Loading data in a partitioned database environment
Using the load utility to load data into a partitioned database environment.
Before you begin
- Ensure that the svcename database manager configuration parameter and the DB2COMM profile registry variable are set correctly. This step is important because the load utility uses TCP/IP to transfer data from the pre-partitioning agent to the partitioning agents, and from the partitioning agents to the loading database partitions.
- Before invoking the load utility, you must be connected to (or be able to implicitly connect to) the database into which you want to load the data.
- Since the load utility issues a COMMIT statement, complete all
transactions and release any locks by issuing either a COMMIT or a
ROLLBACK statement before beginning the load operation. If the PARTITION_AND_LOAD, PARTITION_ONLY,
or ANALYZE mode is being used, the data file that
is being loaded must reside on this database partition unless:
- The CLIENT parameter has been specified, in which case the data must reside on the client machine;
- The input source type is CURSOR, in which case there is no input file.
- Run the Design Advisor to determine the best database partition for each table. For more information, see The Design Advisor.
Restrictions
- The location of the input files to the load operation cannot be a tape device.
- The ROWCOUNT parameter is not supported unless the ANALYZE mode is being used.
- If the target table has an identity column that is needed for distributing and the identityoverride file type modifier is not specified, or if you are using multiple database partitions to distribute and then load the data, the use of a SAVECOUNT greater than 0 on the LOAD command is not supported.
- If an identity column forms part of the distribution key or it is a random distribution table using the random by generation method, only the PARTITION_AND_LOAD mode is supported.
- The LOAD_ONLY and LOAD_ONLY_VERIFY_PART modes cannot be used with the CLIENT parameter of the LOAD command.
- The LOAD_ONLY_VERIFY_PART mode cannot be used with the CURSOR input source type.
- The distribution error isolation modes LOAD_ERRS_ONLY and SETUP_AND_LOAD_ERRS cannot be used with the ALLOW READ ACCESS and COPY YES parameters of the LOAD command.
- Multiple load operations can load data into the
same table concurrently if the database partitions specified by theOUTPUT_DBPARTNUMS and PARTITIONING_DBPARTNUMS options
do not overlap. For example, if a table is defined on database partitions
0 through 3, one load operation can load data into database partitions
0 and 1 while a second load operation can load data into database
partitions 2 and 3. If the database partitions specified by the PARTITIONING_DBPARTNUMS options
do overlap, then load will automatically choose a PARTITIONING_DBPARTNUMS parameter
where no load partitioning subagent is already executing on the table,
or fail if none are available.
Starting with version 9.7 Fix Pack 6, if the database partitions specified by the PARTITIONING_DBPARTNUMS options do overlap, the load utility automatically tries to pick up a PARTITIONING_DBPARTNUMS parameter from the database partitions indicated by OUTPUT_DBPARTNUMS where no load partitioning subagent is already executing on the table, or fail if none are available.
It is strongly recommended that if you are going to explicitly specify partitions with the PARTITIONING_DBPARTNUMS option, you should use that option with all concurrent LOAD commands, with each command specifying different partitions. If you only specify PARTITIONING_DBPARTNUMS on some of the concurrent load commands or if you specify overlapping partitions, the LOAD command will need to pick alternate partitioning nodes for at least some of the concurrent loads, and in rare cases the command might fail (SQL2038N).
- Only non-delimited ASCII (ASC) and Delimited ASCII (DEL) files can be distributed across tables spanning multiple database partitions. PC/IXF files cannot be distributed, however, you can load a PC/IXF file into a table that is distributed over multiple database partitions by using the load operation in the LOAD_ONLY_VERIFY_PART mode.
Example
The following examples illustrate how to use the LOAD command to initiate various types of load operations. The database used in the following examples has five database partitions: 0, 1, 2, 3 and 4. Each database partition has a local directory /db2/data/. Two tables, TABLE1 and TABLE2, are defined on database partitions 0, 1, 3 and 4. When loading from a client, the user has access to a remote client that is not one of the database partitions.
- Distribute and load example
- In this scenario, you are connected to a database partition that might or might not be a database partition where TABLE1 is defined. The data file load.del resides in the current working directory of this database partition. To load the data from load.del into all of the database partitions where TABLE1 is defined, issue the following command:
LOAD FROM LOAD.DEL of DEL REPLACE INTO TABLE1Note: In this example, default values are used for all of the configuration parameters for partitioned database environments: The MODE parameter defaults to PARTITION_AND_LOAD. The OUTPUT_DBPARTNUMS parameter defaults to all database partitions on which TABLE1 is defined. The PARTITIONING_DBPARTNUMS defaults to the set of database partitions selected according to the LOAD command rules for choosing database partitions when none are specified.To perform a load operation where data is distributed over database partitions 3 and 4, issue the following command:LOAD FROM LOAD.DEL of DEL REPLACE INTO TABLE1 PARTITIONED DB CONFIG PARTITIONING_DBPARTNUMS (3,4)Figure 1. Loading data into database partitions 3 and 4.. This diagram illustrates the behavior resulting when the previous command is issued. Data is loaded into database partitions 3 and 4. 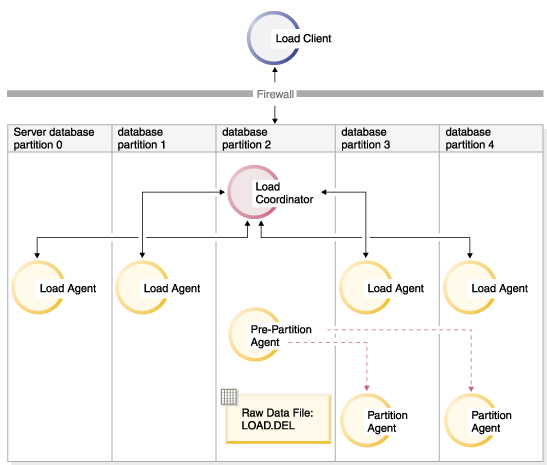
- Distribute only example
- In this scenario, you are connected to a database partition that might or might not be a database partition where TABLE1 is defined. The data file load.del resides in the current working directory of this database partition. To distribute (but not load) load.del to all the database partitions on which TABLE1 is defined, using database partitions 3 and 4 issue the following command:
This results in a file load.del.xxx being stored in the /db2/data directory on each database partition, where xxx is a three-digit representation of the database partition number.LOAD FROM LOAD.DEL of DEL REPLACE INTO TABLE1 PARTITIONED DB CONFIG MODE PARTITION_ONLY PART_FILE_LOCATION /db2/data PARTITIONING_DBPARTNUMS (3,4)To distribute the load.del file to database partitions 1 and 3, using only one partitioning agent running on database partition 0 (which is the default for PARTITIONING_DBPARTNUMS), issue the following command:LOAD FROM LOAD.DEL OF DEL REPLACE INTO TABLE1 PARTITIONED DB CONFIG MODE PARTITION_ONLY PART_FILE_LOCATION /db2/data OUTPUT_DBPARTNUMS (1,3)Figure 2. Loading data into database partitions 1 and 3 using one partitioning agent.. This diagram illustrates the behavior that results when the previous command is issued. Data is loaded into database partitions 1 and 3, using one partitioning agent running on database partition 0. 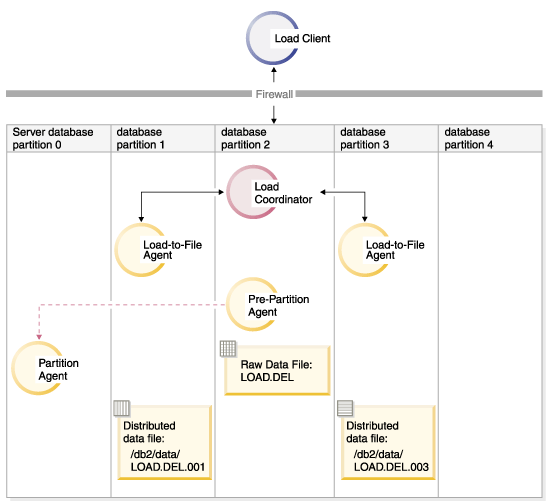
- Load only example
- If you have already performed a load operation in the PARTITION_ONLY mode and want to load the partitioned files in the /db2/data directory of each loading database partition to all the database partitions on which TABLE1 is defined, issue the following command:
LOAD FROM LOAD.DEL OF DEL REPLACE INTO TABLE1 PARTITIONED DB CONFIG MODE LOAD_ONLY PART_FILE_LOCATION /db2/dataFigure 3. Loading data into all database partitions where a specific table is defined.. This diagram illustrates the behavior resulting when the previous command is issued. Distributed data is loaded to all database partitions where TABLE1 is defined. 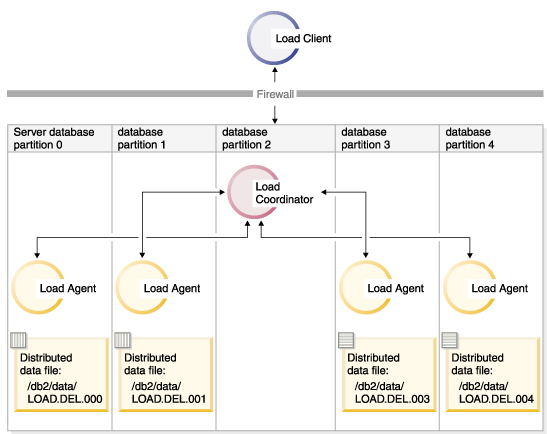 To load into database partition 4 only, issue the following command:
To load into database partition 4 only, issue the following command:LOAD FROM LOAD.DEL OF DEL REPLACE INTO TABLE1 PARTITIONED DB CONFIG MODE LOAD_ONLY PART_FILE_LOCATION /db2/data OUTPUT_DBPARTNUMS (4) - Loading pre-distributed files without distribution map headers
- The LOAD command can be used to load data files without distribution headers directly into several database partitions. If the data files exist in the /db2/data directory on each database partition where TABLE1 is defined and have the name load.del.xxx, where xxx is the database partition number, the files can be loaded by issuing the following command:
LOAD FROM LOAD.DEL OF DEL modified by dumpfile=rejected.rows REPLACE INTO TABLE1 PARTITIONED DB CONFIG MODE LOAD_ONLY_VERIFY_PART PART_FILE_LOCATION /db2/dataTo load the data into database partition 1 only, issue the following command:LOAD FROM LOAD.DEL OF DEL modified by dumpfile=rejected.rows REPLACE INTO TABLE1 PARTITIONED DB CONFIG MODE LOAD_ONLY_VERIFY_PART PART_FILE_LOCATION /db2/data OUTPUT_DBPARTNUMS (1)Note: Rows that do not belong on the database partition from which they were loaded are rejected and put into the dump file, if one has been specified. - Loading from a remote client to a multi-partition database
- To load data into a multi-partition database from a file that is on a remote client, you must specify the CLIENT parameter of the LOAD command. This parameter indicates that the data file is not on a server partition. For example:
LOAD CLIENT FROM LOAD.DEL OF DEL REPLACE INTO TABLE1Note: You cannot use the LOAD_ONLY or LOAD_ONLY_VERIFY_PART modes with the CLIENT parameter. - Loading from a cursor
As in a single-partition database, you can load from a cursor into a multi-partition database. In this example, for the PARTITION_ONLY and LOAD_ONLY modes, the PART_FILE_LOCATION parameter must specify a fully qualified file name. This name is the fully qualified base file name of the distributed files that are created or loaded on each output database partition. Multiple files can be created with the specified base name if there are LOB columns in the target table.
To distribute all the rows in the answer set of the statementSELECT * FROM TABLE1to a file on each database partition named /db2/data/select.out.xxx (where xxx is the database partition number), for future loading into TABLE2, issue the following commands:DECLARE C1 CURSOR FOR SELECT * FROM TABLE1 LOAD FROM C1 OF CURSOR REPLACE INTO TABLE2 PARTITIONED DB CONFIG MODE PARTITION_ONLY PART_FILE_LOCATION /db2/data/select.outThe data files produced by the previous operation can then be loaded by issuing the following LOAD command:LOAD FROM C1 OF CURSOR REPLACE INTO TABLE2 PARTITIONED CB CONFIG MODE LOAD_ONLY PART_FILE_LOCATION /db2/data/select.out