 z/OS MVS Planning: Global Resource Serialization
z/OS MVS Planning: Global Resource Serialization
 z/OS MVS Planning: Global Resource Serialization
z/OS MVS Planning: Global Resource Serialization
|
Previous topic |
Next topic |
Contents |
Contact z/OS |
Library |
PDF
Request processing with ring acceleration z/OS MVS Planning: Global Resource Serialization SA23-1389-00 |
|
|
Ring acceleration is available only when all systems in the ring are running MVS/SP Version 3 or higher. Ring acceleration also requires alternate links, except between systems in a sysplex, and IBM® recommends that the complex be a fully-connected complex. An installation where the complex is the same as the sysplex does not need to perform any additional setup to use ring acceleration; multisystem sysplexes must be fully connected. To achieve full connectivity in a mixed complex, however, see Designing a ring complex for details about how to define the necessary links. Ring acceleration can significantly reduce the amount of time tasks spend waiting for global resources, especially in a large complex. It can, however, affect recovery. Ring acceleration (ACCELSYS) describes the factors involved in determining how your installation should use ring acceleration. Using ring acceleration changes the processing of a global resource
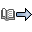
request. Figure 1 summarizes the
processing of a global resource request with ring acceleration. The
steps include:
Figure 1. Global Resource Request Processing with Ring
Acceleration
 
|
 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 |