Procedure Pointer Data Type
Procedure pointers are used to point to procedures or functions. A procedure pointer points to an entry point that is bound into the program. Procedure pointers are defined on the definition specification.
You define a procedure pointer item by specifying the POINTER(*PROC) keyword in a free-form definition or by specifying an asterisk (*) in the Data-Type entry of a fixed-form specification and also specifying the PROCPTR keyword.
The length of the procedure pointer field must be 16 bytes long and must be aligned on a 16 byte boundary. This requirement for boundary alignment can cause a pointer subfield of a data structure not to follow the preceding field directly, and can cause multiple occurrence data structures to have non-contiguous occurrences. For more information on the alignment of subfields, see Aligning Data Structure Subfields.
The default initialization value for procedure pointers is *NULL.
Examples
*.. 1 ...+... 2 ...+... 3 ...+... 4 ...+... 5 ...+... 6 ...+... 7 ...+... 8
DName+++++++++++ETDsFrom+++To/L+++IDc.Keywords+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
*
* Define a basing pointer field and initialize to the address of the
* data structure My_Struct.
*
D My_Struct DS
D My_array 10 DIM(50)
D
D Ptr1 S 16* INZ(%ADDR(My_Struct))
*
* Or equivalently, defaults to length 16 if length not defined
*
D Ptr1 S * INZ(%ADDR(My_Struct))
*
* Define a procedure pointer field and initialize to NULL
*
D Ptr1 S 16* PROCPTR INZ(*NULL)
*
* Define a procedure pointer field and initialize to the address
* of the procedure My_Proc.
*
D Ptr1 S 16* PROCPTR INZ(%PADDR(My_Proc))
*
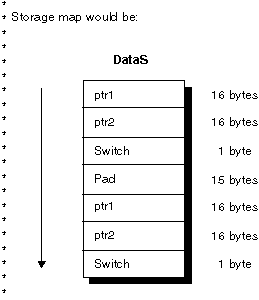
* Define pointers in a multiple occurrence data structure and map out
* the storage.
*
DDataS DS OCCURS(2)
D ptr1 *
D ptr2 *
D Switch 1A