Question & Answer
Question
What is the difference between Start Time, Storage Time, and Log Source Time on the Event Information screen in QRadar?
Cause
QRadar displays three time stamp fields on events when users view the details of an event. These three timestamps can have different values depending on where the data originated, when data arrives, and when it is written to disk in QRadar.
Double-clicking an event displays the Event Summary and information about the timestamps from an event.
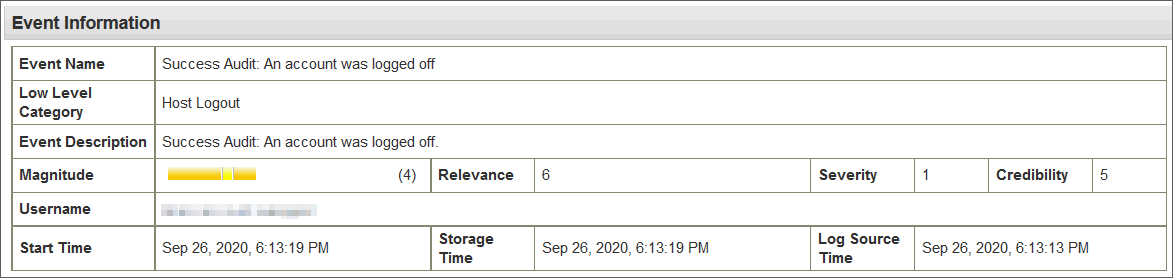
Figure 1: An example event where a six second delay is observed between the payload time represented as Log Source Time and the received time represented as the Start Time.
Double-clicking an event displays the Event Summary and information about the timestamps from an event.

Figure 1: An example event where a six second delay is observed between the payload time represented as Log Source Time and the received time represented as the Start Time.
Answer
Start Time
The Start Time in an event record represents the time at which the the QRadar appliance starts to parse an event. When an event arrives in the event pipeline an object is created in memory, then the start time is set to that time. Users on QRadar V7.3.1 and later the Start Time begins after the EC-ECS Ingress component of the Event Pipeline. As the ingress queue can hold events before they are processed when events burst over license, a delayed Start Time can indicate how long an event was in the ecs-ec-ingress queue on an appliance.
Storage Time
The Storage Time is when data is written out to disk by the Ariel component at the end of the Event Pipeline. Reviewing timestamps can be useful for determining when the Event Pipeline is backed up or experiencing license allocation issues. When the Start Time and Storage Time differ, it can indicate I/O issues, partitions unavailable issues, license issues, or general performance of events being parsed and getting events written to disk (Ariel).
Log Source Time
The Log Source Time is pulled from the event payload itself after the system parsed the event. The Log Source Time that is available in the Syslog header is not always the value that is used to define the Log Source Time. Each log source type in QRadar can look at different values within the event payload to determine what value represents the time when the event occurred. Syslog might use the header timestamp, but other log source types might include two or three different timestamp values. For example, an antivirus event might include a Syslog header timestamp, endpoint time information, scan time, or quarantine time in fields within the payload. Administrators who create custom log source types in the DSM Editor need to evaluate what is the best timestamp for their device type.
The Start Time in an event record represents the time at which the the QRadar appliance starts to parse an event. When an event arrives in the event pipeline an object is created in memory, then the start time is set to that time. Users on QRadar V7.3.1 and later the Start Time begins after the EC-ECS Ingress component of the Event Pipeline. As the ingress queue can hold events before they are processed when events burst over license, a delayed Start Time can indicate how long an event was in the ecs-ec-ingress queue on an appliance.
Storage Time
The Storage Time is when data is written out to disk by the Ariel component at the end of the Event Pipeline. Reviewing timestamps can be useful for determining when the Event Pipeline is backed up or experiencing license allocation issues. When the Start Time and Storage Time differ, it can indicate I/O issues, partitions unavailable issues, license issues, or general performance of events being parsed and getting events written to disk (Ariel).
Log Source Time
The Log Source Time is pulled from the event payload itself after the system parsed the event. The Log Source Time that is available in the Syslog header is not always the value that is used to define the Log Source Time. Each log source type in QRadar can look at different values within the event payload to determine what value represents the time when the event occurred. Syslog might use the header timestamp, but other log source types might include two or three different timestamp values. For example, an antivirus event might include a Syslog header timestamp, endpoint time information, scan time, or quarantine time in fields within the payload. Administrators who create custom log source types in the DSM Editor need to evaluate what is the best timestamp for their device type.
Note:
- If there is no time available in the payload at all, then the log source time field is populated with the same value as the start time.
- If an event includes a time zone, then we adjust the Log Source Time to account for the time zone change.
Example:
If an event includes a time zone that is GMT+8 to the Console, the Log Source Time is listed as GMT-8 from the time stamp in the event payload. This is so users can understand when the event occurred based on the Console time.
If an event includes a time zone that is GMT+8 to the Console, the Log Source Time is listed as GMT-8 from the time stamp in the event payload. This is so users can understand when the event occurred based on the Console time.
[{"Line of Business":{"code":"LOB24","label":"Security Software"},"Business Unit":{"code":"BU059","label":"IBM Software w\/o TPS"},"Product":{"code":"SSBQAC","label":"IBM Security QRadar SIEM"},"ARM Category":[{"code":"a8m0z000000cwtEAAQ","label":"Log Activity"}],"ARM Case Number":"","Platform":[{"code":"PF016","label":"Linux"}],"Version":"All Version(s)"}]
Was this topic helpful?
Document Information
Modified date:
11 May 2023
UID
swg21695264