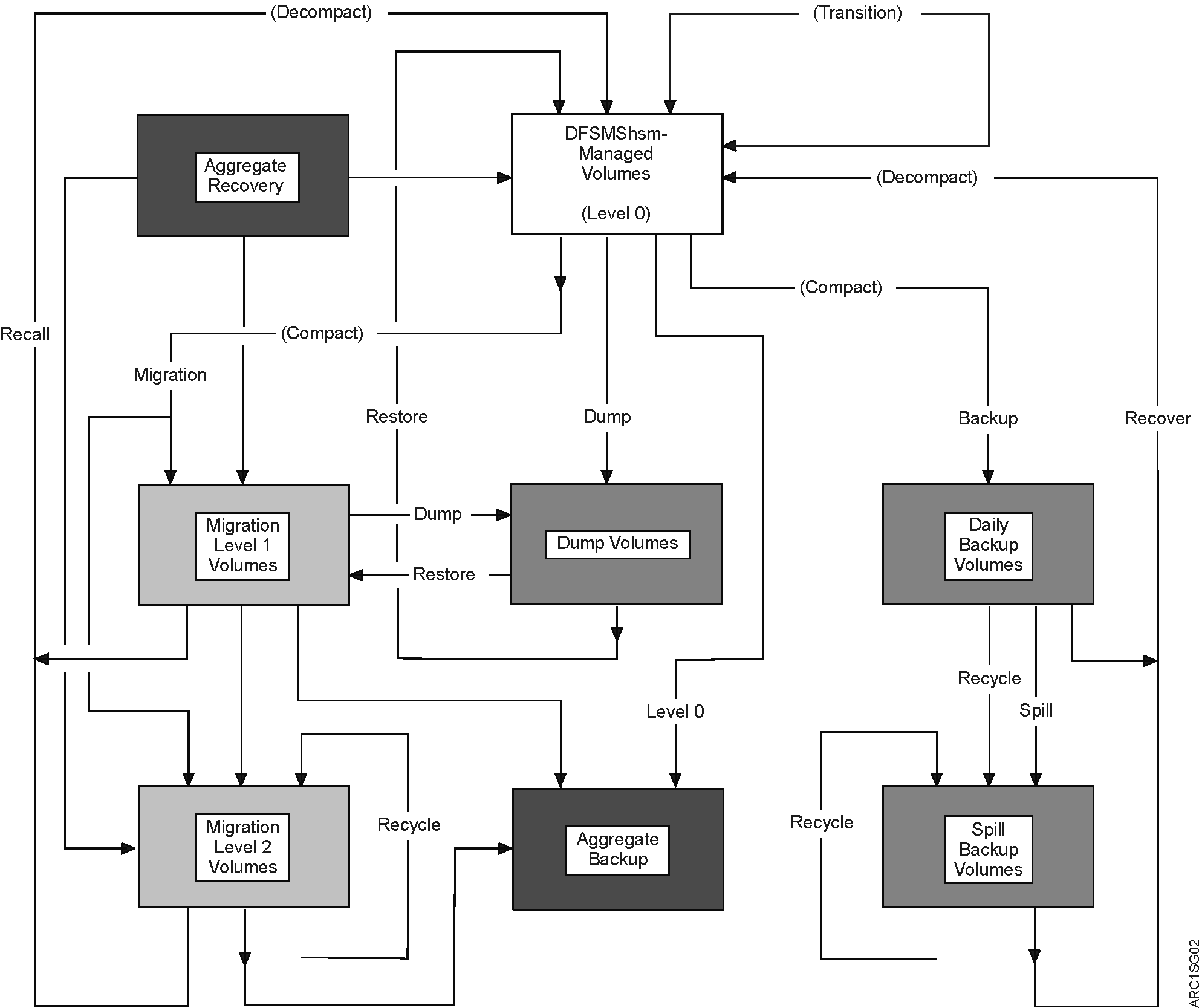
Overview of DFSMShsm functions
Figure 1 shows the generalized flow of data in DFSMShsm. The user’s data is stored on level 0 volumes, either SMS-managed or non-SMS-managed.
Your objective in using DFSMShsm is to make the most efficient
use of all your DASD storage, primarily by making better use of the
level 0 volumes. Better use of the level 0 volumes results when:
- You specify thresholds for DFSMShsm-managed volumes, and you can assure the users that space will be available for extending old data sets or allocating new data sets (space management).
- You can assure the users that a copy of their data sets will be available if the data sets should accidentally be lost from the level 0 volumes (availability management). Such assurance that you can provide backup copies may encourage users not to unnecessarily maintain their own backup copies on level 0 volumes.
Rule: If a data set is larger than the
free space on the DASD backup or migration volume, then the migration
or backup will fail.
DFSMShsm can then restore the volumes and recover the data sets
when they are needed to replace destroyed or damaged data sets.
Note:
- The term "level 0" refers to all DASD volumes that contain user-accessible data. While there is a single level 0 tier within the overall storage hierarchy, it is generally comprised of many different classes of devices. For example, solid state drives (SSD) and SATA drives represent two unique classes. For simplicity, all classes will be generally referred to singularly as level 0.
- Only level 0 DASD volumes can be SMS managed. Migration DASD and backup DASD should never be managed by SMS. Migration, backup, and dump tapes can be SMS-managed in tape libraries.
- DFSMShsm allows use of the cylinder-managed space on extended address volumes (EAVs) for migration copies and backup versions. Use the SETSYS USECYLINDERMANAGEDSPACE command to manage allocation of ML1, ML2, or backup data sets on cylinder managed space. See SETSYS command: Establishing or changing the values of DFSMShsm control parameters for more information.
- Although DFSMShsm performs the same functions of copying, moving, and deleting data sets for both SMS-managed and non-SMS-managed volumes, the kinds and levels of control are different. Therefore, these DFSMShsm functions are described separately for SMS-managed volumes and for non-SMS-managed volumes.
Figure 1. Data Set Flow in DFSMShsm