CICS virtual storage
Each CICS® region operates in its own z/OS® address space. The storage available in a z/OS address space is divided into several different areas.
Figure 1 shows an outline of the storage available in a z/OS address space. Although the theoretical upper limit for this virtual storage is extremely high, there are practical limits to real storage. For this reason, in z/OS, each address space is subject to REGION and MEMLIMIT parameters that limit the amount of storage the address space can use.
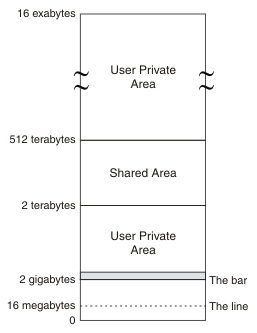
- Storage below the line (0 MB to 16 MB)
- The storage in this area is 24-bit storage.
Addresses below the 16 MB address are accessed by 24-bit addressing, and programs can use this storage when they run in AMODE 24 or higher. The 16 MB address is known as the line, so 24-bit storage is also called storage below the line.
- Storage above the line (16 MB to 2 GB)
- The storage in this area is 31-bit storage.
Addresses above the 16 MB address but below the 2 GB address are accessed by 31-bit addressing, and programs can use this storage when they run in AMODE 31 or higher. The 16 MB address is known as the line, so 31-bit storage is also called storage above the line.
The area that separates the virtual storage area below the 2 GB address from the user private area is known as the bar. 24-bit and 31-bit storage are in storage below 2 GB and can together be referred to as storage below the bar.
- Storage above the bar (4 GB to a theoretical 16 exabytes)
- The storage in this area is 64-bit storage.
The area that separates the virtual storage area below the 2 GB address from the user private area is known as the bar, and 64-bit storage is also known as storage above the bar.
The storage above the bar comprises a user private area between 4 GB and 2 terabytes, a shared area between 2 terabytes and 512 terabytes, and a user private area between the end of the shared area and 16 exabytes.
Addresses above the bar are accessed by 64-bit addressing, and programs can use this storage when they run in AMODE 64.
- CICS dynamic storage areas
- The dynamic storage areas are used to supply the storage requirements of CICS, access methods, and applications running in CICS. See CICS dynamic storage areas.
- MVS™ storage
- MVS storage is available to the operating system to perform region-related services. See 64-bit MVS storage and MVS storage below 2 GB.