server1 running. Additional failure information: CWSIT0103E: No messaging engine was found that matched the following parameters: bus=MDM.SIB.server1, targetGroup=null, targetType=BusMember, targetSignificance=Preferred, transportChain=InboundBasicMessaging, proximity=Bus..at com.ibm.ws.sib.api.jms.impl.JmsManagedConnectionFactoryImpl.createConnection(JmsManagedConnectionFactoryImpl.java:195)
Resolution:
1. Stop the server or cluster.
2. Delete the SIB tables from the MDM database. There should be nine tables starting with SIB*.
3. Restart the server or cluster.
4. Run IVT again.
These steps will recreate the SIB tables with new entries and refresh the instance.
Authorization failure for mdmadmin or MDM user
If there is an authorization failure, then the WebSphere Application Server logs will have errors such as the following example:
[4/29/14 20:07:39:710 CDT] 00000140 SecurityColla A SECJ0053E: Authorization failed for tmwdchou01.tmw.com:389/mdmadmin while invoking (Bean)com.ibm.mdm.hub.server-E001..11.0.0..com.ibm.mdm.server.dwlcommonservices.ejb..11.0.0.FP00IF000_20131005-0518.war#com.ibm.mdm.server.dwlcommonservices.ejb..11.0.0.FP00IF000_20131005-0518.war#DWLServiceController processRequest:java.util.HashMap,java.io.Serializable:1 is not granted any of the required roles: ServiceConsumer ServiceProvider
[4/29/14 20:07:39:714 CDT] 00000140 AxisEngine E org.apache.axis2.engine.AxisEngine receive An error was detected during JAXWS processing
org.apache.axis2.AxisFault: An error was detected during JAXWS processing
at org.apache.axis2.jaxws.server.JAXWSMessageReceiver.receive(JAXWSMessageReceiver.java:208)
at org.apache.axis2.engine.AxisEngine.receive(AxisEngine.java:208)
at org.apache.axis2.transport.http.HTTPTransportUtils.processHTTPPostRequest(HTTPTransportUtils.java:172)
Resolution:
1. Log on to the WebSphere Application Server Integrated Solutions Console (admin console).
2. Navigate to Business-level applications > MDM-operational-server-EBA-E001 > com.ibm.mdm.hub.server.app-E001_0001.eba > Security role to user or group mapping.
3. Click Map Special Subjects > All Authenticated in Application's Realm to the ServiceConsumer.
4. Click Map users..., then select mdmadmin from LDAP server and map it to ServiceProvider.
5. Navigate to Business-level applications > MDM-operational-server-EBA-E001 > com.ibm.mdm.hub.server.app-E001_0001.eba > RunAs roles for users.
6. Add the mdmadmin user to both the ServiceProvider and ServiceConsumer.
The MDM engine instance cannot be found (BlueprintContainer error):
If the MDM engine instance cannot be found, then the WebSphere Application Server logs will have errors such as the following example:
[12/9/14 15:51:38:439 IST] 00000078 BlueprintCont E org.apache.aries.blueprint.container.BlueprintContainerImpl$1 run Unable to start blueprint container for bundle com.ibm.mdm.server.extrules.default due to unresolved dependencies [(objectClass=com.ibm.mdm.server.config.api.ConfigManager)]
java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException
at org.apache.aries.blueprint.container.BlueprintContainerImpl$1.run(BlueprintContainerImpl.java:328)
at org.apache.aries.blueprint.utils.threading.impl.DiscardableRunnable.run(DiscardableRunnable.java:48)
at java.util.concurrent.Executors$RunnableAdapter.call(Executors.java:450)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask$Sync.innerRun(FutureTask.java:314)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run(FutureTask.java:149)
at java.util.concurrent.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor$ScheduledFutureTask.access$301(ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor.java:109)
at java.util.concurrent.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor$ScheduledFutureTask.run(ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor.java:217)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.runTask(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:906)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:929)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:796)
This happens when the EBA name in WebSphere Application Server and the Configuration manager tables are different. This situation can occur when you reinstall InfoSphere MDM, reusing the same database multiple times without cleaning it between installations.
Check the Configuration Manager table APPSOFTWARE and verify the EBA name. The EBA name value should match the EBA name in WebSphere Application Server.


Resolution:
1. Open DB2 or another applicable database command line and connect to the MDM database.
2. Modify the APPSOFTWARE table as follows:
Update APPSOFTWARE set name=”com.ibm.mdm.hub.server-E010” where APPLICATION_ID=1004;
3. Commit the change to the database.
4. Restart the WebSphere Application Server instance.
5. Rerun IVT.
The Standard Edition native component is not available in WebSphere Application Server:
The InfoSphere MDM Standard Edition native component is installed on WebSphere Application Server as MDM-native-<instance>.ear. This file is extracted into the WAS_HOME folder as follows when the server starts: <WAS_HOME>/profiles/<PROFILE_NAME>/installedApps/<CELL_NAME>/MDM-native-E001.ear
This native component is used by the Standard Edition engine for virtual MDM. The native component must have the correct configuration to enable the Standard Edition engine to work correctly. A copy of the component is also kept at <MDM_INSTALL_HOME>/mds and the configuration of both of these instances must be synchronized.
In some cases, an error may cause the MDM-native-E001.ear to not be extracted into WAS_HOME, meaning that the folder is not created. This will cause the following error to occur:
Caused by: com.dwl.base.exception.DWLBaseException: com.dwl.base.exception.DWLBaseException: com.dwl.base.exception.DWLBaseException: Could not locate business object: VirtualMDMBObj
at com.dwl.base.xml.DWLDocumentHandlerHelper.createObject(DWLDocumentHandlerHelper.java:1358)
at com.dwl.base.xml.DWLDocumentHandlerHelper.populateTopObject(DWLDocumentHandlerHelper.java:1221)
at com.dwl.base.xml.DWLDocumentHandlerHelper.endElement(DWLDocumentHandlerHelper.java:891)
at com.dwl.tcrm.coreParty.xmlHandler.TCRMDocumentHandler.endElement(TCRMDocumentHandler.java:160)
at com.ibm.xml.xci.sax.serializer.SAXCursor.writeClosingTag(SAXCursor.java:225)
... 71 more
Resolution:
1. Restart the server.
2. Ensure that the following folder exists and contains the Standard Edition native component:
<WAS_HOME>/profiles/<PROFILE_NAME>/installedApps/<CELL_NAME>/MDM-native-E001.ear
3. If the correct content is present in this folder, rerun IVT. The error should go away. If not, skip to step 7, below.
4. If the correct content is not present, then navigate to <MDM_INSTALL_HOME>/mds/scripts and run the following command:
madconfig install_native_engine_ear -propertyfile ../../properties/install_native_engine_ear.properties
5. Restart the server.
6. Rerun IVT.
7. If the issue persists, then check whether the installation configuration includes Microsoft SQL Server and LDAP. If so, then contact your database administrator (DBA) to run the following SQL scripts.
Note: These scripts are only required if you are using SQL Server. Turn on snapshot isolation for SQL Server. This only needs to be done once.
ALTER DATABASE <database name> SET ALLOW_SNAPSHOT_ISOLATION ON
ALTER DATABASE <database name> SET SINGLE_USER WITH ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE
ALTER DATABASE <database name> SET READ_COMMITTED_SNAPSHOT ON
ALTER DATABASE <database name> SET MULTI_USER \
After the scripts have been run, then restart the application server.
8. If the issue is still not fixed, then uninstall and reinstall InfoSphere MDM.
Product Synonym
MDS;Master Data Service;MDM;MDM SE;MDMSE;Master Data Management;IBM Infosphere Master Data Service;MDM Standard Edition;MDM Hybrid Edition;Initiate;Hybrid;Physical MDM;Virtual MDM;Hybrid MDM;PME
Was this topic helpful?
Document Information
Modified date:
27 April 2022
UID
swg27045725