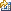You can start, stop, validate, and reset jobs using the -run option.
dsjob -run [ -mode [ NORMAL | RESET | VALIDATE | RESTART ] ] [ -param name=value ] [ -paramfile filename ] [ -warn n ] [ -rows n ] [ -wait ] [ -stop ] [ -jobstatus ] [ -userstatus ] [ -local ] [ -opmetadata [ TRUE | FALSE ] ] [ -disableprjhandler ] [ -disablejobhandler ] [useid] project job | job_id
-mode specifies the type of job run. NORMAL starts a job run, RESET resets the job, VALIDATE validates the job, and RESTART resumes a restartable job sequence from the last checkpoint using the original job parameter values. If -mode is not specified, a normal job run is started.
-param specifies a parameter value to pass to the job. The value is in the format name=value, where name is the parameter name, and value is the value to be set. If you use this to pass a value of an environment variable for a job (as you might do for parallel jobs), you need to quote the environment variable and its value, for example -param '$APT_CONFIG_FILE=test.apt' otherwise the current value of the environment variable will be used.
-paramfile specifies a file that contains parameter values to pass to the job. The parameter values are in the same format as the values specified for -param. If a parameter name is specified by both -param and -paramfile, the last value specified is passed to the job.
-warn n sets warning limits to the value specified by n (equivalent to the DSSetJobLimit function used with DSJ_LIMITWARN specified as the LimitType parameter).
-rows n sets row limits to the value specified by n (equivalent to the DSSetJobLimit function used with DSJ_LIMITROWS specified as the LimitType parameter).
-wait waits for the job to complete (equivalent to the DSWaitForJob function).
-stop terminates a running job (equivalent to the DSStopJob function).
-jobstatus waits for the job to complete, then returns an exit code derived from the job status.
-userstatus waits for the job to complete, then returns an exit code derived from the user status if that status is defined. The user status is a string, and it is converted to an integer exit code. The exit code 0 indicates that the job completed without an error, but that the user status string could not be converted. If a job returns a negative user status value, it is interpreted as an error.
-local use this when running a job from within a shell script on a UNIX system. Provided the script is run in the project directory, the job will pick up the settings for any environment variables set in the script and any setting specific to the user environment.
-opmetadata use this to have the job generate operational metadata as it runs. If you specify TRUE, operational metadata is generated, whatever the default setting for the project. If you specify FALSE, the job will not generate operational metadata, whatever the default setting for the project.
-disableprjhandler use this to disable any error message handler that has been set on a project wide basis.
-disablejobhandler use this to disable any error message handler that has been set for this job.
useid specify this if you intend to use a job alias (jobid) rather than a job name (job) to identify the job.
project is the name of the project containing the job.
job is the name of the job. To run a job invocation, use the format job.invocation_id.
job_id is an alias for the job that has been set using the dsjob -jobid command.
 This topic is also in the IBM InfoSphere DataStage Programmer's Guide.
This topic is also in the IBM InfoSphere DataStage Programmer's Guide.