InfoSphere® MDM includes an SQLJ query implementation class, AbstractSQLJBObjQuery, to support SQLJ-based queries.
The core query implementations provided with the InfoSphere MDM product are based on JDBC. If you choose to use SQLJ-based database access instead of or together with JDBC, you should still base your queries on the BObjQuery interface.
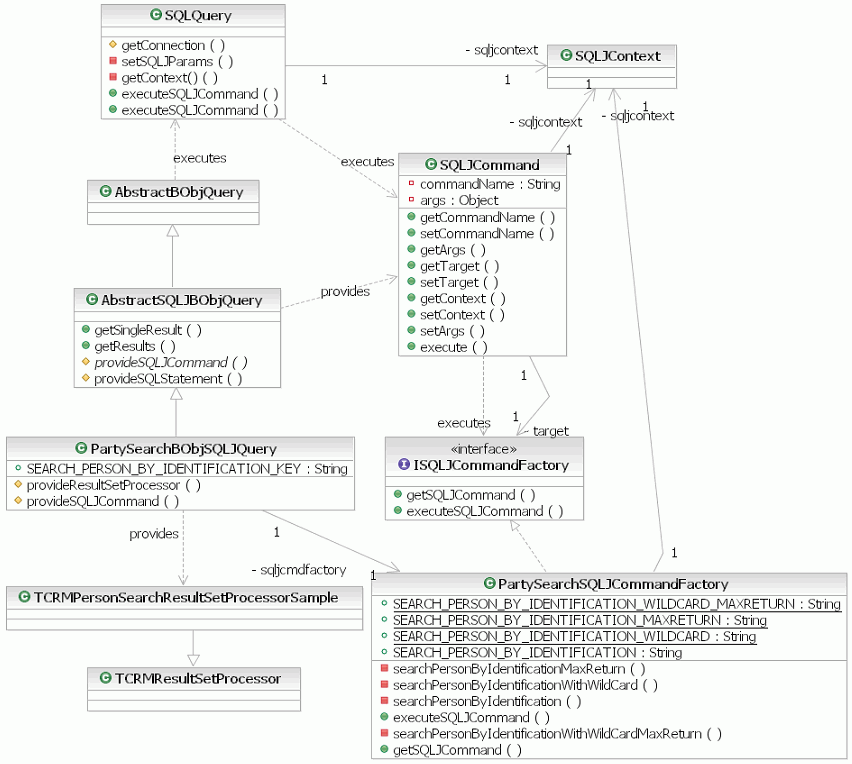
The SQLJ query implementation class AbstractSQLJBObjQuery supports SQLJ-based queries. Instead of implementing the BObjQuery interface directly, the AbstractSQLJBObjQuery class extends AbstractBObjQuery class implementation to reuse most of the implementation code.
- SQLJCommand class
- ISQLJCommandFactory interface
Each SQLJ statement should be defined in a method of its factory class that implements ISQLJCommandFactory. Upon request, the factory class is also responsible for executing each specific SQLJ statement. The result of an SQLJ statement is always converted to a ResultSet object. This enables the SQLJ implementation to reuse the same ResutSetProcessor classes to fetch query results as are used for JDBC.
Each SQLJ statement runs in a given connection context. If you are working in a multithreaded environment, do not use the default context; instead use the empty class, SQLJContext.
The following class diagram depicts the interfaces and abstract classes discussed in this topic, along with the implementation class that is used by the sampleMDM Query Connect transaction.
The method for introducing a SQLJ-based pluggable query is similar to creating a JDBC based business object query. Sample code is used in this section to provide a simplified illustration of the necessary steps. Actual code samples are provided with the InfoSphere MDM Query Connect Samples that are available for download from the InfoSphere MDM Support site.
In order to fully understand the procedures described in this section, you must read and be familiar with New pluggable business object queries.