Tutorial introduction
This tutorial demonstrates some of the features of IBM® z/OS® Encryption Readiness Technology (zERT) Network Analyzer and includes exercises to help you to become familiar with generating IBM zERT Network Analyzer reports.
IBM zERT Network Analyzer is a web-based tool that provides z/OS network security administrators with the ability to import, query and analyze data recorded in SMF 119 zERT Summary (subtype 12) records by the z/OS Communications Server zERT aggregation function. IBM zERT Network Analyzer helps you answer the following questions:
- What TCP and Enterprise Extender (EE) traffic is being protected, and what traffic is not?
- How is that traffic being protected? For example, what cryptographic protocols are being used, which cryptographic algorithms are being used, and what are the key lengths?
- Who on my z/OS system is consuming or producing the network traffic, whether it is protected or not?
- Where is the remote endpoint of that traffic?
This tutorial covers the basic steps for using IBM zERT Network Analyzer. The tutorial scenario is based on a fictional company that uses different types of cryptographic protocols for TCP and EE connection traffic. The scenario is simplified for ease of reference and learning.
Learning Objectives
The tutorial does not cover all features of IBM zERT Network Analyzer, but demonstrates an overall approach that you can apply when analyzing your own business cryptographic coverage.
By completing the tutorial, you learn about the following aspects of IBM zERT Network Analyzer:
- Importing SMF data into the IBM zERT Network Analyzer database
- Creating and running queries to identify security sessions with specific cryptographic protection characteristics
- Examining the results of a query
- Exporting query results to an external comma-separated values (CSV) format file
Tutorial scenario
Prepare for the tutorial by reviewing the scenario.
The tutorial scenario is based on a fictitious company Example.com that uses different types of cryptographic protocols for TCP traffic. Example.com is looking to increase its usage of TLS 1.2 protocols, particularly connections to server applications operating in two specific subnets. To do this, Example.com wants to identify existing traffic that uses either TLS 1.0 or TLS 1.1 protocols, as well as traffic that does not use any recognized cryptographic protocols. Only traffic that occurred after 2017 needs to be considered.
- Import Example.com's SMF records into IBM zERT Network Analyzer.
- Prune security session information that does not need to be examined.
- Create a query to identify specific TCP connection traffic involving the local server applications of interest, provided that traffic also uses the cryptographic protection of interest.
- Run the query, and examine the results of the query processing on the database contents.
- Export a report of the query results to a comma-separated values (CSV) format file and use a spreadsheet to examine the results.
The following diagram shows a simplified view of the scenario:
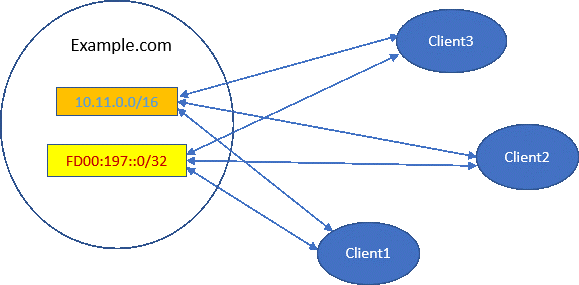
- IPv4 subnet 10.11.0.0/16
- IPv6 subnet FD00:197::0/32
Example.com wants to use IBM zERT Network Analyzer to identify TCP traffic to the server applications in those subnets that use no recognized cryptographic protection, or that still use TLS 1.0 or TLS 1.1 protection.
Time Required
The tutorial takes about 60 minutes.
Audience
This tutorial is for z/OS network security administrators who want to explore features of IBM zERT Network Analyzer task and gain an understanding on how to use the task to identify cryptographic characteristics of their z/OS TCP traffic.
How to use this tutorial?
- You can read the tutorial without first customizing your z/OS system to use IBM zERT Network Analyzer.
This approach allows you to gain understanding of IBM zERT Network Analyzer concepts, but you are unable to perform similar actions on your system as you take the tutorial. You also cannot perform any of the optional steps in the tutorial.
- You can follow along with the tutorial interactively as an introductory exercise for using the IBM zERT Network Analyzer task after you have customized your z/OS systems to use IBM zERT Network Analyzer.
This approach requires more setup work before taking the tutorial, but you are able to perform each step using your own SMF dump data sets while you learn IBM zERT Network Analyzer concepts. You are also able to perform any optional additional steps in the tutorial for further exploration of the IBM zERT Network Analyzer task. Using this approach, you gain real-time experience with the IBM zERT Network Analyzer task.
Note: If you are using your own SMF dump data sets, you will want to tailor the query to your own network IP addresses, and your results will differ from the screen shots included in this tutorial. You can still use the tutorial process as a guide for analyzing the cryptographic protection attributes of your network.
Prerequisites
Before getting started with the tutorial, you need familiarity with basic zERT concepts. For more information about zERT concepts, see z/OS Encryption Readiness Technology (zERT) Concepts in z/OS Communications Server: IP Configuration Guide for more information.
If you are going to just read the tutorial, click on Module 1: Populating the IBM zERT Network Analyzer database to begin.
- If you haven't customized your z/OS system for IBM zERT Network Analyzer yet, complete the following steps:
- Authorize the user IDs that will be using the tutorial and accessing IBM zERT Network Analyzer to the necessary SAF resources. See Authorize users to the IBM zERT Network Analyzer task in the z/OSMF Configuration Guide for instructions.
- Work with your Db2® for z/OS database administrator (DBA) to complete the following steps:
- Define and create the required Db2 database objects for the IBM zERT Network Analyzer to operate. See Db2 for z/OS customization for the IBM zERT Network Analyzer task in the z/OSMF Configuration Guide for instructions.
- Connect IBM zERT Network Analyzer to the Db2 for z/OS database. See Defining database setting for more information.
- Create or identify the SMF dump data sets you plan to use in the tutorial. See Obtaining SMF dump data sets for more information.
- Optional: Start IBM zERT Network Analyzer if you haven't started it yet.
- If you are in the traditional view of z/OSMF, select IBM zERT Network Analyzer from Analysis section in the navigation area.
- If you are in the desktop view of z/OSMF, select the IBM zERT Network Analyzer icon
 .
.
Modules in this tutorial
Module 1: Populating the IBM zERT Network Analyzer database
Populate the IBM zERT Network Analyzer database with zERT Summary (Type 119 subtype 12) SMF records.
Module 2: Querying records in the IBM zERT Network Analyzer database
Create and run a query against the contents of the IBM zERT Network Analyzer database.
Module 3: Viewing IBM zERT Network Analyzer query results
Examine the results of running your query against the contents of the IBM zERT Network Analyzer database.
Module 4: Exporting query results to a CSV format file
Export the results of a query run against the IBM zERT Network Analyzer database to a comma-separated values (CSV) format file.