Authentication for the DB2® database
system is done using security plug-ins. A security plug-in
is a dynamically-loadable library that provides authentication security
services.
The DB2 database system provides
the following types of plug-ins:
- Group retrieval plug-in: retrieves group membership information
for a given user.
- Client authentication plug-in: manages authentication on a DB2 client.
- Server authentication plug-in: manages authentication on a DB2 server.
The DB2 database manager
supports two mechanisms for plug-in authentication:
- User ID/password authentication
- This involves authentication using a user ID and password. The
following authentication types are implemented using user ID/password
authentication plug-ins:
- - CLIENT
- - SERVER
- - SERVER_ENCRYPT
- - DATA_ENCRYPT
- - DATA_ENCRYPT_CMP
These authentication types determine how and where authentication
of a user occurs. The authentication type used depends on the authentication
type specified by the authentication database
manager configuration parameter. If the SRVCON_AUTH parameter is
specified it takes precedence over AUTHENTICATION when dealing with
connect or attach operations.
- GSS-API authentication
- GSS-API is formally known as Generic Security Service Application
Program Interface, Version 2 (IETF RFC2743) and Generic Security
Service API Version 2: C-Bindings (IETF RFC2744). Kerberos authentication
is also implemented using GSS-API. The following authentication types
are implemented using GSS-API authentication plug-ins:
- - KERBEROS
- - GSSPLUGIN
- - KRB_SERVER_ENCRYPT
- - GSS_SERVER_ENCRYPT
KRB_SERVER_ENCRYPT and GSS_SERVER_ENCRYPT support both GSS-API
authentication and user ID/password authentication; however, GSS-API
authentication is the preferred authentication type.
Note: Authentication types determine how and where
a user is authenticated. To use a particular authentication type,
update the authentication database manager configuration parameter.
Each of the plug-ins can be used independently or in conjunction
with one or more of the other plug-ins. For example, you might only
use a server authentication plug-in and assume the DB2 defaults for client and group authentication.
Alternatively, you might have only a group or client authentication
plug-in. The only situation where both a client and server plug-in
are required is for GSS-API authentication plug-ins.
The default behavior is to use a user ID/password plug-in that
implements an operating-system-level mechanism for authentication.
In previous releases, the default behavior is to directly use operating-system-level
authentication without a plug-in implementation. Client-side Kerberos
support is available on Solaris, AIX®, Windows, and Linux operating systems. For Windows platforms, Kerberos support is enabled
by default.
DB2 database systems include
sets of plug-ins for group retrieval, user ID/password authentication,
and for Kerberos authentication. With the security plug-in architecture
you can customize DB2 client
and server authentication behavior by either developing your own plug-ins,
or buying plug-ins from a third party.
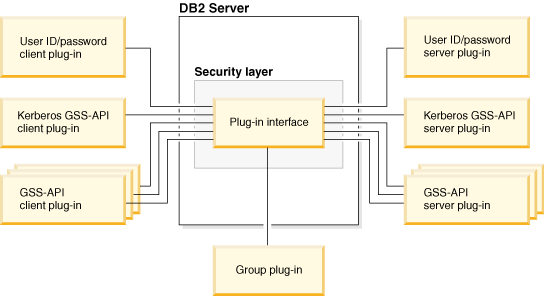
Deployment of security plug-ins on DB2 clients
DB2 clients can support one group plug-in, one
user ID/password authentication plug-in, and will negotiate with the DB2 server for a particular GSS-API
plug-in. This negotiation consists of a scan by the client of the DB2 server's list of implemented
GSS-API plug-ins for the first authentication plug-in name that matches
an authentication plug-in implemented on the client. The server's
list of plug-ins is specified in the
srvcon_gssplugin_list database
manager configuration parameter value, which contains the names of
all of the plug-ins that are implemented on the server. The following
figure portrays the security plug-in infrastructure on a DB2 client.
Figure 1. Deploying Security Plug-ins on DB2 Clients
Deployment of security plug-ins on DB2 servers
DB2 servers can support one group plug-in, one
user ID/password authentication plug-in, and multiple GSS-API plug-ins.
The multiple GSS-API plug-ins are specified in the srvcon_gssplugin_list
database manager configuration parameter value as a list. Only one
GSS-API plug-in in this list can be a Kerberos plug-in.
In
addition to server-side security plug-ins, you might also need to
deploy client authorization plug-ins on your database server. When
you run instance-level operations like
db2start and
db2trc,
the DB2 database manager performs
authorization checking for these operations using client authentication
plug-ins. Therefore, you should install the client authentication
plug-in that corresponds to the server plug-in that is specified by
the
authentication database manager configuration
parameter. There is a main distinction between
authentication and
srvcon_auth.
Specifically, they could be set to different values to cause one
mechanism to be used to authenticate database connections and another
mechanism to be used for local authorization. The most common usage
is
srvcon_auth set as GSSPLUGIN and
authentication set
as SERVER. If you do not use client authentication plug-ins on the
database server, instance level operations such as
db2start will
fail. For example, if the authentication type is SERVER and no user-supplied
client plug-in is used, the DB2 database
system will use the IBM-shipped default client operating-system plug-in.
The following figure portrays the security plug-in infrastructure
on a DB2 server.
Figure 2. Deploying Security Plug-ins on DB2 Servers
Note: The integrity of your DB2 database
system installation can be compromised if the deployment of security
plug-ins are not adequately coded, reviewed, and tested. The DB2 database system takes precaution
against many common types of failures, but it cannot guarantee complete
integrity when user-written security plug-ins are deployed.
Enabling security plug-ins
The system administrator
can specify the names of the plug-ins to use for each authentication
mechanism by updating certain plug-in-related database manager configuration
parameters. If these parameters are null, they will default to the
DB2-supplied plug-ins for group retrieval, user ID/password management,
or Kerberos (if authentication is set to Kerberos -- on the server). DB2 does not provide a default GSS-API
plug-in. Therefore, if system administrators specify an authentication
type of GSSPLUGIN in authentication parameter,
they must also specify a GSS-API authentication plug-in in srvcon_gssplugin_list.
How DB2 loads
security plug-ins
All of the supported plug-ins identified
by the database manager configuration parameters are loaded when the
database manager starts.
The DB2 client
will load a plug-in appropriate for the security mechanism negotiated
with the server during connect or attach operations. It is possible
that a client application can cause multiple security plug-ins to
be concurrently loaded and used. This situation can occur, for example,
in a threaded program that has concurrent connections to different
databases from different instances.
Actions other than connect
or attach operations require authorization (such as updating the
database manager configuration, starting and stopping the database
manager, turning DB2 trace on
and off) as well. For such actions, the DB2 client
program will load a plug-in specified in another database manager
configuration parameter. If authentication is
set to GSSPLUGIN, DB2 database
manager will use the plug-in specified by local_gssplugin.
If authentication is set to KERBEROS, DB2 database manager will use the
plug-in specified by clnt_krb_plugin. Otherwise, DB2 database manager will use the
plug-in specified by clnt_pw_plugin.
Security
plug-ins APIs can be called from either an IPv4 platform or an IPv6
platform. An IPv4 address is a 32-bit address that has a readable
form a.b.c.d, where each of a-d represents a decimal number from
0-255. An IPv6 address is a 128-bit address of the form a:b:c:d:e:f:g:h,
where each of a-h represents 4 hex digits.
Developing security plug-ins
If you are
developing a security plug-in, you need to implement the standard
authentication functions that DB2 database
manager will use. If you are using your own customized security plug-in,
you can use a user ID of up to 255 characters on a connect statement
issued through the CLP or a dynamic SQL statement. For the available
types of plug-ins, the functionality you will need to implement is
as follows:
- Group retrieval
- Gets the list of groups to which a user belongs.
- User ID/password authentication
-
- Identifies the default security context (client only).
- Validates and optionally changes a password.
- Determines if a given string represents a valid user (server only).
- Modifies the user ID or password provided on the client before
it is sent to the server (client only).
- Returns the DB2 authorization
ID associated with a given user.
- GSS-API authentication
-
- Implements the required GSS-API functions.
- Identifies the default security context (client only).
- Generates initial credentials based on a user ID and password
and optionally changes password (client only).
- Creates and accepts security tickets.
- Returns the DB2 authorization
ID associated with a given GSS-API security context.