Technical Blog Post
Abstract
IBM AIX MPIO support for iSCSI
Body
Introduction
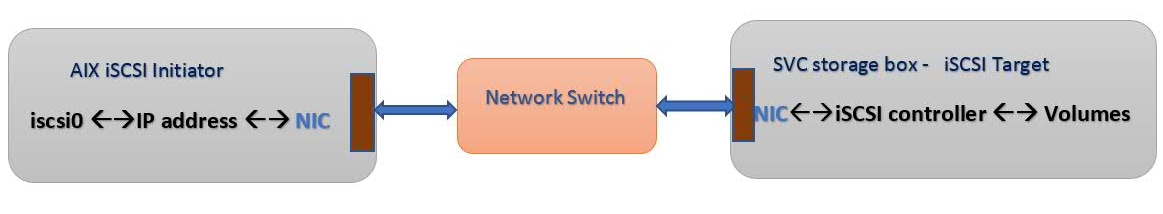
iSCSI software initiator is an AIX software device driver instance to discovery and access the iSCSI disks using SCSI over TCP/IP protocol i.e iSCSI protocol. iSCSI software initiator will work with any type NIC interface such as PF, VF, VNIC, VEA or Virtio NIC, So no more explicit iSCSI adapter is required.
Earlier with iSCSI initiator is supported only with one path attachment to the iSCSI target. With new AIX 7.2TL3 level, MPIO support for iSCSI software initiator is introduced. An iSCSI disk to be discovered with MPIO requires ODM definition similar to FC. AIX ships ODM definition for SVC, XIV and NetApp family of Target storage devices.
iSCSI MPIO support is no more adapter dependent.
iSCSI component description
Typical core components of iSCSI.
iSCSI Initiator node:
It is a host that connects to storage device and send SCSI command to the SCSI target, the SCSI commands and data are packed into TCP packets as per RFC3720 standard.
iSCSI Target node:
It is a device end node that responds to iSCSI commands and exports local volumes as LUNS to the initiator node.
iSCSI Connections:
TCP connection between initiator and target node where SCSI command and data within iSCSI PDUs are transmitted and received.
SSID(Session ID):
A session between as iSCSI initiator and iSCSI target is defined by a session ID that is a tuple composed of an initiator part(ISID) and a target port. The ISID is explicitly specified by the initiator as session establishment.
Here ‘iscsi0’ device is iSCSI initiator instance in AIX O.S which is software device driver and exits only one instance per O.S regardless number of physical or virtual NIC interfaces present on the host. The NIC interfaces can be either PF, VF, VNIC, VEA or Virtio NIC.
CHAP : (Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol) .
Security and Authentication provision between Initiator and Target.
AIX MPIO support for iSCSI:
MPIO support for iSCSI software initiator provides multiple I/O paths between initiator
and target node. Based on disk algorithms and reserve policy, I/O can follow on all the paths or single path. In real time, any NIC adapter fails still few alternate paths can be used without affecting I/O flow between host and target.
1.iSCSI initiator without MPIO
2. iSCSI initiator with MPIO
iSCSI naming and addressing convention:
The three different naming convention exists for iSCSI.
- IQN - iSCSI Qualified Name, it is reversed hostname(DNS) as naming authority.
Format: iqn.2018-06.com.ibm.stglabs.aus.p9fwc-iscsi2.hostid.2
- EUI – It is IEEE EUI-64 format(Extended Unique identifier)
Format: eui.{EUI-64 bit address} (e.g. eui.02004567A425678D)
- NAA - Network Address Authority (NAA)
Format: naa.{NAA 64 or 128 bit identifier} e.g naa.200456B64678d
iSCSI uses TCP ports 3260 typically for target nodes.
AIX iSCSI discovery methods.
Typically there are 2 methods of discovery, mostly used are.
- File based discovery
- ODM based discovery.
How to Configure iSCSI disks and iSCSI MPIO disks in AIX.
- iSCSI configuration using odm:
Before configuring the iscsi device instant, make sure there network
Connectivity between initiator and target using ping operation.
Step-1 : By default, iscsi0 device discovery policy will be file based if not change to odm based.
Change the discovery policy of iscsi0 device attribute to odm.
chdev -a disc_policy=odm -l iscsi0
step-2: Add the iscsi target info using the mkiscsi command.
mkiscsi -l iscsi0 -g static -t iqn.1986-03.com.ibm:node1 -n 3260 -i 2.168.1.254
Step -3: Run cfgmgr to discovery the disks.
cfgmgr -vl iscsi0
Step -4: To list the iscsi disks, run ’ lsdev -p iscsi0’ to get discovered disks.
Note: To add one or more Target IQN or controller, multiple mkiscsi command need to run explicit to those Target IQN’s controller or IP address of the targets.
- iSCSI configuration using files based:
Step-1: Add the required iscsi target info in ‘/etc/iscsi/targets’ file.
The target could be multiple controller with single IQN or
Single controller and single IQN.
Add the respective details in the ‘/etc/iscsi/targets’ file.
Step -2: Run cfgmgr to discovery the disks.
cfgmgr -vl iscsi0
Step -3: To list the iscsi disks, run ’ lsdev -p iscsi0’ to get discovered disks.
Note:
if we know the target IP, we can get target IQN info and tcp ports using command ‘iscsi_st’.
#iscsi_st -f -i 10.10.30.10
IP Address Port Target Name
---------- ---- -----------
10.10.10.10:3260,1 iqn.1986-03.com.ibm:2145.d59-v7k2.node1
10.10.20.10:3260,1 iqn.1986-03.com.ibm:2145.d59-v7k2.node2
10.10.30.10:3260,1 iqn.1986-03.com.ibm:2145.d59-v7k2.node1
10.10.40.10:3260,1 iqn.1986-03.com.ibm:2145.d59-v7k2.node2
Configuration of iSCSI MPIO disk
Both methods explained above i.e odm and file based methods can be used for iSCSI MPIO disks configuration.
Inorder to have multipath between initiator and target, make sure we have different IP subnets.
Let say, we want to configure 4 iSCSI MPIO paths between AIX host and SVC storage box.
Step 1: IP subnet configuration for AIX host and SVC storage box.
On AIX host, configure 4 different IP subnets with below commands.
If AIX host has 4 NIC ports connected to switch.
#ifconfig en1 10.10.10.100 255.255.255.0 up
#ifconfig en2 10.10.20.100 255.255.255.0 up
#ifconfig en3 10.10.30.100 255.255.255.0 up
#ifconfig en4 10.10.40.100 255.255.255.0 up
If AIX host has 2 NIC ports connected to switch, using alias per NIC port we will configure 2 IP subnets.
#ifconfig en1 10.10.10.100 255.255.255.0 up
#ifconfig en1 alias 10.10.20.100 255.255.255.0 up
#ifconfig en2 10.10.30.100 255.255.255.0 up
#ifconfig en2 alias 10.100.40.10 255.255.255.0 up
From GUI of SVC storage box,
Goto <SVC box name>settings-->network--> Ethernet ports
Below picture depicts how to configure required IP subnets.
Step2: For ODM based configuration, need to run ‘mkiscsi’ command multiple times with respect to target IP and IQN.
#mkiscsi -l iscsi0 -g static -t iqn.1986-03.com.ibm:2145.d59-v7k2.node1 -n 3260 -i 10.10.10.10
#mkiscsi -l iscsi0 -g static -t iqn.1986-03.com.ibm:2145.d59-v7k2.node2 -n 3260 -i 10.10.20.10
#mkiscsi -l iscsi0 -g static -t iqn.1986-03.com.ibm:2145.d59-v7k2.node1 -n 3260 -i 10.10.30.10
#mkiscsi -l iscsi0 -g static -t iqn.1986-03.com.ibm:2145.d59-v7k2.node2 -n 3260 -i 10.10.40.10
The command ‘lsiscsi’ gives configure multiple targets.
To discover multipath iscsi disks run ‘cfgmgr -vl iscsi0’ and to check the discovered disks having multipath use the command ‘lsmpio -l hdiskX’.
Step3: For File based configuration iSCSI MPIO disks discovery.
Follow the steps mentioned under “iSCSI configuration using files based”.
iSCSI MPIO advantages
- Reliablity
- PFC, ETS, and DCBX supports lossless transport.
- Redundancy and Resiliency
- Protocol Link aggregation (LACP) or iSCSI multipathing.
- Support for transparent failover in case of port/node failures and recover back once .
- It can be achieved using failover at disk level and link failover at etherchannel level.
- High availability
- Due to Multipath and etherchannel(bonding) technology, high availability is achieved.
Conclusion:
What makes iSCSI and MPIO interesting.
- With one path I/O fails, application using iSCSI disks will now not be affected as there will be alternate paths where I/O will continue using MPIO functionality.
- MPIO functionality for iSCSI helps in replacing the damage network adapters or storage ports or switch ports without affect affecting system/application down time.
- More IOPS and low latency can be achieved using iSCSI MPIO functionality.
UID
ibm16156189