How To
Summary
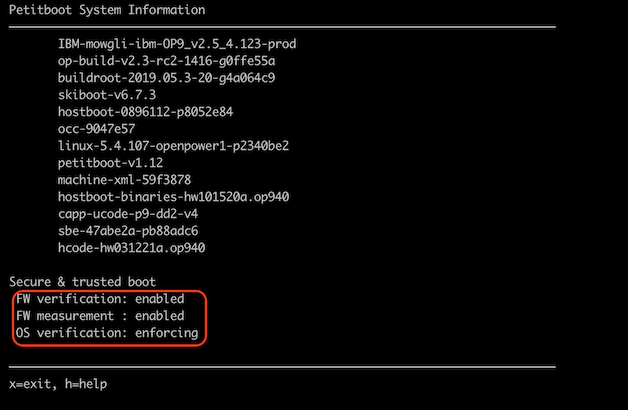
This document contains the steps required to enable secure boot on the HMC.
Objective
Guide the user through the process of enabling or re-enabling secure boot on the HMC.
Environment
Secure boot was introduced in the 7063-CR2 HMC with v10r1.1010.
Pre-requisites:
- 7063-CR2 HMC at v10r1.1010 or newer
- PNOR: IBM-mowgli-ibm-OP9_v2.5_4.140-prod or newer
- BMC: op940.hmc-36 or newer
Steps
Additional Information
Document Location
Worldwide
[{"Type":"MASTER","Line of Business":{"code":"LOB57","label":"Power"},"Business Unit":{"code":"BU058","label":"IBM Infrastructure w\/TPS"},"Product":{"code":"7063-CR2","label":"Hardware Management Console (7063-CR2)"},"ARM Category":[],"ARM Case Number":[],"Platform":[{"code":"PF025","label":"Platform Independent"}]}]
Was this topic helpful?
Document Information
Modified date:
28 March 2025
UID
ibm16489435