Component requirements
Ensure that you have the required system configuration and a supported browser to deploy and run IBM Spectrum® Protect Plus.
To help ensure that backup and restore operations can be run successfully, your system must meet the hardware and software requirements. Use the following requirements as a starting point. For the most current requirements, which might include updates, see technote 304861.
IBM Spectrum Protect Plus support for third-party platforms, applications, services, and hardware depend on the third-party vendors. When a third-party vendor product or version enters extended support, self-serve support, or end of life, IBM Spectrum Protect Plus supports the product or version at the same level as the vendor.
IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server requirements
IBM Spectrum Protect Plus as a virtual appliance requirements
IBM Spectrum Protect Plus is installed on a VMware or Microsoft Hyper-V virtual appliance. The virtual appliance contains the application and the inventory. Maintenance tasks are completed in vSphere Client or Hyper-V Manager by using the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus command line, or in the web-based administrative console.
Maintenance tasks are completed by a system administrator. A system administrator is usually a senior-level user who designed or implemented the vSphere and Elastic Sky X (ESX) or Hyper-V infrastructure, or a user with an understanding of IBM Spectrum Protect Plus, VMware, and Linux® command-line usage.
Infrastructure updates are managed by IBM® update facilities. The IBM Spectrum Protect Plus user interface serves as the primary means for updating IBM Spectrum Protect Plus features and underlying infrastructure components, including the operating system and file system.
Virtual appliance configuration
- VMware vSphere 6.0, including all updates and patch levels
- vSphere 6.5, including all updates and patch levels
- vSphere 6.7, including all updates and patch levels (beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect Plus V10.1.2)
- vSphere 7.0, including all updates and patch levels (beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect Plus V10.1.6)
- Microsoft® Hyper-V 2016
- Microsoft Hyper-V 2019 (beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect Plus V10.1.3)
Virtual appliance hardware
- 64-bit 8-core server
- 48 GB memory
- 548 GB disk storage for the virtual machine (VM)
IBM Spectrum Protect Plus as a set of containers requirements
IBM Spectrum Protect Plus can be installed on a Red Hat® OpenShift® cluster environment. The installation process uses the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus operator, which deploys and manages all the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus components on Red Hat OpenShift.
The IBM Spectrum Protect Plus operator is a Docker image that uses Ansible® Operator technology. The image contains the Kubernetes configuration files that are required to deploy and upgrade IBM Spectrum Protect Plus.
If you plan to install IBM Spectrum Protect Plus in an environment that has IBM Cloud Pak® for Multicloud Management 2.2 installed, you must use the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus operator for IBM Cloud Pak for Multicloud Management. This operator also works on environments that do not have the IBM Cloud Pak for Multicloud Management installed.
Container configuration
- Supported container platform: Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform Version 4.5 and later maintenance and modification levels
- Supported cloud management platform: IBM Cloud Pak for Multicloud Management Version 2.2 and later maintenance and modification levels
- Supported cloud: On premises (private cloud)
- IBM Cloud® Private command-line interface (cloudctl) v3.5.0 or later
- Kubernetes command-line tool (kubectl) v1.16.0 or later
- OpenShift command-line tool (oc) v4.3.0 or later
You must run all commands on the Linux® operating system.
- virgo
- vadp
- UI
- Node.js
- kc
- postgres
- MongoDB (three containers)
- redis
- awsebs
- awsec2
- proxy: Used for internal communications between the virgo container and other containers
- manager: Used to update the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus instance from the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus instance user interface
For an example of system configuration, see the Figure 1.
Container hardware
Persistent storage: In order for IBM Spectrum Protect Plus to run on an OpenShift cluster, persistent storage is required. The IBM Spectrum Protect Plus operator submits requests for storage by using persistent volume claims (PVCs). The OpenShift cluster completes these requests by using an existing storage driver. A storage class must be configured to allow IBM Spectrum Protect Plus to create persistent volumes dynamically. The following table list the minimum storage capacity for the persistent volumes (PVs):
| Persistent volume | Size | Mount Path | Permissions | Containers that access the PVC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| virgo logs | 10 GB | /data/log | drwxrwsr-x | virgo |
| plugin logs | 10 GB | /data/platform/log | drwxrwsr-x | awsec2 awsebs |
| MongoDB | 50 GB | /var/lib/mongodb/data | drwxrwsr-x | mongodb |
| MongoDB catalog | 100 GB | /var/lib/mongodb/data | drwxrwsr-x | mongodb2 |
| Postgres | 2 GB | /var/lib/pgsql/data | drwxrwsr-x | postgres |
| Apache Lucene | 150 GB | /data/lucene | drwxrwsr-x | virgo |
| nodejs logs | 2 GB | /data/log/node-cdm-service | drwxrwsr-x | nodejs |
| VMware vStorage API for Data Protection proxy (VADP proxy) logs | 10 GB | /data/log/vmdkbackupproxy | drwxrwsr-x | vadp |
Networking: An ingress controller on OpenShift handles external communications for IBM Spectrum Protect Plus. The IBM Spectrum Protect Plus operator deploys the ingress controller, which decrypts the encrypted traffic and directs it to the proxy container. The proxy container then routes the request internally to the proper service. Each IBM Spectrum Protect Plus container uses a corresponding Kubernetes service to communicate internally with other containers.
Timeouts: By default, the ingress timeout is set to 900 seconds. This value can be updated
by using the haproxy.router.openshift.io/timeout annotation of the ingress resource definition. Proxy timeouts can also be updated from the spp-proxy-config ConfigMap. The default value for the proxy timeout is set to 600 seconds. On any external load balancers that are being used, also set the timeout values to at least 900 seconds. For example, for an OpenShift cluster on Amazon Web Services (AWS), change the default value for the idle timeout setting of
the Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) service from 60 seconds to 900 seconds.
CPU and memory resources: The following table lists the minimum CPU and memory resources that are required for each IBM Spectrum Protect Plus container:
| Container | CPU (request) | CPU (limit) | Memory (request) | Memory (limit) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| virgo | 1000m | 2000m | 4Gi | 8Gi |
| vadp | 100m | 250m | 300Mi | 500Mi |
| ui | 50m | 100m | 100Mi | 250Mi |
| nodejs | 50m | 100m | 50Mi | 150Mi |
| kc | 50m | 100m | 300Mi | 500Mi |
| postgres | 50m | 100m | 50Mi | 150Mi |
| mongodb (x3) | 50m | 150m | 250Mi | 2Gi |
| redis | 100m | 250m | 100Mi | 500Mi |
| awsebs | 50m | 250m | 500Mi | 2Gi |
| awsec2 | 50m | 250m | 500Mi | 2Gi |
| The CPU resource is measured in Kubernetes cpu units. Memory is specified in units of bytes. For more information about CPU units and memory, see Managing Resources for Containers | ||||
IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server additional requirements
The Connectivity requirements must be met.
Use a Network Time Protocol (NTP) server to synchronize the time zone across IBM Spectrum Protect Plus resources in your environment, such as the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server, storage arrays, hypervisors, and application servers. If the clocks on the various systems are significantly out of sync, you might experience errors during application registration, metadata cataloging, inventory operations, backup jobs, or file restore jobs. For more information about identifying and resolving timer drift, see the following VMware knowledge base article: Time in virtual machine drifts due to hardware timer drift
IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server browser support
IBM Spectrum Protect Plus was tested and validated with the following web browsers:
- Firefox 55.0.3 and later
- Google Chrome 60.0.3112 and later
- Microsoft Edge 40.15063 and later
- Microsoft EdgeHTML 15.15063 and later
If your screen resolution is lower than 1024 x 768, some items might not fit in the window. Enable pop-up windows in your browser to access the help system and some IBM Spectrum Protect Plus operations.
IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server ports
IBM Spectrum Protect Plus and associated services use the following ports.
| Port | Protocol | Initiator | Target | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22 | Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) | vSnap server | IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server | Provides access for troubleshooting and maintenance tasks on the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server by using Secure Shell (SSH) protocol. |
| 443 | TCP | IBM Spectrum Protect Plus user interface | IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server | Provides web access by using the Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) protocol. This port is the main entry point for client onnections that use the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol. This port is also used for Representational State Transfer application programming interface (REST API) queries. |
| 443 | TCP | VADP proxy host | IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server | Provides web access by using the HTTPS protocol. This port is the main entry point for client connections that use the TLS protocol. This port is also used for REST API queries. |
| 8090 | TCP | IBM Spectrum Protect Plus administrative console | IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server | Provides access for system administration. This extensible framework supports plug-ins that run operations such as system and network updates. |
- Port 9090: In earlier versions, this port was used for online help. Starting with V10.1.4, this port is no longer required for online help. No further action is required.
- Port 8761: In earlier versions, this port was used to automatically discover VADP proxies and for IBM Spectrum Protect Plus VM backup operations. Beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect Plus V10.1.6, the VADP proxy architecture is modified and port 8761 is no longer required to be open. When IBM Spectrum Protect Plus is updated to V10.1.6 or later, the associated VADP proxies in the environment are also upgraded.
- Port 5671: In earlier versions, this port was used for internal and external message and log management. Beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect Plus V10.1.7, the VADP proxy architecture is modified and port 5671 is no longer required to be open.
- Ports 111, 2029, and 20048: In earlier versions, these ports were used for catalog backup operations to vSnap server via the Network File System (NFS) client. Beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect Plus V10.1.7, the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server uses the Secure File Transfer protocol (SFTP) to back up catalogs to vSnap servers. For that reason, ports 111, 2029, and 20048 are no longer required.
- Port 3260: In earlier versions, this port was used for Internet Small Computer System Interface (iSCSI) data transfer by the vSnap server. Beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect Plus V10.1.7, the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server does not include an onboard vSnap server. For that reason, the port is no longer required.
| Port | Protocol | Initiator | Target | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22 | TCP | IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server | vSnap server or VADP proxy host | Provides access for troubleshooting and maintenance tasks on remote vSnap servers and the VADP proxy by using the SSH protocol. |
| 25 | TCP | IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server | Email server that can be accessed by using the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) | Provides access to an email service. |
| 389 | TCP | IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server | Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) server | Provides access to Active Directory Services. |
| 443 | TCP | IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server | Hypervisor: VMware Elastic Sky X Integrated (ESXi) host and vCenter | Provides access to ESXi and vCenter for managing operations. |
| 636 | TCP | IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server | LDAP server | Provides access to Active Directory Services by using the SSL protocol. |
| 902 | TCP | IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server | Hypervisor: VMware ESXi host | Used for the Network File Copy (NFC) protocol, which provides a file-type-aware File Transfer Protocol (FTP) service for vSphere components. By default, ESXi uses NFC for operations such as copying and moving data between datastores. |
| 5985 | TCP | IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server | Hypervisor: Hyper-V or agents that use the iSCSI initiator | Provides access to the Microsoft Windows Remote Management (WinRM) service for Windows-based servers. |
| 5986 | TCP | IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server | Hypervisor: Hyper-V or agents that use the iSCSI initiator | Provides access to the Microsoft Windows Remote Management (WinRM) service for Windows-based servers. |
| 8098 | TCP | IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server | VADP proxy host | Supports REST API communications between the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server and the VADP proxy by using the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol. |
| 8900 | TCP | IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server | vSnap server | Supports REST API communications between the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server and the vSnap server by using the TLS protocol. |
- Ports 111, 2029, and 20048: In earlier versions, these ports were used for catalog backup operations to vSnap server via the Network File System (NFS) client. Beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect Plus V10.1.7, the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server uses the Secure File Transfer protocol (SFTP) to back up catalogs to vSnap servers. For that reason, ports 111, 2029, and 20048 are no longer required.
IBM Spectrum Protect communication paths diagram
The following diagram is an overview of the communication paths that are managed by IBM Spectrum Protect Plus. This diagram is intended to provide a high level representation of components and their associated ports. This diagram can provide assistance for troubleshooting and network configuration for deployment scenarios. The diagram may not contain all communication paths. For a list of initiator and receiver ports, see the component communication port tables.
- The labeled resources on the gray background represent the core services of the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus virtual appliance.
- The colors of the various modules represent different types of services as defined by the key.
- The area that is labeled Firewall represents the network firewall.
- Services that appear in the Firewall area are indicative of the ports that are open on the firewall.
- Dashed arrows represent communication among resources and services.
- Arrows flow toward the listening port.
-
The port numbers that must be open are indicated by the listening port.
For example:- The vSnap service is represented as being external to the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus virtual appliance. The vSnap service is listening on port 8900 and other ports.
- A component in the virtual appliance establishes a communication path with a connection to the vSnap service at port 8900.
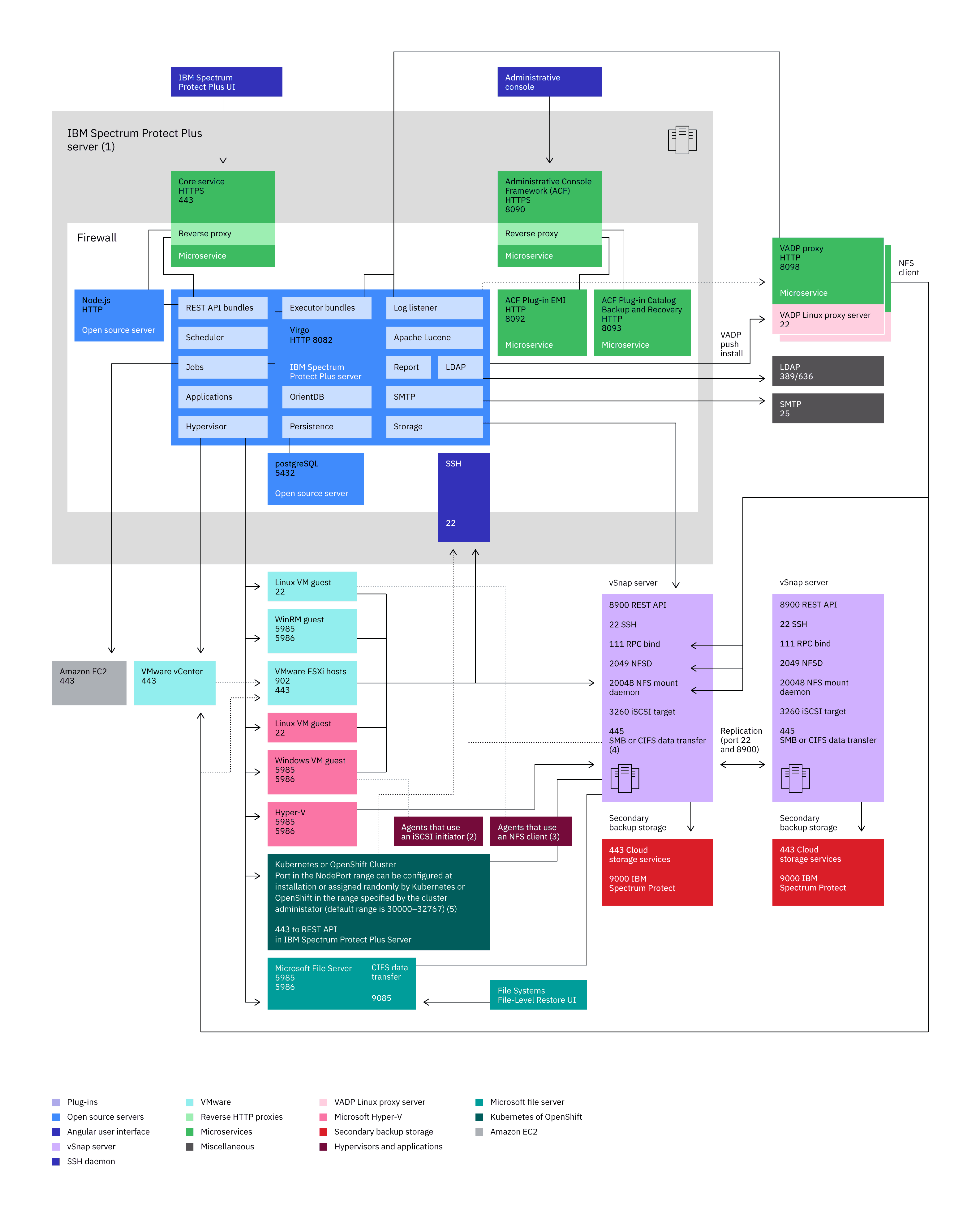
- The IBM Spectrum Protect Plus virtual appliance contains several base components, for detailed information, see Product components.
- The following agents use an iSCSI initiator: Microsoft Hyper-V, Microsoft SQL Server, and Microsoft Exchange.
- The following agents use an NFS client: VMware, Oracle, IBM Db2®, MongoDB, Kubernetes, and Microsoft Office 365.
- The following agents use a Server Message Block (SMB) or the Common Internet File System (CIFS) protocol client: Microsoft SQL Server (only for transaction log backup and restore operations), Microsoft Exchange (only for transaction log backup and restore operations), and file systems.
- An SSH port connects the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server to the Kubernetes Backup Support agent. If you do not select a port, a random port number is selected by the NodePort Services in the default range. If you specify a value for this port, use a port number within the NodePort range that is set by the Kubernetes administrator that is not already in use.
vSnap server requirements
A vSnap server is the primary backup destination for IBM Spectrum Protect Plus.
vSnap server configuration
vSnap server VM installation
Before you deploy the vSnap server to the host, ensure that one of the following requirements is met:-
- vSphere 6.0, including all updates and patch levels
- vSphere 6.5, including all updates and patch levels
- vSphere 6.7, including all updates and patch levels (beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect V10.1.2)
- vSphere 7.0, including all updates and patch levels (beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect V10.1.6)
- Microsoft Hyper-V 2016
- Microsoft Hyper-V 2019 (beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect Plus V10.1.3)
vSnap server physical installation
Beginning with V10.1.3, IBM Spectrum Protect Plus provides new functions that require the kernel levels that are supported in Red Hat Enterprise (RHEL) 7.5 and CentOS 7.5. If you must use operating systems earlier than RHEL 7.5 and CentOS 7.5, use IBM Spectrum Protect Plus V10.1.2 for physical vSnap installations.- The following Linux operating systems are supported for IBM Spectrum Protect
Plus physical vSnap server installations:
- CentOS 7.1804 (7.5) (x86_64) (beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect V10.1.2)
- CentOS 7.1810 (7.6) (x86_64) (beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect V10.1.3 patch 1)
- CentOS 7.1908 (7.7) (x86_64) (beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect V10.1.5 patch 1)
- CentOS 7.2003 (7.8) (x86_64) (beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect V10.1.7)
- RHEL 7.5 (x86_64) (beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect V10.1.2)
- RHEL 7.6 (x86_64) (beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect V10.1.3 patch1)
- RHEL 7.7 (x86_64) (beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect V10.1.5 patch1)
- RHEL 7.8 (x86_64) (beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect V10.1.7)
- CentOS 7.3.1611 (x86_64)
- CentOS 7.4.1708 (x86_64)
- RHEL 7.3 (x86_64)
- RHEL 7.4 (x86_64)
vSnap server hardware
The listed requirements are the minimum requirements for installation. Depending on the capacity and configuration of the storage pool, additional resources might be required. For more information about how to size and build an IBM Spectrum Protect Plus solution, see the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus Blueprints
For initial deployment, ensure that your VM or physical Linux server meets the following minimum requirements:
- 64-bit 8-core server
- 32 GB memory
- 16 GB free space on the root file system
- 128 GB free space in a separate file system mounted at /opt/vsnap-data
vSnap server additional requirements
The Connectivity requirements must be met.
vSnap server ports
The following ports are used by vSnap servers.
| Port | Protocol | Initiator | Target | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22 | TCP | IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server, hypervisors, or agents that use the NFS client | vSnap server | Provides access for troubleshooting and maintenance tasks on vSnap servers by using SSH protocol. |
| 111 | TCP and UDP | Hypervisors, VADP proxy, or agents that use the NFS client | vSnap server | Used for NFS file sharing by the vSnap server. |
| 445 | TCP | Application agents that use the SMB or the CIFS protocol | vSnap server | Used for SMB or CIFS file sharing by the vSnap server. |
| 2049 | TCP and UDP | Hypervisors, VADP proxy, or agents that use the NFS client | vSnap server | Used for NFS file sharing by the vSnap server. |
| 3260 | TCP | Hypervisors, VADP proxy, or agents that use the iSCSI client | vSnap server | Used for iSCSI data transfer by vSnap servers. |
| 8900 | TCP | IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server or vSnap server. | vSnap server | Supports REST API communications between the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server and the vSnap server by using the TLS protocol. Also used for REST API communications between two vSnap servers during replication. |
| 20048 | TCP and UDP | Hypervisors, VADP proxy, or agents that use the NFS client | vSnap server | Used for NFS file sharing by the vSnap server. |
Important security information: Process requests to vSnap data ports (NFS, SMB, and iSCSI) only when the request comes from a node in the internal network. Requests that come from external (non-private) network nodes must be blocked. To ensure that proper security practices are followed, work with your network security administrator.
- In earlier versions, ports 137, 138, and 139 on the vSnap server were used by application agents that use SMBv1. Beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect Plus V10.1.6, the SMBv1 protocol is not used. All agents use SMBv2 or later, which does not require ports 137, 138, or 139.
- Ports 111, 2029, and 20048: In earlier versions, these ports were used for catalog backup operations to vSnap server via the Network File System (NFS) client. Beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect Plus V10.1.7, the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server uses the Secure File Transfer protocol (SFTP) to back up catalogs to vSnap servers. For that reason, ports 111, 2029, and 20048 are no longer required.
VADP proxy requirements
In IBM Spectrum Protect Plus, running VM backup jobs through VADP requires significant system resources. By creating VADP backup job proxies, you enable load sharing and load balancing for IBM Spectrum Protect Plus backup jobs. If proxies exist, the entire processing load is shifted from the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server onto the proxies.
VADP proxy configuration
This feature is supported only in 64-bit quad core or higher configurations with a minimum kernel version of v2.6.32 in the following Linux environments:
- CentOS 6.5 and later maintenance and modification levels (beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect Plus V10.1.1 patch 1)
- CentOS 7.0 and later maintenance and modification levels (beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect Plus V10.1.1 patch 1)
- RHEL 6.4 and later maintenance and modification levels (beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect Plus V10.1.1)
- RHEL 7 and later maintenance and modification levels (beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect Plus V10.1.1)
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES) 12 and later maintenance and modification levels (beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect Plus V10.1.1)
- SLES 15 and later maintenance and modification levels (beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect Plus V10.1.7)
For more information about how to build an IBM Spectrum Protect Plus solution, see the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus Blueprints
VADP proxy hardware
For initial deployment of a VADP proxy server, ensure that your Linux server meets the following minimum requirements:
- 64-bit quad core processor
- 8 GB of random access memory (RAM) required, 16 GB preferred
- 60 GB of free disk space
Because of increased processor usage and concurrency on the VADP proxy server, the memory that is allocated on the proxy server must be increased.
VADP proxy additional requirements
The Connectivity requirements must be met.
To create VADP proxies, you must have a user ID with the SYSADMIN role assigned. For more information about roles, see Managing roles.
VADP proxies support the following VMware transport modes: File, SAN, HotAdd, NBDSSL, and NBD. For more information about VMware transport modes, see Virtual Disk Transport Methods
VADP proxy ports
The following ports are used by VADP proxies.
| Port | Protocol | Initiator | Target | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22* | TCP | IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server | VADP proxy host | Provides access for troubleshooting and maintenance tasks on VADP proxy hosts by using the SSH protocol. |
| 8098** | TCP | IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server | VADP proxy host | Supports REST API communications between the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server and the VADP proxy by using the TLS protocol. |
|
* VADP proxies can be pushed and installed to Linux-based servers over SSH port 22. ** Port 8098 on the VADP proxy server must be open when the proxy server firewall is enabled. |
||||
| Port | Protocol | Initiator | Target | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 111 | TCP and UDP | VADP proxy host | vSnap server | Used for SMB or CIFS file sharing by the vSnap server. |
| 443 | TCP | VADP proxy host | Hypervisor: VMware ESXi host and vCenter | Provides access to ESXi and vCenter for managing operations. |
| 443 | TCP | VADP proxy host | IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server | Provides web access by using the HTTPS protocol. This port is the main entry point for client connections that use the TLS protocol. This port is also used for REST API queries. |
| 902 | TCP | VADP proxy host | Hypervisor: VMware ESXi host | Used for the Network File Copy (NFC) protocol, which provides a file-type-aware File Transfer Protocol (FTP) service for vSphere components. By default, ESXi uses NFC for operations such as copying and moving data between datastores. |
| 2049 | TCP and UDP | VADP proxy host | vSnap server | Used to transfer NFS file sharing by the vSnap server. |
| 20048 | TCP and UDP | VADP proxy host | vSnap server | Used for SMB or CIFS file sharing by the vSnap server. |
Port updates:
- Port 8761: In earlier releases, this port was used to automatically discover VADP proxies and for IBM Spectrum Protect Plus VM backup operations. Beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect Plus V10.1.6, the VADP proxy architecture is modified and port 8761 is no longer required to be open. When IBM Spectrum Protect Plus is updated to V10.1.6 or later, the associated VADP proxies in the environment are also updated.
- Port 5671: In earlier versions, this port was used for internal and external message and log management. Beginning with IBM Spectrum Protect Plus V10.1.7, the VADP proxy architecture is modified and port 5671 is no longer required to be open.
If the firewall command script is not available on your system, edit the firewall manually to open or close the necessary ports, and restart the firewall. For instructions about editing firewall ports, see Editing firewall ports.
VADP proxy on vSnap server
VADP proxies can be installed on the vSnap servers in your IBM Spectrum Protect Plus environment. A combination VADP proxy and vSnap server must meet the minimum requirements of both devices. Consider the system requirements of both devices and add the core and RAM requirements together to identify the minimum requirements of the combination VADP proxy and vSnap server.
For a VADP proxy installed on a virtual vSnap server, the following requirements must be met:
- 64-bit 8-core processor
- 48 GB RAM
All required VADP proxy ports and vSnap server ports must be open on the combination VADP proxy and vSnap server.
Connectivity requirements
- The secure file transfer protocol (SFTP) subsystem for Secure Shell (SSH) is enabled on the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server, VADP proxies, and vSnap servers.
- The Secure Shell (SSH) service is running on port 22 on the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server, VADP proxies, and vSnap servers.
- Firewalls are configured to allow IBM Spectrum Protect Plus components to connect with each other by using SSH.
- VADP proxy servers use the Network File System (NFS) to mount storage volumes for backup and restore operations. On Linux, ensure that the native Linux NFS client is installed.
- All servers, proxies, applications, and hypervisors that are added to the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus environment can be registered by using a Domain Name System (DNS) name or Internet Protocol (IP) address.
- If DNS names are used, they must be resolvable over the network by the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus server and from the vSnap server. All IBM Spectrum Protect Plus components must also be resolvable by their DNS names.
- If DNS is not available, you must add the server to the
/etc/hostsfile on the IBM Spectrum Protect server by using the command line.
Repository server storage requirements
If you plan to use IBM Spectrum Protect as a repository server for copying data to cloud storage, ensure that you are using IBM Spectrum Protect V8.1.11.
Cloud storage requirements
Disk cache area
For all functions related to data copy and restore operations to and from cloud and archival targets, the vSnap server requires a disk cache area to be present on the vSnap server:
- During copy operations, this cache is used as a temporary staging area for objects that are pending upload to the cloud endpoint.
- During restore operations, the disk cache area is used to cache downloaded objects and to store any temporary data that might be written into the restore volume.
For instructions about sizing and installing the cache, see the IBM Spectrum Protect Plus Blueprints.
Multipath
During copy operations to object storage, IBM Spectrum
Protect attaches and detaches virtual cloud devices on
vSnap servers. If a mutipath configuration is enabled on the vSnap server by using
dm-multipath, the configuration can interfere with the copy operation. To avoid
this interference, the virtual cloud devices must be excluded from the multipath
configuration. Add the following lines under the blacklist section of the multipath
configuration file /etc/multipath.conf:
blacklist { device { vendor
"LIO-ORG" product ".*" } }After you make this change, reload the
multipath configuration by using the following command:
sudo systemctl
reload multipathdCertificates
-
Self-signed certificates
If the cloud endpoint or repository server uses a self-signed certificate, you must specify the certificate in Privacy Enhanced Mail (PEM) format when you register the cloud or repository server in the IBM Spectrum Protect user interface.
-
Certificates signed by a private certificate authority
If the cloud endpoint or repository server uses a certificate signed by a private certificate authority (CA), the endpoint certificate must be specified (in PEM format) when you register the cloud or repository server in the IBM Spectrum Protect user interface.
In addition, you must add the root or intermediate certificate of the private CA to the system certificate store in each vSnap server by using the following procedure:- Log in to the vSnap server console as the
serveradminuser and upload any private CA certificates (in PEM format) to a temporary location. - Copy each certificate file to the system certificate store directory (
/etc/pki/ca trust/source/anchors/) by running the following command:$ sudo cp /tmp/private-ca-cert.pem /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/ - To incorporate the newly added custom certificate and update the system certificate bundle, run
the following command:
$ sudo update-ca-trust
- Log in to the vSnap server console as the
-
Certificates signed by public certificate authority
If the cloud endpoint uses a public CA-signed certificate, no special action is required. The vSnap server validates the certificate by using the default system certificate store.
-
Wildcard certificates
If the cloud endpoint uses a wildcard certificate, note that the wildcard applies only to one subdomain level of the domain name. For example, if the certificate is for *.example.com, the certificate will match hostname level1.example.com but will not match level1.level2.example.com. If the bucket name contains periods (for example, "my.bucket") and it is part of the hostname used for registering the cloud endpoint in IBM Spectrum Protect (for example, "my.bucket.example.com"), certificate validation can fail. In such cases, ensure that the bucket name does not contain periods.
Network
The following ports are used for communication between the vSnap servers and cloud or repository server endpoints.
Table 8. Communication ports when the target is a cloud server or repository server endpoint Port Protocol Initiator Target Description 443 TCP vSnap server Cloud server endpoints Allows the vSnap server to communicate with Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3), Microsoft Azure, or IBM Cloud Object Storage endpoints. 9000 TCP vSnap server Repository server endpoints Allows the vSnap server to communicate with IBM Spectrum Protect (repository server) endpoints.
Any firewalls or network proxies that inspect SSL or conduct a deep packet inspection of traffic between the vSnap servers and cloud endpoints might interfere with SSL certificate validation on vSnap servers. This interference can also cause cloud copy job failures. To prevent this interference, the vSnap servers must be exempted from SSL interception and inspection in the firewall or proxy configuration.
Cloud provider
Native lifecycle management is not supported. IBM Spectrum Protect manages the lifecycle of uploaded objects automatically by using an incremental-forever approach where older objects can still be used by newer snapshots. Automatic or manual expiration of objects outside of IBM Spectrum Protect leads to data corruption.
If the cloud provider uses an SSL certificate that is self-signed or signed by a private certificate authority, see Connectivity requirements.
- Amazon S3 cloud requirements
- Standard object storage: When the cloud provider is registered in IBM Spectrum Protect, an existing bucket in one of the supported storage tiers must be specified: S3 Standard, S3 Intelligent-Tiering, S3 Standard-Infrequent Access, or S3 One Zone-Infrequent Access.
-
Archive object storage: When the cloud provider is registered in IBM Spectrum Protect, an existing bucket in one of the supported storage tiers must be specified: S3 Standard, S3 Intelligent-Tiering, S3 Standard-Infrequent Access, or S3 One Zone-Infrequent Access. IBM Spectrum Protect directly uploads data files to the Glacier tier. Some small metadata files are stored in the default tier for the bucket. A copy of these metadata files is also placed into the Glacier tier for disaster recovery purposes.
- IBM Cloud Object Storage requirements
- Standard object storage: When the cloud provider is registered in IBM Spectrum
Protect, an existing bucket must be specified. If the
specified bucket has a Write Once Read Many (WORM) policy that locks objects for a certain time
period, IBM Spectrum
Protect automatically detects the
configuration and deletes snapshots after the WORM policy removes the lock. The bucket must have the
Name Indexsetting enabled. -
Archive object storage: When the cloud provider is registered in IBM Spectrum Protect, an existing bucket must be specified. If the specified bucket has a WORM policy that locks objects for a certain time period, IBM Spectrum Protect automatically detects the configuration and deletes snapshots after the WORM policy removes the lock. IBM Spectrum Protect creates a single lifecycle management rule on the bucket to migrate data files to the archive tier. The bucket must have the
Name Indexsetting enabled.
- Standard object storage: When the cloud provider is registered in IBM Spectrum
Protect, an existing bucket must be specified. If the
specified bucket has a Write Once Read Many (WORM) policy that locks objects for a certain time
period, IBM Spectrum
Protect automatically detects the
configuration and deletes snapshots after the WORM policy removes the lock. The bucket must have the
| Operation | Provider | Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Copy | Amazon S3 | An existing bucket must be specified from one of the supported storage tiers. |
| Copy | IBM Cloud Object Storage | An existing bucket must be specified. The bucket must have the Name Index setting enabled. |
| Copy | Microsoft Azure | An existing container must be specified from a hot or cool storage tier. |
| Copy | IBM Spectrum Protect | IBM Spectrum Protect Plus creates its own unique bucket. |
| Archive copy | Amazon S3 | vSnap server must be able to communicate with IBM Spectrum Protect (repository server) endpoints. |
| Archive copy | IBM Cloud Object Storage | An existing bucket must be specified from the archive tier. The bucket must have the
Name Index setting enabled. |
| Archive copy | Microsoft Azure | An existing container must be specified from the hot storage tier and archive tier. |
| Archive copy | IBM Spectrum Protect | IBM Spectrum Protect Plus creates its own unique bucket to be copied to IBM Spectrum Protect tape. |