IBM InfoSphere Change Data Capture software architecture and concepts for shadow tables
To implement the InfoSphere CDC software as the replication solution to maintain shadow tables, get familiar with the required software architecture and important concepts.
- InfoSphere CDC for Db2®
This software is the replication engine for Db2. The replication engine reads the transaction logs and captures all the DML operations for the source row-organized table. Then, the apply agent applies these changes to the shadow table.
- InfoSphere CDC Access
Server
This software is a server application that directs communications between the replication engine processes and the InfoSphere CDC Management Console or the command line processor (CHCCLP).
- InfoSphere CDC Management
Console
This software is an administration application that you can use to configure and monitor replication for shadow tables. This GUI interface runs on only Windows operating systems. It includes an event log and a monitoring tool.
These InfoSphere CDC software components are included with the Db2 Advanced Workgroup Server Edition, Db2 Advanced Enterprise Server Edition, and IBM Db2 version 11.1 Developer Edition. Check the license agreement for details about the use of these components.
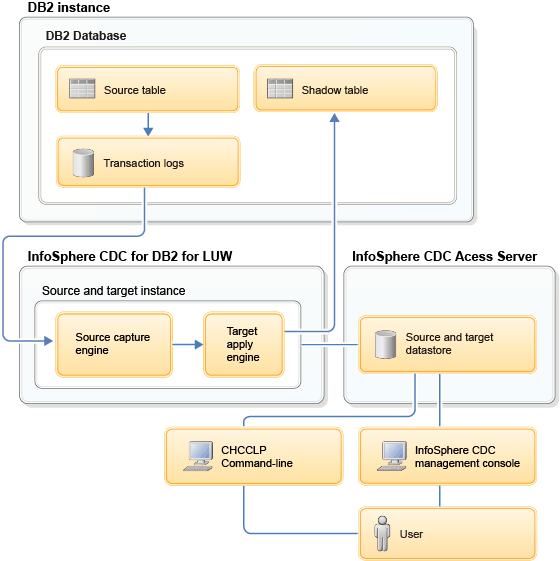
- InfoSphere CDC instance
- The InfoSphere CDC instance is an instance of the replication engine. For shadow tables, the replication engine that is used is the InfoSphere CDC for Db2 replication engine. Because the source and target database are the same, replication for shadow tables requires only one InfoSphere CDC instance. For shadow table replication, create one single InfoSphere CDC instance for replication of all shadow tables in a database.
- Datastores
- A datastore is an abstraction that represents an InfoSphere CDC instance. It holds information about the database and data files that are required for replication. InfoSphere CDC Management Console and the CHCCLP command-line interface interact with the database by connecting to only a datastore. While general InfoSphere CDC environments contain source and target datastores, shadow tables require only one datastore because the source and target are the same database.
- Subscriptions
- A subscription is a container for table mappings. It logically links source and target datastores and contains various parameters that determine the replication behavior. For shadow tables, you must create one single subscription that replicates all shadow tables in a database. Also, mark the subscription as persistent, which allows for better fault tolerance in situations where replication is disrupted.
- Table mappings
- Table
mappings contain information on how individual tables (or columns
of tables) are replicated from the source to the target datastores.
For shadow tables, choose standard replication with a one-to-one table
mapping between a row-organized (source) table and the shadow (target)
table. For the target table key, specify the unique index corresponding
to the primary key of the shadow table to provide a one-to-one table
mapping and performance improvements.
Before you add, modify, or delete table mappings that belong to a subscription, you must end replication.
- Replication
- Replication is the process of maintaining an ongoing synchronization between the contents of source tables and shadow tables. It is the process of sending changes from source tables to shadow tables. The methods of transferring data are refreshing and mirroring.
- Mirroring
- Mirroring is the process of replicating changed data from the source table to a target table. The replication method for shadow tables is continuous mirroring, which continuously replicates changes to shadow tables from the source table as they happen. Replication is explicitly started by starting mirroring. You can start or stop mirroring for a particular subscription.
- Refresh
- Refresh is the process that synchronizes the shadow table with the current contents of the source table. For shadow tables, a standard refresh first clears all the rows in the shadow table and then loads all the data from the source table. After you create a table mapping, starting mirroring for the first time automatically performs a refresh to populate the shadow table.
- Latency
- The latency of the shadow table indicates how closely synchronized it is with the source table. For example, if all the changes to the source tables that occurred more than 30 seconds ago are applied to the target table, but some changes to the source tables that occurred in the last 30 seconds are not yet applied, then the latency of the shadow table is 30 seconds. Routing of queries to shadow tables depends on latency, so latency is one of the most important InfoSphere CDC concepts for shadow tables.
- CHCCLP command-line interface
- Use CHCCLP to accomplish InfoSphere CDC Management Console tasks from the command line. You can run the CHCCLP in interactive mode, in a similar way that you run the Db2 CLP in interactive mode, or in batch mode.