Outliers
Shifts in the level of a time series that cannot be explained are referred to as outliers. These observations are inconsistent with the remainder of the series and can dramatically influence the analysis and, consequently, affect the forecasting ability of the time series model.
The following figure displays several types of outliers commonly occurring in time series. The blue lines represent a series without outliers. The red lines suggest a pattern that might be present if the series contained outliers. These outliers are all classified as deterministic because they affect only the mean level of the series.
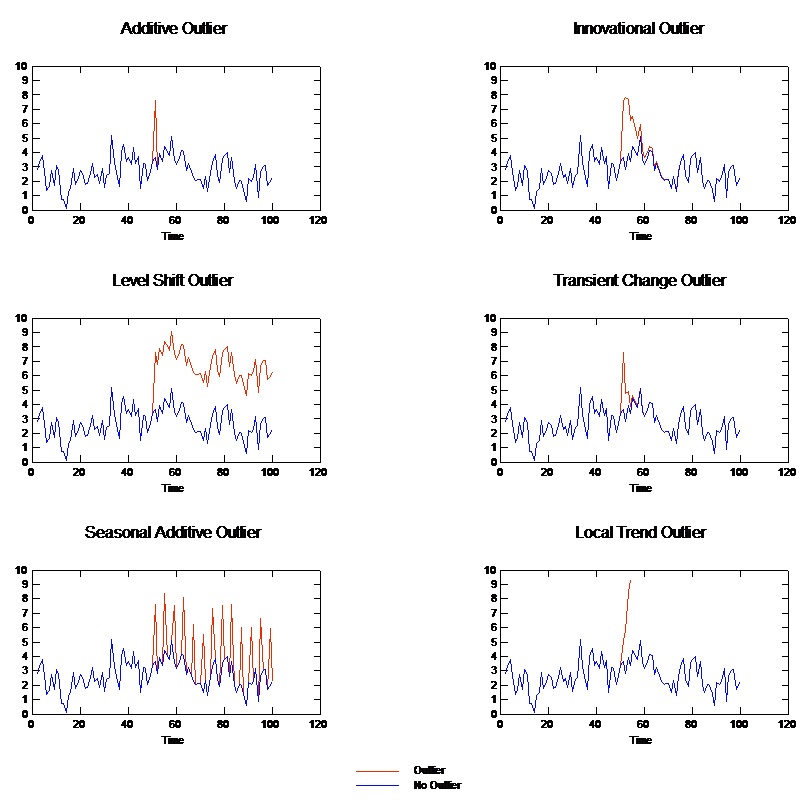
- Additive Outlier. An additive outlier appears as a surprisingly large or small value occurring for a single observation. Subsequent observations are unaffected by an additive outlier. Consecutive additive outliers are typically referred to as additive outlier patches.
- Innovational Outlier. An innovational outlier is characterized by an initial impact with effects lingering over subsequent observations. The influence of the outliers may increase as time proceeds.
- Level Shift Outlier. For a level shift, all observations appearing after the outlier move to a new level. In contrast to additive outliers, a level shift outlier affects many observations and has a permanent effect.
- Transient Change Outlier. Transient change outliers are similar to level shift outliers, but the effect of the outlier diminishes exponentially over the subsequent observations. Eventually, the series returns to its normal level.
- Seasonal Additive Outlier. A seasonal additive outlier appears as a surprisingly large or small value occurring repeatedly at regular intervals.
- Local Trend Outlier. A local trend outlier yields a general drift in the series caused by a pattern in the outliers after the onset of the initial outlier.
Outlier detection in time series involves determining the location, type, and magnitude of any outliers present. Tsay (1988) proposed an iterative procedure for detecting mean level change to identify deterministic outliers. This process involves comparing a time series model that assumes no outliers are present to another model that incorporates outliers. Differences between the models yield estimates of the effect of treating any given point as an outlier.