Import or Extract, Transform, Load (ETL)
The import of data or Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) is a process in the database usage that combines three database functions that transfer data from one database to another. The first stage, Extract, involves reading and extracting data from various source systems. The second stage, Transform, converts the data from its original format into the format that meets the requirements of the target database. The last stage, Load, saves the new data into the target database, thus finishing the process of transferring the data.
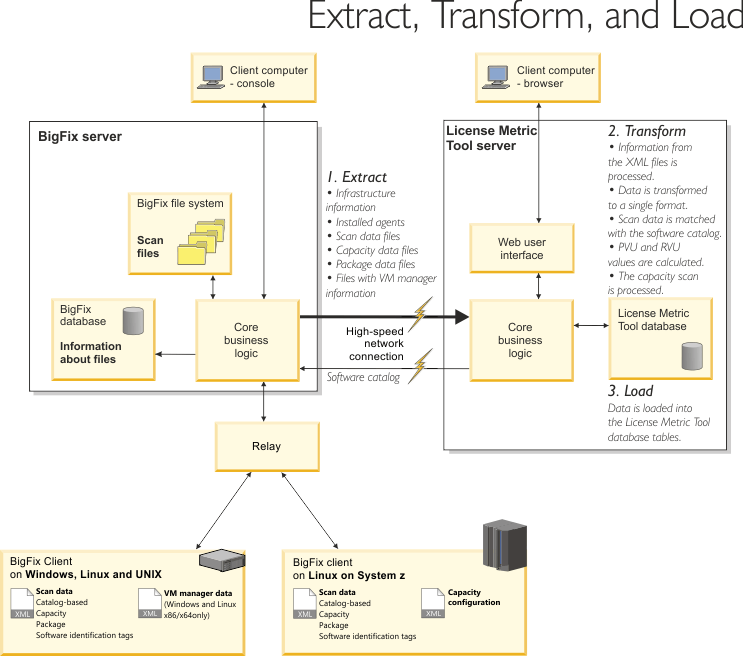
Extract
During the Extract stage, data is extracted from the BigFix® server. The data includes information about the infrastructure, installed clients, and detected software. ETL also imports a new version of the software catalog after the upgrade of the License Metric Tool server, gathers information about the software scan and files that are present on the computers. It also collects data from VM managers.
Transform
During the Transform stage, the extracted data is transformed to a single format that can be loaded to the License Metric Tool database. This stage also involves matching scan data with the software catalog, calculating processor value units (PVUs), and converting information that is contained in the XML files.
Load
During the Load stage, the data that was extracted and transformed is loaded to the License Metric Tool database and can be used by License Metric Tool.
ETL performance
- A large number of small files is retrieved from the BigFix server (Extract).
- Many small and medium files that contain information about installed software packages are parsed (Transform).
- The database is populated with the parsed data (Load).
Performance of the ETL process depends on the number of scan files, and package analyses that are processed during a single import. The main bottleneck is storage performance because many small files must be read, processed, and written to the License Metric Tool database in a short time. By properly scheduling scans and distributing them over the computers in your infrastructure, you can reduce the length of the ETL process and improve its performance.
An important factor that influences the duration of the ETL process is the amount of updates on the file system since the last scan. Such operations as security updates or significant system upgrades can cause ETL to run longer, because it has to process information about all modified files.