 z/OS Communications Server: SNA Diagnosis Vol 1, Techniques and Procedures
z/OS Communications Server: SNA Diagnosis Vol 1, Techniques and Procedures
 z/OS Communications Server: SNA Diagnosis Vol 1, Techniques and Procedures
z/OS Communications Server: SNA Diagnosis Vol 1, Techniques and Procedures
|
Previous topic |
Next topic |
Contents |
Contact z/OS |
Library |
PDF
Channel programs for CTC data transfer: Blocking protocol z/OS Communications Server: SNA Diagnosis Vol 1, Techniques and Procedures GC27-3667-00 |
|
|
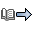
MAXBFRU defines a single read buffer. The write buffer in the other host is allocated to be the same size. PIUs are blocked for transfer, and are written by a single write, and read by a single read. VTAM® uses only three CCWs in its Data Transfer channel program: a Write CCW, a Read CCW, and another that is either a WCTL CCW or an SCB CCW. Output control information is included within the write buffer and input control information is received in the first bytes of the read buffer. Normal data transfer for channel programs is a Write CCW followed by a Read CCW (on the X-side) or a Read CCW followed by a Write CCW (on the Y-side). VTAM uses the procedure described in Channel programs for activating the CTC connection to determine which side will be X and which will be Y. During the XID exchange, each host informs the other host of the size (in pages) of the buffer that will be used in the read portion of its channel programs. Each host then allocates a write buffer to match exactly the read buffer of the other host. Figure 1. Buffers used for
normal data transfer
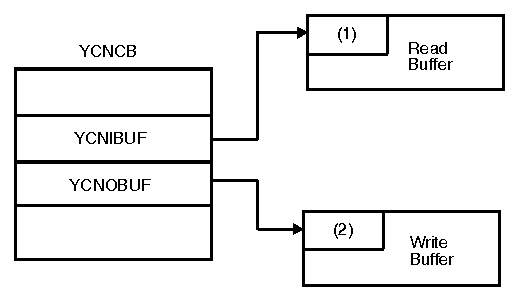 The numbers 1 and 2 in Figure 1 represent:
|
 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 |