Obtaining second opinions or expert referrals
Use a message flow that contains a DICOMInput node and one or more DICOMOutput nodes to transfer images to specialists at remote locations.
In locations where radiology skills are limited, it might be necessary for specialists to receive DICOM images (for diagnosis or research purposes) from across a healthcare system.
To transfer these DICOM images, an IBM® App Connect Enterprise message flow that contains a DICOMInput node is configured to receive DICOM images that are sent by a modality, such as a Computerized Tomography (CT) scanner. The DICOMInput node extracts the metadata that is associated with the images. Based on key attributes in the metadata (for example, the Systematized Nomenclature Of Medicine (SNOMED) code), the message is routed to one or more DICOMOutput nodes. From the DICOMOutput nodes, the DICOM images are transferred to DICOM Picture Archiving Communications Systems (PACS) at the specialist locations.
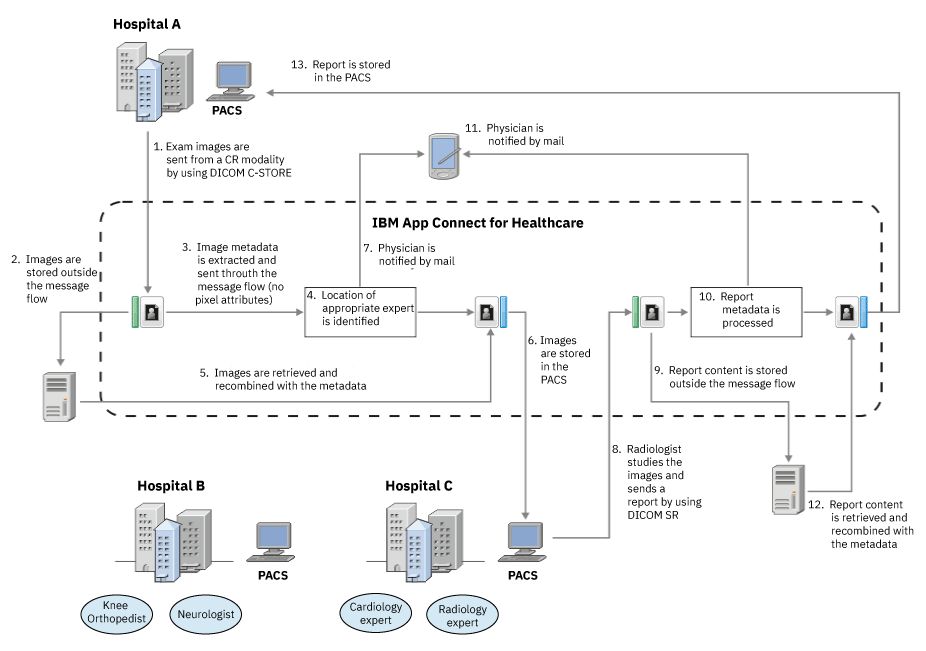
- A patient in Hospital A has a Computed Radiography (CR) exam. The DICOM images from the CR exam are sent to a DICOMInput node in the message flow.
- The DICOMInput node stores the DICOM images in a file system directory.
- The metadata that is associated with the DICOM images is propagated into the message flow as a DICOM XML message.
- From the metadata and other logic in the message flow, the appropriate expert radiologist is identified as being at Hospital C, and the DICOM XML message is sent to a DICOMOutput node.
- The DICOMOutput node retrieves the pixel data for each DICOM image from the DICOMInput node's directory.
- The pixel data from each DICOM image is recombined with the metadata from the DICOM XML message and the resulting DICOM images are stored in the PACS at Hospital C.
- A message is also sent from the message flow to the patient's physician, and includes details of the actions taken.
- The expert radiologist studies the DICOM images and creates a DICOM Structured Report (SR), which is sent to a DICOMInput node in the message flow.
- The DICOMInput node stores the DICOM SR in a file system directory.
- The metadata that is associated with the DICOM SR is propagated into the message flow as a DICOM XML message, and forwarded to a DICOMOutput node.
- A message is also sent from the message flow to the patient's physician, and includes details of the actions taken.
- The DICOMOutput node retrieves the pixel data for the DICOM SR from the DICOMInput node's directory and recombines it with metadata from the DICOM XML message.
- The resulting DICOM SR is sent to the PACS at Hospital A for the local clinical staff to review.