Example gateways
The following samples illustrate how to model several types of gateways.
When modeling processes or case instances in IBM® Business Process Manager, you have several options for implementing gateways. See Converging and diverging flows to understand the available options and to see a sample implementation of a parallel gateway. Review the following samples to learn more about exclusive and inclusive gateways.
- To implement an exclusive and inclusive gateway in a business process definition (BPD), you must declare variables for that BPD, as described in Declaring and passing variables.
- To implement an exclusive gateway in a client-side human service,
you must specify the JavaScript conditions that determine the path
to be followed by the service flow, as described in Implementing exclusive gateways.Restriction: Support for gateway implementation in human services is provided for exclusive gateways only.
Sample exclusive gateways
Use an exclusive gateway in a BPD or in a human service when you model a point in the flow in which only one of several paths can be followed. JavaScript conditions that you define for the sequence flows that emerge from the gateway determine which path is to be followed by the flow.
In the Implementation properties, decisions are evaluated from top to bottom. The flow follows the first condition that evaluates to true. If all conditions evaluate to false, the flow follows the default sequence flow, which does not have a condition.
- Sample exclusive gateway in a BPD
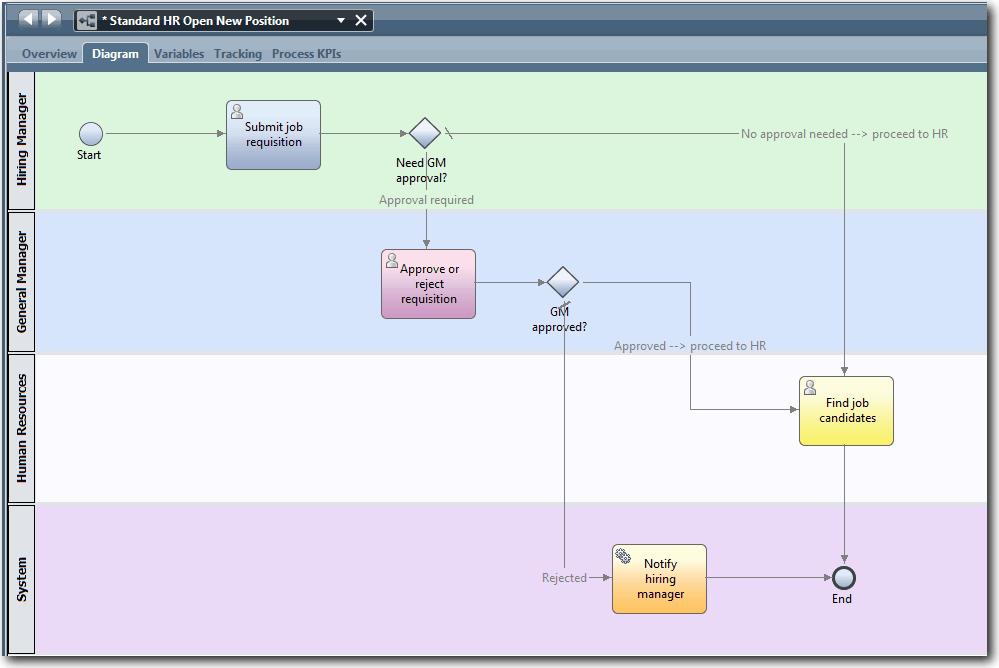
- For example, you might have two exclusive gateways in a BPD diagram.Note: You can access the HR Open New Position BPD in the Hiring Sample process application or see Hiring Sample tutorial: Add event gateways and Hiring tutorial: Implement gateways in the Hiring tutorial section.
In the sample and tutorial, the first gateway, named Need GM Approval?, determines which path to follow based on whether the submitted job requisition requires approval. To see how this works, click the gateway in the BPD diagram and then click the Implementation option in the properties. The approval options are then shown under the Decisions section.
 Remember: To enable the advanced editing feature in your preferences, click , expand , and then select Advanced Editors.
Remember: To enable the advanced editing feature in your preferences, click , expand , and then select Advanced Editors.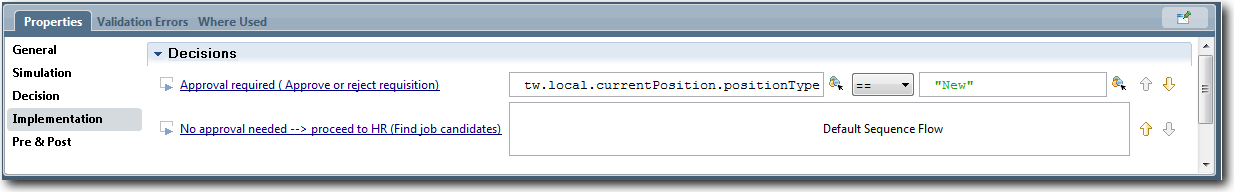
The Approval required path is followed to the Approve/reject requisition activity only when the tw.local.currentPosition.positionType variable is equal to "New". This logic ensures that those requisitions from Hiring Managers for new headcount are approved by General Managers before HR processing. If a position is not new, the process follows the default path to the Find job candidates activity. Notice in the BPD diagram that the default path is marked with a forward slash (/).
The second gateway, named GM Approved?, determines which path to follow based on whether a new position is approved. To see how this works, click the GM Approved? gateway in the BPD diagram to select it, and then click the Implementation option in the properties. The approval information is then shown under the Decisions section.
The Approved --> proceed to HR path is followed to the Find job candidates activity only when the tw.local.requisition.gmApproval variable is equal to "Approved". This logic ensures that those requisitions that require approval are approved before HR processing. If a requisition is not approved, the process follows the default path (Rejected path) to the Notify hiring manager activity.
- Sample exclusive gateway in a human service
- The following example shows the implementation of an exclusive
gateway in a human service. To model the exclusive gateway in the
service flow, JavaScript conditions that evaluate to true or false are
defined in the implementation properties of the gateway, under Decisions.
A default sequence path is also specified in the Default
Flow list, with no JavaScript condition associated with
it. The flow follows the first condition that evaluates to true or,
if all conditions evaluate to false, it follows the
default sequence path.
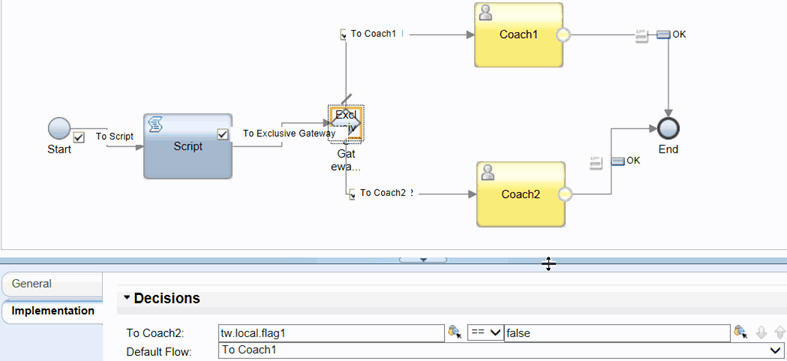
The default sequence path is selected in the Default Flow list, and is followed to the Coach1 activity. Note that the default path is marked with a forward slash (/) sign in the diagram. The sequence flow to Coach2 evaluates to false.
Sample inclusive gateway
Use an inclusive gateway in a BPD when you need to split or diverge the process along more than one path, and you want to follow one or more available paths based on conditions that you establish.
For example, suppose that you want to model a process where the steps are different based on whether the customer type is new or existing. For new customers, you want activities 1 and 2 to be completed. For existing customers, only activity 3 is needed. You can use an inclusive gateway (split) for this type of process so that two activities are set for new customers and a third activity is set for existing customers.
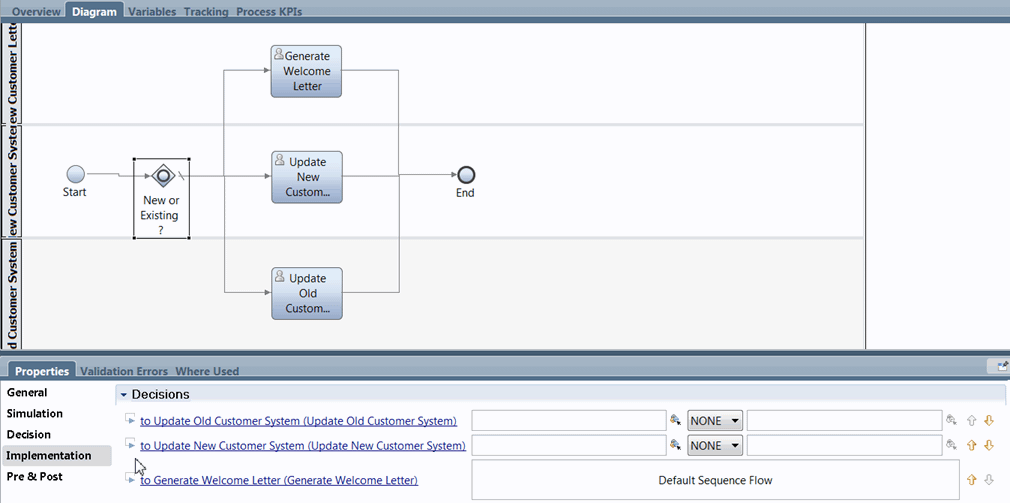
With exclusive gateways, only one available path is followed from the gateway. With inclusive gateways or splits like the one described in the preceding example, one or more paths from the gateway can be followed. The inclusive split gateway in the preceding example determines the path or paths to follow based on the type of customer that is processed. The conditions for this split are configured in the implementation properties for the gateway as follows:
- If the value of the tw.local.customerType variable is "New", the path to activity 1 is followed.
- If the value of the tw.local.customerType variable is "New", the path to activity 2 is also followed.
- If none of the preceding conditions evaluate to true, the path to activity 3 is followed.
Using this logic, you are able to run two separate activities for new customers and a different activity when the customer is an existing one.