Federated systems
A federated system is a special type of distributed database management system (DBMS) that consists of a database instance that operates as a federated server, a database that acts as the federated database, one or more data sources, and clients (users and applications) that access the database and data sources.
A federated system serves as the foundation on which one or more data virtualization solutions can be built.
Within a federated system, a single SQL statement can access data that is distributed among several data sources. For example, a single SQL statement can join data that is located in a Db2® table, an Oracle table, and an XML tagged file. The following figure shows the components of a federated system and examples of data sources that comprise it.
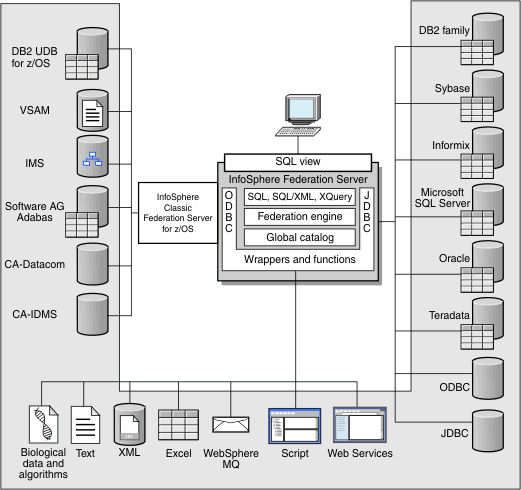
- Correlate data from local tables and remote data sources, as if all the data is stored locally in a single database
- Update data in relational data sources, as if the data is stored in a single database
- Move data to and from relational data sources
- Take advantage of data source's processing strengths, by sending requests to particular data sources for processing
- Compensate for SQL limitations at a data source by having the federated server process parts of a distributed request.