Space audits
A space audit is a snapshot or capture of the space details in a building or structure to evaluate the accuracy, efficiency, and utility of spaces. You can conduct space audits regularly to track and compare space allocations, space usage, and space costs over time.
- Estimating the accuracy of the building layout and floor plans.
- Improving the utility area of the space to reduce leasing or renting costs.
- Enhancing the utility of extra space as storage areas or parking lots.
- Organizing the arrangement of furniture and equipment in the space.
- Tracking the prorated space allocations and costs to organizations over time.
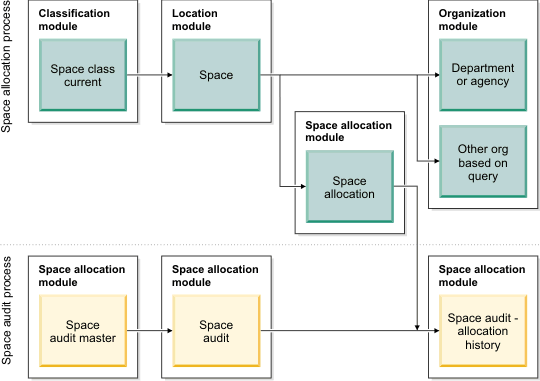
Space allocation process and space audit process
The space allocation process is the simple process of associating or de-associating an organization from the space. Adding or removing an association triggers the application to archive any currently active allocation records and to generate a new space level allocation record for each associated organization. With this process, the application reallocates 100% of the space in the space record evenly across all of the associated organizations.
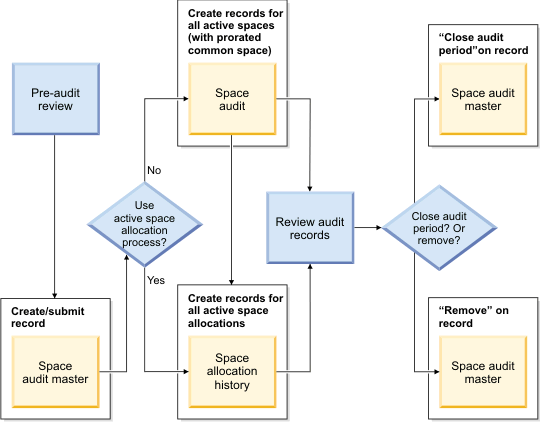
Space audit process
- Pre-audit review: When the process begins, you must verify that all affected floor and space records are in the "Active" state, not "Draft" or "Revision in Progress" state. You can validate that all space allocations to organizations are correct before the audit, or wait to validate until step 4, or do both.
- Select the building and floors: To select the building and floors for the audit, you must create the space audit master record. This information includes the space audit period, space audit process to be used, buildings to be audited, and floors to be audited within each building. When your information is ready to be submitted, activate the record.
- Audit is processed: After the space audit master record is activated,
the application processes the information. Only "Active" floors in
"Active" spaces are processed. Any records in the "Draft" or "Revision
in Progress" state are not processed.
- If you selected active space allocation, the space audit process evaluates allocated spaces only, calculates chargeback amounts only, and generates the space allocation history records. As a result, this method is faster.
- If you did not select active space allocation, the space audit process evaluates all spaces, calculates chargeback amounts, and calculates prorated areas. The process also generates the space audit records and space allocation history records. As a result, this method takes longer.
- Review the audit: After the space audit process ends, you can review the generated records from the space audit master record. You can also validate that all space allocations to organizations are correct.
- Close or remove the audit: After your review ends, you can close
the audit period or remove the space audit master record.
- If you close the audit period, the space audit master, space audit, and space allocation history records are moved to a read-only "History" state.
- If you remove the space audit master record, the space audit master, space audit, and space allocation history records are deleted.
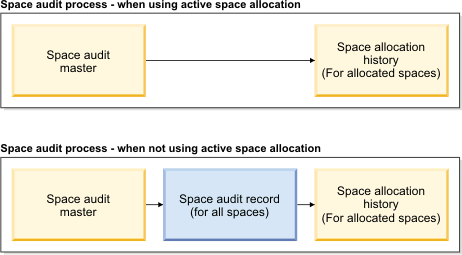
Active versus non-active space allocation
If you selected active space allocation in the space audit master record, the space audit process evaluates allocated spaces only. For each space level allocation record that is in the "Active" state, a space audit allocation history record is created. Finally, each new space audit allocation history record is associated to, and listed in, the space audit master record that activated the audit process.
If you did not select active space allocation in the space audit master record, the space audit process evaluates all spaces. For each space within the floor, a space audit record is created. For each new space audit record, a list of space allocations is retrieved for the related space. Next, for each space allocation, a space audit allocation history record is created and associated to the new space audit record. Finally, the new space audit records are listed in the space audit master record that activated the audit process.