Troubleshooting
Problem
This document provides information on creating spooled files from PC files using the TCP/IP File Transfer Protocol (FTP) and the Copy File (CPYF) command.
Resolving The Problem
Note: This document was last updated on 27 September 2011.
To create a Spooled File from a PC File using FTP and the Copy File (CPYF) command, do the following:
| 1. | Creating the PC File Locate or create your PC file, and save the file in a text only format. The following file was created in Microsoft Windows Notepad and saved as c:\testsplf.txt. |
 | |
| 2. | FTPing the File to the iSeries or AS/400 System Use the FTP command to connect to your IBM System i system. This can be done from a DOS prompt or from the Windows Run dialog box by typing FTP <SYSTEMNAME>. Sign on with your user ID and password. Type ASCII to set the file transfer mode to ASCII. Use the CD command to change to the library where you want to create your physical file/member, and then type put <filename>, and press the Enter key. Once the file has transferred, type BYE to exit the FTP program. |
 | |
| 3. | Viewing the Member From your display session, use the Work with Members Using PDM (WRKMBRPDM) or Start Source Entry Utility (STRSEU) Command to view your newly created member and physical file. |
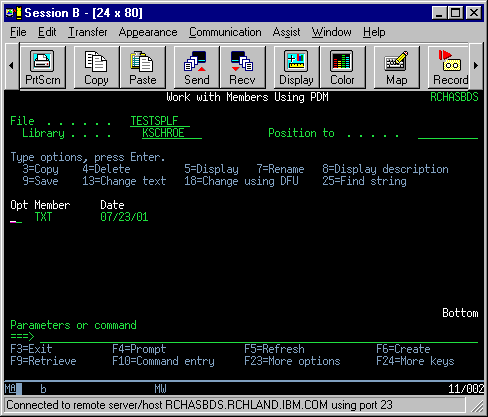 | |
| 4. | Creating the Spooled File Now that the PC file is copied into a physical file member, use the Copy File (CPYF) command to copy the member to a Printer File. Doing this creates a spooled file. Keep in mind that your new spooled file will take its attributes from the printer file that it is copied to. Copying a member to the QSYSPRT printer file creates a spooled file with a length of 66, a width of 132, and a CPI value of 10. If these attributes do not match your requirements, use the Override with Printer File (OVRPRTF) command to override the printer file, or create a new printer file with the specific attributes that you require. For most people, OVRPRTF will be all that they need to make any adjustments. Use the CPYF command to copy the file to a printer file. In this example, the QSYSPRT printer file was used: |
 | |
| When the resulting spooled file is displayed, it will be 132 characters wide; however, only the first 90 will have data in them: | |
 | |
| If you want to create a spool file with a width equal to that of the original file, use the OVRPRTF command. To create a spooled file that is exactly 90 wide, use the OVRPRTF FILE(QSYSPRT) PAGESIZE(*N 90) command. If the CPYF command is used again, it will create a spooled file that is 90 characters wide and contains 90 characters of data: | |
 | |
| Your spooled file can now be printed. |
Creating Spooled Files Using Text Files That Contain Unicode
Special instructions are required for copying Unicode text files to spooled files on the iSeries family system. Many Windows programs have now added support for Unicode and using the drag-and-drop feature within iSeries Navigator on a PC running R530 iSeries Access for Windows will produce Unicode text files if the PC is running Windows XP Professional. One of the following methods can be used to copy text files to an operating system spooled file when the text file contains Unicode data.
| o | The first method involves using FTP in binary format to copy the text file to a stream file in the IFS. Once this is done, use the following Convert from the Unicode (CNVFRMUNIC) command: CNVFRMUNIC PTHNAM('/folder/unicode.txt') OUTFIL(UNICODE) OUTLIB(library) OUTMBR(UNICODE) STMFCODPAG(*STMF) There will be a few garbage characters at the beginning of the spooled file when using this method. |
| o | The second method involves creating a printer file that has a page width that is twice the normal width (for example, a width of 264 columns rather than 132), and that has the Unprintable character action (RPLUNPRT) parameter set to *NO. Therefore, the extra bytes in the Unicode data are ignored. For example, this can be done using the following Create Printer File (CRTPRTF) command: CRTPRTF FILE(library/printer-file) PAGESIZE(66 264) RPLUNPRT(*NO) Once the printer file has been created, use FTP in character format (not in binary format) to copy the text file directly to the printer file. This creates a viewable spooled file. However, the Nulls (X'00' characters) will still be in the spooled file data and the size has not diminished. There will be a few garbage characters at the beginning of the spooled file when using this method. However, if the Copy Spooled File (CPYSPLF) command is used to copy the spooled file to a data base file, that will remove the Null characters. Then, the data base file can be copied back to a printer file again. |
[{"Type":"MASTER","Line of Business":{"code":"LOB57","label":"Power"},"Business Unit":{"code":"BU058","label":"IBM Infrastructure w\/TPS"},"Product":{"code":"SWG60","label":"IBM i"},"Platform":[{"code":"PF012","label":"IBM i"}],"Version":"6.1.0"}]
Historical Number
23924647
Was this topic helpful?
Document Information
Modified date:
18 December 2019
UID
nas8N1017285