Sysplex distributor optimization with the OPTLOCAL keyword
Figure 1 shows a sample configuration that uses the OPTLOCAL keyword.
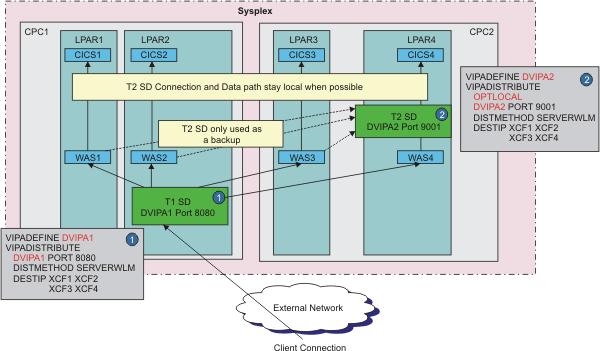
In Figure 1, two tiers of servers are configured across four LPARs that are on two central processor complexes (CPCs) in a sysplex environment. The tier 1 servers consist of z/OS® WebSphere® Application Server (WAS) instances that are listening on port 8080 and that are represented by distributed DVIPA1. Sysplex distributor is configured on LPAR2 to receive and distribute any incoming connections for DVIPA1 to any of the active WAS instances in the four LPARs, based on server-specific WLM recommendations for each WAS instance (designated by the dynamic XCF address of each target LPAR). After a request is directed to a tier 1 WAS instance, the request is processed by that server. One or more secondary TCP connections can be established to a back-end tier 2 server, which is a cluster of CICS® regions (one CICS region per LPAR).
You can use other sysplex distributor functions to distribute the tier 2 connections in this scenario, but that configuration does add some additional pathlength and processing, because all connection requests and traffic for those connections are forwarded through the sysplex distributor routing stack on LPAR4 so that they can get forwarded to the selected tier 2 server instance. This additional pathlength and processing occurs even in the case where the selected tier 2 server for a given connection is on the same LPAR as the tier 1 server that originated the connection.
To reduce excess pathlength but still retain high availability, you can specify the OPTLOCAL keyword for DVIPA2 to optimize processing in several ways:
- As long as local target resources are available and are not constrained, extra network flows and overhead through the distributor are avoided, because the local system makes the decision to route the connection to the local instance.
- When the decision is made to make the connection local, TCP/IP enables this connection for fast local sockets processing. This provides a more efficient path through the TCP/IP stack for these communications. All traffic for this connection remains on the local system and is not routed to the distributing stack.
- Optionally, multi-tier applications can also provide their own optimizations by using the Sysplex Sockets API (SO_CLUSTERCONNTYPE) or the trusted TCP connections API (SIOCGPARTNERINFO ioctl). These APIs enable the multi-tier applications to dynamically determine that they both are on the same system, and as a result, to optimize their processing based on their locality (for example, avoiding encryption of data, sharing memory, and so on). For more information about trusted TCP connections, see z/OS Communications Server: IP Programmer's Guide and Reference.
- If local target resources are unavailable or constrained, normal sysplex distributor processing is performed on the connections as a fallback, enabling the sysplex distributor to select another application that is available.
The OPTLOCAL feature provides for optimal performance in the most common scenario in which the local applications and systems are available and healthy, yet the feature also provides a high availability solution when the local applications or systems are not available or are overly constrained.
You can implement the OPTLOCAL feature using the OPTLOCAL keyword on the VIPADISTRIBUTE statement in the VIPADYNAMIC block, which enables a target stack to keep outbound connections for local resources on the local stack without having to send the connection request to the distributing stack. The level of preference that is shown to the local stack can be adjusted using the integer value specified on the OPTLOCAL keyword.
- Value
- Meaning
- 0
- Specifying 0 means that the connections should remain local as long as the server is healthy. The relative capacity of the other systems is not considered in this case.
- 1
- Specifying 1 is the same as specifying 0, except that if the WLM weight for the server on the local stack is 0, the connection request is forwarded to the sysplex distributor to find the best available server.
- 2 - 16
- The values 2 through 16 are used as multipliers against the WLM weight for the server on the local stack, causing its weight to increase and therefore be favored over servers on other stacks. The larger the value specified, the more the local stack is favored.
If the OPTLOCAL keyword is specified with the value 0 or 1, the distribution method is not used for connections that originate from the specified target stack, if that target application is on the same stack and is able to handle its current workload. Regardless of the value that is specified on the OPTLOCAL keyword, connections are sent to the distributing stack if any of the following conditions are true:
- No local server is available.
- The server's accept efficiency fraction (SEF) has fallen below 75.
- The abnormal transaction completions value is greater than 250.
- The health indicator is less than 75.
For more information about the OPTLOCAL keyword on the VIPADISTRIBUTE statement in the VIPADYNAMIC block, see z/OS Communications Server: IP Configuration Reference.