Figure 1 illustrates the information available in the Language Environment dump and the order of information for multiple enclaves. If multiple enclaves are used, the dump service generates data and storage information for the most current enclave and moves up the chain of enclaves to the starting enclave in a LIFO order. For example, if two enclaves are used, the dump service first generates output for the most current enclave. Then the service creates output for the previous enclave. A thread terminating in a non-POSIX environment is analogous to an enclave terminating because Language Environment Version 1 supports only single threads.
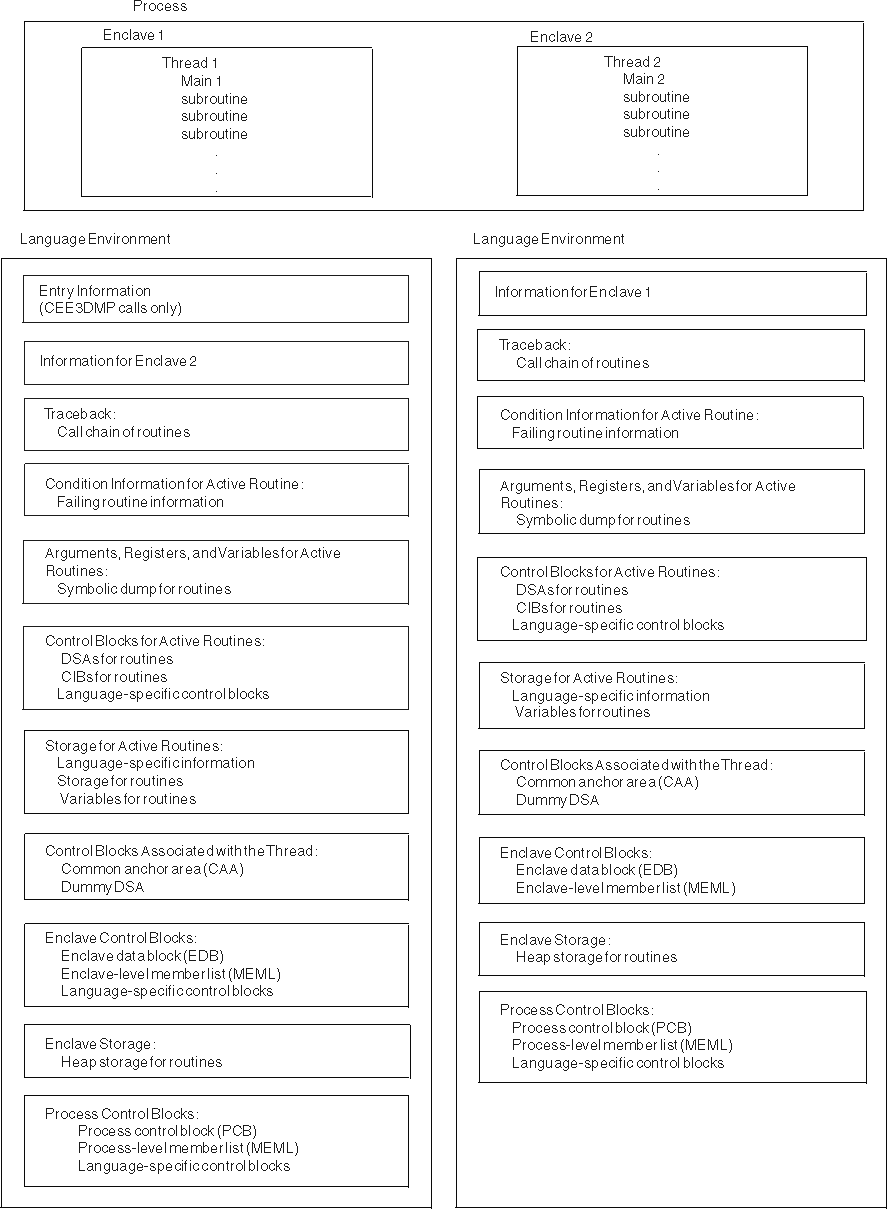
 If multiple nested CEEPIPI Main-DP environments are
present, the dump service generates data and storage information for
the most current Main-DP environment and moves up the chain of Main-DP
environments to the starting Main-DP environment in LIFO order.
If multiple nested CEEPIPI Main-DP environments are
present, the dump service generates data and storage information for
the most current Main-DP environment and moves up the chain of Main-DP
environments to the starting Main-DP environment in LIFO order. 
 When multiple nested CEEPIPI Main-DP environments
are present in the dump output, the information in Figure 1 appears for the most current Main-DP environment.
For the other chained Main-DP environments, only the traceback section
appears. The following is an example:
When multiple nested CEEPIPI Main-DP environments
are present in the dump output, the information in Figure 1 appears for the most current Main-DP environment.
For the other chained Main-DP environments, only the traceback section
appears. The following is an example: **** Information for CEEPIPI token xxxxxxxx ****
information for newest enclave
information for next older enclave
information for oldest enclave
Other information
**** Information for CEEPIPI token xxxxxxxx ****
traceback for newest enclave
traceback for next older enclave
traceback for next older enclave
traceback for next older enclave
traceback for oldest enclave
**** Information for CEEPIPI token xxxxxxxx ****
traceback for newest enclave
traceback for next older enclave
traceback for next older enclave
traceback for oldest enclave