 z/OS MVS Programming: Sysplex Services Guide
z/OS MVS Programming: Sysplex Services Guide
 z/OS MVS Programming: Sysplex Services Guide
z/OS MVS Programming: Sysplex Services Guide
|
Previous topic |
Next topic |
Contents |
Contact z/OS |
Library |
PDF
List Structure Enhancements z/OS MVS Programming: Sysplex Services Guide SA23-1400-00 |
|
|
With a coupling facility of CFLEVEL=3 or higher, a keyed list structure can optionally support event queues that are associated with sublist monitoring. (A sublist is a subset of a list — see Understanding List Entry Key Assignment for a description of a sublist.) The system uses the event queues to hold control objects called event monitor controls (EMCs), which contain information about the user and the sublist being monitored. Whenever a monitored sublist transitions from an empty to a nonempty state, an EMC is queued to the user's event queue. The system withdraws the EMC from the user's event queue when the sublist transitions from a nonempty to an empty state. Figure 1 shows the optional parts of a keyed list structure allocated in a coupling facility of CFLEVEL=3 or higher. Figure 1. Event Queues in a List Structure
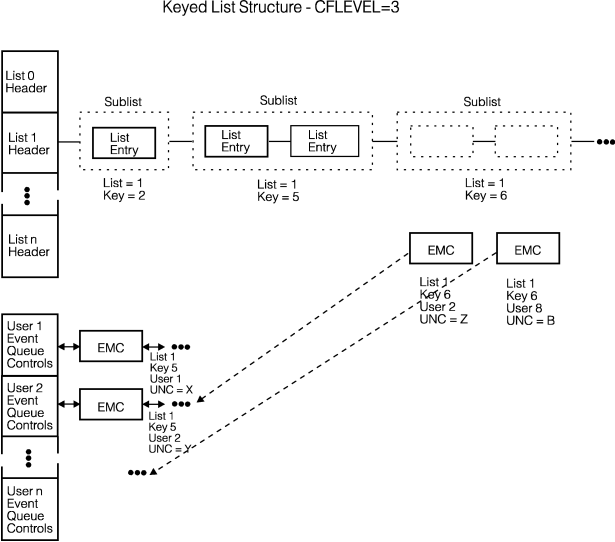 The additional parts of the keyed list structure in a coupling
facility of CFLEVEL=3 or higher are:
Figure 1 shows that for the sublist (List=1, Key=5) there are two EMCs allocated. When the sublist transitioned to a nonempty state, the EMCs were queued to the appropriate users' event queues. If the sublist transitioned to an empty state, the system would withdraw the EMCs from the users' event queues. The figure also shows that for the sublist (List=1, Key=6), there are as yet no list entries. However, there are two EMCs allocated — for users 2 and 8. When the sublist transitions to a nonempty state, the system will queue these EMCs to the appropriate users' event queues. 

|
 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 |