 z/OS Communications Server: SNA Diagnosis Vol 1, Techniques and Procedures
z/OS Communications Server: SNA Diagnosis Vol 1, Techniques and Procedures
 z/OS Communications Server: SNA Diagnosis Vol 1, Techniques and Procedures
z/OS Communications Server: SNA Diagnosis Vol 1, Techniques and Procedures
|
Previous topic |
Next topic |
Contents |
Contact z/OS |
Library |
PDF
When to use the buffer contents trace for CMIP services API z/OS Communications Server: SNA Diagnosis Vol 1, Techniques and Procedures GC27-3667-00 |
|
|
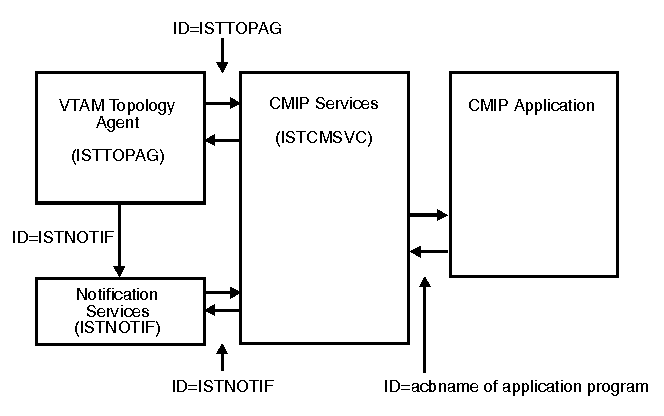
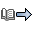
The buffer contents trace can be used to help diagnose problems suspected in CMIP services or the VTAM® topology agent. In addition, it can be used to trace data on the CMIP services API for external CMIP application programs, such as the NetView® program. Figure 1 illustrates the buffer trace points within CMIP services and the VTAM topology agent. There are several types of problems that might occur:
For each problem, you might see the following symptoms: For problem 1, you might have activated some resources but never saw anything show up on graphical monitor facility (GMF). If you were monitoring the network by commands, you should start the buffer contents trace with the ID=ISTTOPAG and ID=acbname operands. If you were monitoring the network implicitly by notifications, for example, by receiving topology updates for definition group objects and the LU object (for the NetView program), or you do not know where the update should be coming from, start the buffer contents trace with the ID=ISTNOTIF operand, in addition to the ID=ISTTOPAG and ID=acbname operands. For problem 2, the NetView program
issues an FFST™ probe. For information
about what values to specify for the ID operand for the buffer contents
trace, see the NetView publications.
If you cannot determine what buffer trace IDs to run, run the buffer
contents trace with the following values for the ID operand:
For problem 3, in most cases, use the ISTTOPAG value for the buffer contents trace. In a few cases, you need to specify the ISTNOTIF value for the ID operand. If you were monitoring the network by commands, you should start the buffer contents trace with the ID=ISTTOPAG operand. If you were monitoring the network implicitly by notifications, for example, by receiving topology updates for definition group objects and the LU object (for the NetView program), or you do not know where the update should be coming from, start the buffer contents trace with the ID=ISTNOTIF operand. If you are not sure which value to specify, specify both ISTTOPAG and ISTNOTIF. For problem 4, if you can re-create the problem, start the buffer trace with the ID=acbname operand that specifies the acbname of each CMIP application program using CMIP services on this host. If you are using the VTAM topology agent, specify the ID=ISTTOPAG operand as well. Re-create the problem. For problem 5, if you can re-create the problem, start the buffer trace with the ID=ISTTOPAG operand and re-create the problem. If you cannot distinguish between problem 4 and 5 and the VTAM topology agent abended, try to re-create the problem and start the buffer trace with the ID=ISTTOPAG and ID=ISTNOTIF operands. If you do not know what caused the problem, start the buffer trace with all three values for the ID operand. In Figure 1, you can see what is traced when each value for the ID operand is specified for the user buffer trace. Figure 1. Trace points for the user buffer
trace for CMIP services
|
 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 |