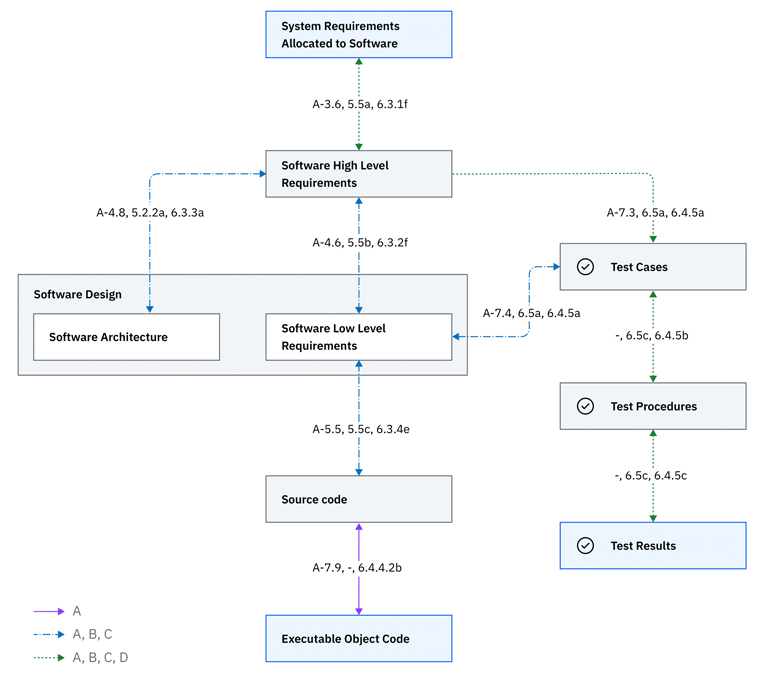
The companies designing and building safety-critical systems need robust processes and collaborative platforms. This paper introduces best practices for software development leveraging the DO-178C standard, and how the IBM Engineering Lifecycle Management solution can help organizations deliver safety-critical products, improve collaboration, and increase efficiency and profitability.

The aerospace and defense (A&D) industry, is seeing new levels of innovation and disruption at every turn1 – putting significant pressure on A&D companies to do more with less by optimizing their development processes to meet cost pressures. Software development and testing alone may be a significant factor in these rising costs, and the DO-178C standard and its related technology supplements have the potential of adding even further stress if not handled optimally.
Projects that need to comply with DO-178C standards could see cost increases anywhere from 25 percent to 40 percent compared to projects that don’t require compliance.2
The sources of additional impacts may include the following:
- Reduced developer productivity due to increases in process complexity
- Manual reporting and documentation processes that are not suited to the level of detail required to comply with DO-178C
- Qualification activities involved in compliance