Introduction to InfoSphere Information Server
IBM® InfoSphere® Information Server provides a single platform for data integration and governance. The components in the suite combine to create a unified foundation for enterprise information architectures, capable of scaling to meet any information volume requirements. You can use the suite to deliver business results faster, while maintaining data quality and integrity throughout your information landscape.
InfoSphere Information Server helps your business and IT personnel collaborate to understand the meaning, structure, and content of information across a wide variety of sources. By using InfoSphere Information Server, your business can access and use information in new ways to drive innovation, increase operational efficiency, and lower risk.
Figure 1 shows key capabilities of InfoSphere Information Server that your business can use to implement a complete data integration strategy. The core of these capabilities is a common metadata repository that stores imported metadata, project configurations, reports, and results for all components of InfoSphere Information Server. When you share imported data in the metadata repository, other users in your organization can interact with and use the imported assets in other InfoSphere Information Server components.
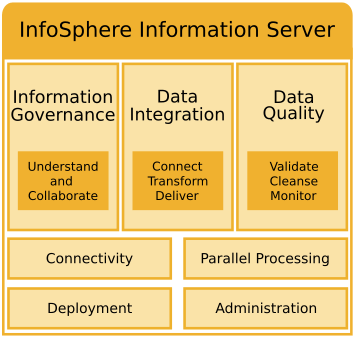
InfoSphere Information Server includes the following core capabilities:
- Understand and collaborate
Improve visibility and information governance by enabling complete, authoritative views of information with proof of lineage and quality. These views can be made widely available and reusable as shared services, while the rules inherent in them are maintained centrally.
- Transform and deliver
Design and develop your data integration project to improve visibility and reduce risk. Discover relationships among systems and define migration rules that integrate asset metadata across multiple sources and targets. Understanding relationships and integrating data reduces operating costs and promotes data quality.
Collect, transform, and distribute large volumes of data. Use built-in transformation functions that reduce development time, improve scalability, and provide for flexible design. Deliver data in real time to your business applications through bulk data delivery (ETL), virtual data delivery (federated), or incremental data delivery (change data capture).
- Cleanse and monitor
Standardize, cleanse, and validate information in batch processing and real time. Load cleansed information into analytical views to monitor and maintain data quality. Reuse these views throughout your enterprise to establish data quality metrics that align with business objectives, enabling your organization to quickly uncover and fix data quality issues.
Link related records across systems to ensure consistency and quality of your information. Consolidate disparate data into a single, reliable record to ensure that the best data survives across multiple sources. Load this master record into operational data stores, data warehouses, or master data applications to create a trusted source of information.