Introduction to Q Replication
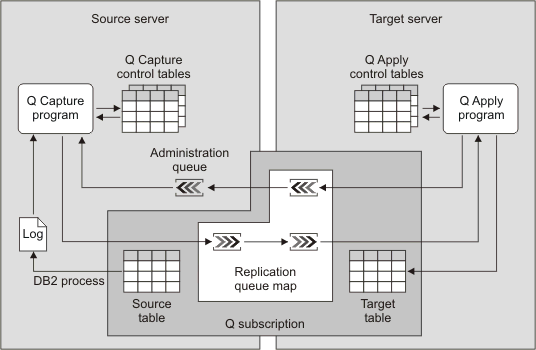
Q Replication is a replication solution that can replicate large volumes of data at low levels of latency. Q Replication captures changes to source tables and converts committed transactional data to messages.
The data is not staged in tables. As soon as the data is committed at the source and read by Q Replication, the data is sent. The messages are sent to the target location through IBM® MQ message queues. At the target location, the messages are read from the queues and converted back into transactional data. The transactions are then applied to your target tables with a highly parallelized method that preserves the integrity of your data.
You can use Q Replication for a variety of purposes that require replicated data, including failover, capacity relief, geographically distributed applications, and data availability during rolling upgrades or other planned outages.
- Db2® for Linux®, UNIX, and Windows
- Db2 for z/OS®
- Oracle (source or target )
- Informix® (target only)
- Microsoft SQL Server (target only)
- Sybase (target only)
You can replicate a subset of columns and rows from the source tables. All subsetting occurs at the source location so that only the data that you want is transported across the network. If you want to perform data transformations, you can use the SQL column expressions feature in Q Apply or pass replicated data to your own stored procedures.
The following figure shows a simple configuration in Q Replication. The topics in this section describe different parts of this figure.