Introduction to IBM Spectrum Scale Erasure Code Edition
IBM Spectrum Scale Erasure Code Edition provides IBM Spectrum Scale RAID as software, allowing customers to create IBM Spectrum Scale clusters that use scale-out storage on any hardware that meets the minimum hardware requirements.
All of the benefits of IBM Spectrum Scale and IBM Spectrum Scale RAID can be realized using your own commodity hardware.
- Reed-Solomon highly fault tolerant declustered Erasure Coding, protecting against individual drive failures as well as node failures.
- Disk Hospital to identify issues before they become disasters.
- End-to-end checksum to identify and correct errors introduced by network and/or media
IBM Spectrum Scale Erasure Code Edition uses the same software and most of the same concepts that are used in the Elastic Storage Server (ESS). Elastic Storage Server (ESS) is a solution consisting of two I/O (storage) servers and between one and several JBOD disk enclosures, with each storage device (pdisk) attached to both servers. In Elastic Storage Server (ESS), there are two recovery groups (RGs). Each RG takes half of each enclosure among all enclosures. Under normal conditions, each I/O server supports one of the two RGs. If either I/O server fails, the remaining I/O server takes over and supports both RGs.
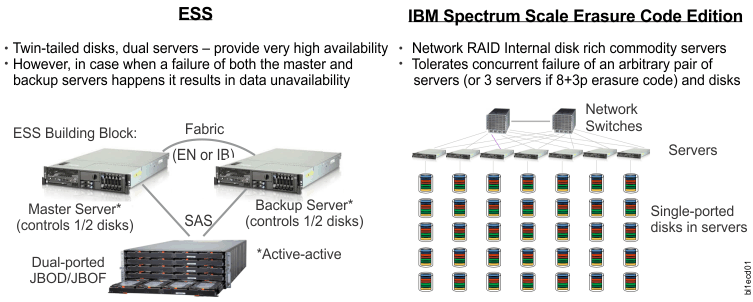
IBM Spectrum Scale Erasure Code Edition, in contrast, can have one or more recovery groups, but each RG is associated with between 4 and 32 storage servers, and each storage server belongs to only one RG. All of the storage servers in a recovery group must have a matching configuration, including identical CPU, memory, network, and storage device configurations. The storage devices (pdisks) are directly attached to only one storage server. Each storage server typically serves two log groups, each log group managing one half of the virtual disks (vdisk NSDs) assigned to a server. If a storage server fails, the log groups (and vdisk NSDs) it was serving are distributed to the remaining storage servers; any storage server failure will cause the remaining storage servers to serve at most one additional log group.
In both Elastic Storage Server (ESS) and IBM Spectrum Scale Erasure Code Edition, the placement of data is topology aware using a failure domain hierarchy of rack, node, enclosure, and storage device (pdisk). The RAID code makes placement decisions to maximize fault tolerance, depending on the RAID level you choose. IBM Spectrum Scale Erasure Code Edition supports the following erasure codes and replication levels: 8+2p, 8+3p, 4+2p, 4+3p, 3WayReplication, and 4WayReplication.
With IBM Spectrum Scale Erasure Code Edition it is possible for either IBM Spectrum Scale Cluster Export Services with protocol software or customer applications to run directly on the storage servers if sufficient hardware resources are available. Customer applications must run in a constrained environment using Linux® cgroups or Docker containers. For protocol workloads with high performance requirements, the Cluster Export Services should run on separate nodes.
In both Elastic Storage Server (ESS) and IBM Spectrum Scale Erasure Code Edition, the IBM Spectrum Scale file system, and file system features are independent of the storage configuration. A file system can be composed of NSDs provided by more than one recovery group, and the recovery groups can be from Elastic Storage Server (ESS) or IBM Spectrum Scale Erasure Code Edition or a combination of both. All of the IBM Spectrum Scale file system features can be used in a cluster with IBM Spectrum Scale Erasure Code Edition storage servers, but there are strict guidelines as to where the various components might run.
For an overview of IBM Spectrum Scale RAID, see the Introducing IBM Spectrum® Scale RAID topic in the IBM Spectrum Scale RAID: Administration.
Minimum hardware requirements
At a high level, you must have between 4 and 32 storage servers per Recovery Group (RG), and each server must be an x86 server running Red Hat® Enterprise Linux version 7.5 or 7.6. The storage configuration must be identical for all storage servers. The supported storage types are SAS-attached HDD or SSD drives, using specified LSI adapters, or enterprise-class NVMe drives. Each storage server must have at least one SSD or NVMe drive, this is used for a fast write cache as well as user data storage. For more information on hardware requirement, see Minimum hardware requirements and precheck.
Maximum storage nodes in a cluster
There can be up to 128 IBM Spectrum Scale Erasure Code Edition storage nodes in a IBM Spectrum Scale cluster, for example 4 RGs with 32 nodes each or 8 RGs with 16 nodes each, or some other combination that results in no more than 128 total storage nodes.
Network configurations
The network can be either Ethernet or InfiniBand, and must be at least 25 Gbps bandwidth, with an average latency of 1.0 msec or less between any two storage nodes. It is recommended to have a dedicated network for storage server traffic. In most cases, the overall storage performance is dictated by network bandwidth and latency. Your performance requirements must be carefully considered when selecting the network hardware and the network architecture for your IBM Spectrum Scale Erasure Code Edition cluster. For more information on networking requirements, see Network requirements and precheck.
Administration and maintenance procedures
IBM Spectrum Scale Erasure Code Edition administration and maintenance procedures are similar to Elastic Storage Server (ESS), but not identical. With IBM Spectrum Scale Erasure Code Edition, the customer is responsible for managing the storage server hardware and software. For example, the customer is responsible for updating any firmware as well as the operating system, including security updates, when needed. The majority of the IBM Spectrum Scale RAID maintenance commands are accomplished using the mmvdisk command. For details of IBM Spectrum Scale Erasure Code Edition admin and maintenance procedures, see Administering IBM Spectrum Scale Erasure Code Edition.
Health monitoring and problem determination
IBM Spectrum Scale Erasure Code Edition health monitoring and problem determination procedures rely on IBM Spectrum Scale mmhealth capabilities, as well as IBM Spectrum Scale RAID troubleshooting guidelines. For more details, see Troubleshooting.