Web services transactions, high availability, firewalls and intermediary nodes
You can configure your system to enable propagation of Web Services Atomic Transactions (WS-AT) message contexts and Web Service Business Activities (WS-BA) message contexts across firewalls or outside the WebSphere® Application Server domain. With these configurations, you can distribute web service applications that use WS-AT or WS-BA across disparate systems. The topology that you use can affect the high availability and affinity behavior of the transactions.
Web services transactions (WS-AT or WS-BA) can use all the transactional high availability functions. This includes peer recovery of a server by another active server in the same cluster, and redirection of protocol messages to the peer server to complete units of work for the failed server. To enable high availability for web services transactions, see the topic about configuring transaction properties for peer recovery. For general information about high availability and peer recovery in WebSphere Application Server, see the topic about transactional high availability.
When web services transactions are distributed between applications in different servers or clusters or to systems that are not WebSphere Application Server systems, you must consider the transaction-routing affinity of web service requests, as well as the impact on high availability of the transaction service on WebSphere Application Server. If a remote client sends a series of transactional requests to a target service that is deployed in a cluster, usually you want the first request to establish a transactional affinity from the client application to the target server, such that subsequent requests in the same transaction are delivered to the same target server. When the transaction completes, the transaction protocol messages are also sent to this same target server, unless and until transaction high availability failover occurs.
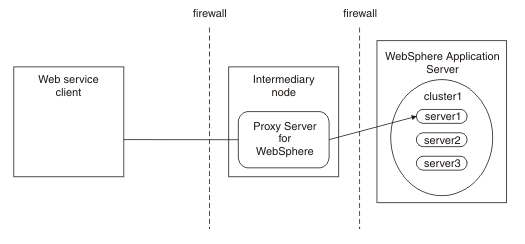
- Direct connection
-
Use this topology for non-clustered configurations. No intermediary node exists in this topology. The client communicates directly with the specificWebSphere Application Server on which the target service is hosted. This topology supports transaction affinity and high availability, but only when the client runs on a WebSphere Application Server Version 6.0.2 or later in the same administrative cell as the target service.
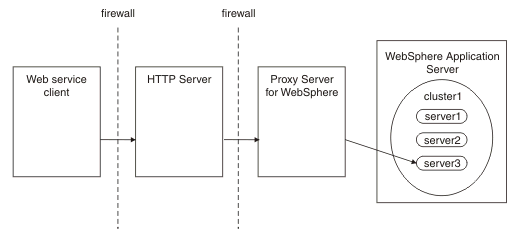
- WebSphere Application Server proxy server
-
Use this topology when the client is not part of the same administrative cell as the target service, and you require transaction affinity or transaction high availability. In this topology, the client communicates with a Proxy Server for IBM® WebSphere Application Server, which dynamically routes the client requests and web services transaction protocol messages to the appropriate server in a WebSphere Application Server cluster. The proxy server is configured in the same administrative cell as the target service.
Avoid trouble: WebSphere Application Server does not provide on demand router (ODR) support for this scenario. Only the WebSphere Application Server proxy server can act as a proxy for web service transaction endpoints.The proxy server provides the routing support for transaction high availability and affinity at the edge of the administrative cell. As for any HTTP proxy configuration, you must provide HTTP endpoint URL information, that is, configure the HTTP server URL prefix for the target web service module.
Also, you must configure the proxy server for web services transactions to deliver web services transaction protocol messages to the appropriate WebSphere Application Server. To do this, configure the transaction service HTTP proxy prefix, which is described in the topic about enabling WebSphere Application Server to use an intermediary node for web services transactions.
- HTTP server, such as IBM HTTP Server
-
Use this topology when transaction high availability and affinity routing is not required by the client, for example because the target service is deployed to a non-clustered server.
In this topology, the client communicates with an HTTP server, which always routes the client requests and web services transaction protocol messages to a specific WebSphere Application Server. As for any HTTP proxy configuration, you must provide HTTP endpoint URL information, that is, configure the HTTP server URL prefix for the target web service module. Also, typically you need to configure the HTTP server for web services transactions, that is, configure it to deliver web services transaction protocol messages to the appropriate WebSphere Application Server. To do this, configure the transaction service HTTP proxy prefix, which is described in the topic about enabling WebSphere Application Server to use an intermediary node for web services transactions.
The HTTP server cannot provide either affinity or high availability for transactions. However, transactional integrity is assured, because recovery processing occurs after the failed server restarts.Note: You can still enable high availability on the WebSphere Application Server. Non-WebSphere Application Server clients that access this server through an HTTP server cannot benefit from the high availability of transactions, but other clients that access the same server can. When the client is on WebSphere Application Server, full high availability capability is still available if the server that acts as the client can address transaction protocol messages directly to the application server without the HTTP proxy routing those protocol messages. In this specific scenario, you must not specify a transaction service HTTP proxy prefix.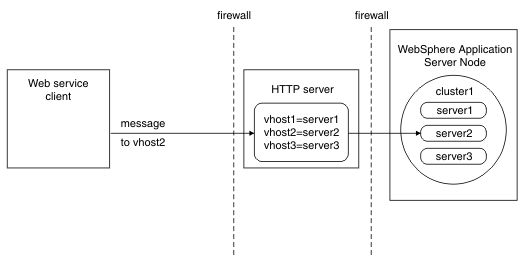
You might have an existing HTTP server that is a reverse proxy for all received messages, including transaction protocol messages. If you want this server to have the high availability and workload management capabilities of a Proxy Server for IBM WebSphere Application Server, create a Proxy Server for IBM WebSphere Application Server and configure the HTTP server to route all requests to the proxy server, as in the following scenario.
- HTTP server in conjunction with a Proxy Server for IBM WebSphere Application Serverr
-
Use this topology when the client is not part of the same administrative cell as the target service and you require transaction affinity or transaction high availability. The topology is similar to the Proxy Server for IBM WebSphere Application Server topology, but supports the use of any HTTP server as the external reverse proxy.
In this topology, the client communicates with an HTTP server, which you configure, by routing requests from a plug-in to a proxy server, to forward the client requests and web services transaction protocol messages to a Proxy Server for IBM WebSphere Application Server. The proxy then dynamically routes the requests to the appropriate server in WebSphere Application Server. The proxy server is configured in the same administrative cell as the target service.
The proxy server provides the routing support for transaction high availability and affinity at the edge of the administrative cell. As for any HTTP proxy configuration, you must provide HTTP endpoint URL information, that is, configure the HTTP server URL prefix for the target web service module.
Also, you must configure the HTTP server and proxy server for web services transactions, that is, configure them to deliver web services transaction protocol messages to the appropriate WebSphere Application Server. To do this, configure the transaction service HTTP proxy prefix, which is described in the topic about enabling WebSphere Application Server to use an intermediary node for web services transactions.