To access kernel services using TSO/E, you need the same
hardware as other
z/OS components.
You also need the workstation connections that TSO/E uses and the
processor and network connections that JES2 or JES3 uses. Network
connections can be made through:
- Systems
Network Architecture (SNA) network: Configure the workstation
hardware and software to access TSO/E through z/OS® Communications Server, formerly known as
Virtual Telecommunications Access Method (VTAM®).The system requires no additional network definitions
for access to z/OS UNIX through
TSO/E.
- TCP/IP network: Configure the workstation hardware and
software to communicate with z/OS Communications
Server, . For the Telnet (TN3270) server, define the Telnet VTAM parameters.
- rlogin or telnet: For rlogin or telnet, configure the
workstation hardware and software to communicate with z/OS Communications Server. If you use rlogin,
you might need additional network capacity to support additional rlogin
users.
Figure 1 shows an example of
workstation and network connections for the z/OS system
with kernel services.
Figure 1. Example of workstation
and network connections.
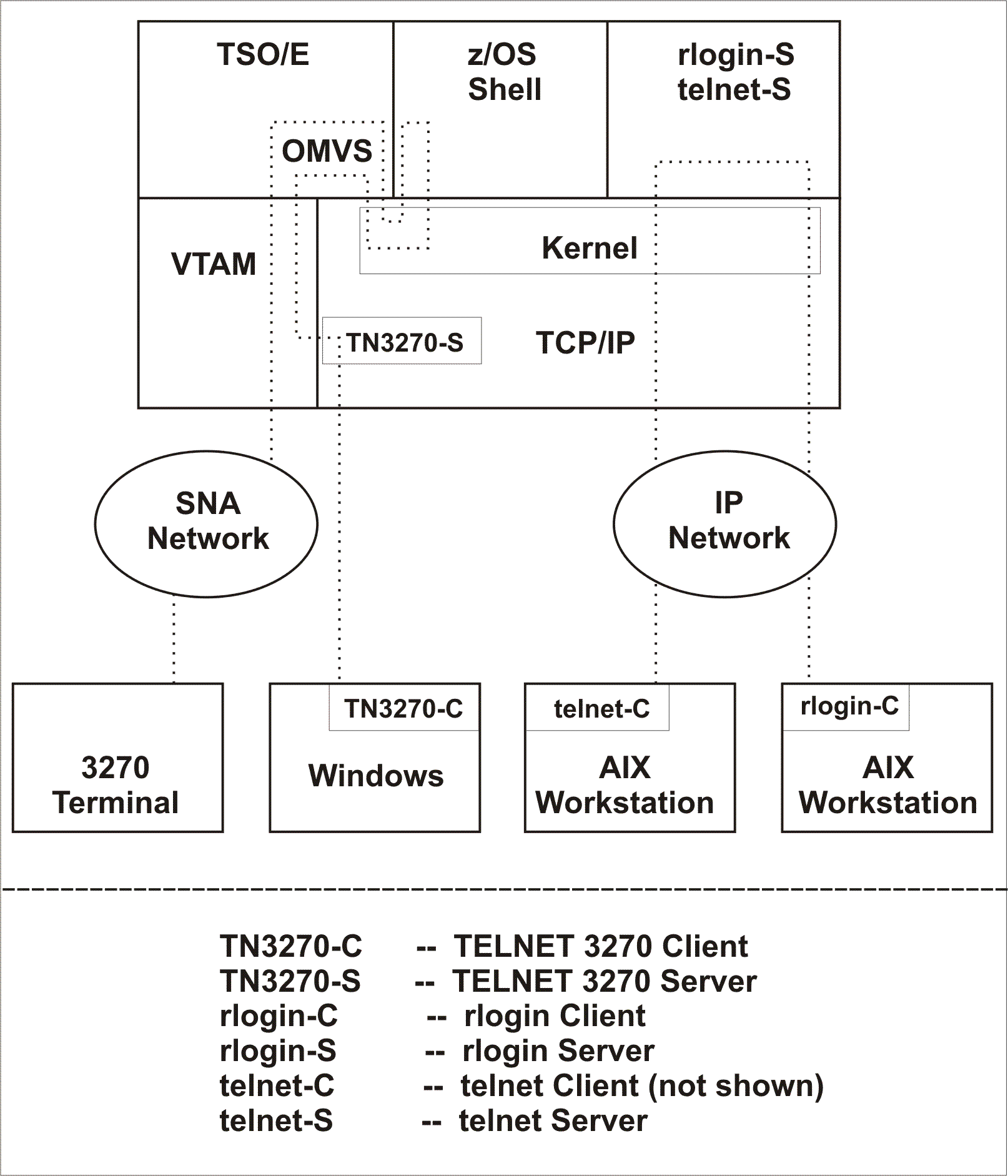
Table 1 shows several ways that you can access
the
z/OS UNIX shells:
When you first log in to one of the z/OS UNIX shells,
you are in line mode. Depending on how you access the shell, you might
be able to use utilities that require raw mode (such as vi)
or run an X-Windows application.
- Line mode
- Input is processed after you press <Enter>. Line mode is also
called canonical mode.
- Raw mode
- Each character is processed as it is typed. Raw mode is also called
non-canonical mode.
- Graphical
- A graphical user interface for X-Windows applications.
Table 1. Accessing z/OS UNIX| Terminal |
Software at the terminal |
Connection to the host |
Shell access |
Supported modes |
|---|
| 3270 |
|
Front-end processor such as 3174
or 3172 |
OMVS (TSO command) |
Line |
| Workstation |
3270 emulator (such as pc3270 or
tn3270) |
Front-end processor such as 3174
or 3172 |
OMVS (TSO command) |
Line |
| rlogin or telnet client |
Front-end processor such as 3174
or 3172 |
rlogin or telnet |
Line or raw |
| X-Window server |
Front-end processor such as 3174
or 3172 |
X-Window client |
Graphical |
| X-terminal |
rlogin or telnet client |
Front-end processor such as 3174
or 3172 |
rlogin or telnet |
Line or raw |
| X-Window server |
Front-end processor such as 3174
or 3172 |
X-Window client |
Graphical |
Noncanonical mode cannot be used with a 3270 because
a 3270 does not send data until ENTER, PA, CLEAR, or PF keys are pressed.
 z/OS UNIX System Services Planning
z/OS UNIX System Services Planning
 z/OS UNIX System Services Planning
z/OS UNIX System Services Planning


 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014
Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014