枚举
枚举 是由一组表示整数常量 (称为 枚举常量) 的指定值组成的数据类型。 枚举也称为 枚举类型 ,因为在为每个枚举类型创建名称时,必须列出 (枚举) 每个值。 除了提供定义和分组整数常量集的方法外,枚举对于具有少量可能值的变量也很有用。
您可以将枚举类型与该类型的变量定义分开声明,如 枚举类型定义 和 枚举变量声明中所述; 也可以定义枚举数据类型以及在一个语句中具有该类型的所有变量,如 枚举类型和单个语句中的变量定义中所述。
枚举类型定义
枚举类型定义包含 enum、 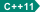
enum class 或 enum struct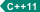 关键字 ,后跟可选标识符(枚举标记)、 可选基础类型说明符
关键字 ,后跟可选标识符(枚举标记)、 可选基础类型说明符 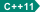 、可选基础类型说明符
、可选基础类型说明符 以及用花括号括起来的枚举项列表。
以及用花括号括起来的枚举项列表。 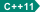 对于范围列举,标识符是必须的。
对于范围列举,标识符是必须的。 逗号分隔枚举列表中的每个枚举项。 C99 允许在最后一个枚举符与右花括号之间使用尾部逗号。
逗号分隔枚举列表中的每个枚举项。 C99 允许在最后一个枚举符与右花括号之间使用尾部逗号。 C++11 标准也采用了这一功能。
C++11 标准也采用了这一功能。
关键字 enum 声明未限定范围的枚举类型,其枚举是未限定范围的枚举。 关键字 enum class 或 enum struct 声明作用域枚举类型,其枚举是作用域枚举。 关键字 enum class 和 enum struct 在语义上等效。
对于未限定作用域的枚举,将同时在枚举说明符的作用域和立即包含枚举说明符的作用域中声明每个枚举符。
int, char, float或任何其他标量类型。 例如:enum class Colour { orange, green, purple };
enum class Fruit { apple, pear, grape, orange };
void functionx(int) {}
void functionx(Colour) {}
void functionx(Fruit) {}
int main()
{
functionx(green); // error, green is not introduced into
// the global scope
functionx(Colour::green); // calls functionx(Colour)
functionx(Fruit::apple); // calls functionx(Fruit)
int i = Colour::orange; // error, no conversion from Colour to int
int j = (int)Colour::green; // valid, explicit cast to integer is allowed
}

tag_identifier 为枚举类型提供名称。 如果未提供标记名称,那么必须将所有引用枚举类型的变量定义放在该类型的声明中,如 枚举类型和变量定义在单个语句中中所述。 同样,不能将类型限定符与枚举定义配合使用; 放在 enum 关键字前面的类型限定符只能应用于在类型定义中声明的变量。
 type_specifier 明确指定枚举的底层类型。 每个枚举都具有底层类型。 type_说明符 可以是任何整数类型。 请注意,枚举类型不是整数类型。 通过指定枚举的底层类型,可以确保程序正确性并在结构中可靠地使用枚举。 如果未指定 type_说明符 ,那么将按如下所示确定枚举的底层类型:
type_specifier 明确指定枚举的底层类型。 每个枚举都具有底层类型。 type_说明符 可以是任何整数类型。 请注意,枚举类型不是整数类型。 通过指定枚举的底层类型,可以确保程序正确性并在结构中可靠地使用枚举。 如果未指定 type_说明符 ,那么将按如下所示确定枚举的底层类型:- 如果枚举具有作用域,那么底层类型具有固定类型
int。 - 如果枚举未限定范围,那么底层类型是可以表示枚举中定义的所有枚举符值的整数类型。
// the underlying type is "unsigned int"
enum Colour : unsigned int { orange = 0, green = 1, purple = 0x02U };
// the underlying type is "unsigned long"
enum class E : unsigned long { E1 = 0, E2 = 1, Emax = 0xFFFFFFF0U };
// if the type_specifier is not specified, the underlying type
// is "int" for the scoped enumeration
enum class A { A1, A2, A3 = 100, A4 };
// the underlying type is an integer type enough to represent the given
// enumerator values, eg. [signed/unsigned] long long
enum A { A1, A2, A3 = 100000000000000000000, A4 };
class C{
//Declaration of a scoped enumeration A.
enum class A;
};
// C is the nested_name_specifier that refers to the class where
// the enumeration A was declared.
enum class C::A { a, b }; 您可以在不提供枚举符列表的情况下转发声明枚举。 枚举的正向声明可以减少编译时间和依赖关系,因为它可以物理地分离枚举的实现细节及其用法。
- 稍后不能将限定范围的枚举重新声明为未限定范围或具有其他底层类型。
- 以后不能将未限定范围的枚举重新声明为限定范围的枚举,并且每个重新声明都必须包含指定相同底层类型的 type_说明符 。
enum E1 : unsigned long; // valid, forward declaration of an unscoped
// enumeration with the underlying type
// "unsigned long"
enum class E2 : char; // valid, forward declaration of a scoped
// enumeration with the underlying type
// "char"
enum class E3; // valid, forward declaration of a scoped
// enumeration with the implied underlying
// type "int"
enum E4; // error, you must specify the underlying type
// when you forward declare an unscoped
// enumeration
enum E1 : unsigned long; // valid, the redeclaration of E1 matches the
// previous declaration of E1
enum class E2 : short; // error, the previously declared enumeration
// E2 had the underlying type "char", and it
// cannot be redeclared with a different
// underlying type
enum E3 : int; // error, the previously declared enumeration
// E3 was a scoped enumeration, and it cannot
// be redeclared as an unscoped enumeration
enum class E3 : int { a, b, c };// valid, definition of E3

详细说明类型说明符
阐述的类型说明符引用先前声明的枚举。 x 是类型为 tag_identifier的变量。
enum 关键字可用于在变量声明或定义期间引用限定范围或未限定范围的枚举。 例如:// a scoped enumeration
enum class color { red, white, black, yellow };
// an unscoped enumeration
enum letter {A, B, C, D};
// valid, regular type name usage
color pic1 = color :: white;
// valid, elaborated type usage
enum color pic2 = color :: red;
enum class 或 enum
struct 。 例如:enum class color pic3 = color :: black; // invalidenum letter let1 = letter :: A; // valid枚举成员
枚举成员或 枚举器的列表为数据类型提供了一组值。
 在C语言中, 枚举常量属于 类型。
在C语言中, 枚举常量属于 类型。 int 如果将一个常量表达式用作初始化器,则表达式的值不能超过 int 的范围(即头文件 limits.h 中定义的INT_MIN到INT_MAX)。 
 在C++中,每个枚举常量都有一个可以提升为有符号或无符号整数值,且不必是整数类型的不同类型。 在允许使用整数常量的任何地方,或者允许使用枚举类型值的任何地方,都可以使用枚举常量。
在C++中,每个枚举常量都有一个可以提升为有符号或无符号整数值,且不必是整数类型的不同类型。 在允许使用整数常量的任何地方,或者允许使用枚举类型值的任何地方,都可以使用枚举常量。
枚举常量的值通过以下方式确定:
- 枚举常量后的等号 (
=) 和常量表达式给出了枚举常量的显式值。 枚举常量表示常量表达式的值。 - 如果没有为第一个枚举符指定显式值,那么它将采用值 0 (零)。
- 没有显式分配值的枚举常量将接收到大于先前枚举常量所表示的值的整数值。
- 有作用域的枚举
- 指定了显式底层类型的未限定范围的枚举
- 底层类型是不大于
int的实现定义的整数类型,可以表示枚举的所有值。 - 如果枚举的值不可由
int或unsigned int表示,那么底层类型是足以表示所有枚举符值的实现定义的整数类型。 - 如果没有类型可以表示所有枚举符值,那么枚举格式不正确。

oats, wheat, barley, corn和 rice 作为枚举常量列出。 每个常量下的数字显示整数值。enum grain { oats, wheat, barley, corn, rice };
/* 0 1 2 3 4 */
enum grain { oats=1, wheat, barley, corn, rice };
/* 1 2 3 4 5 */
enum grain { oats, wheat=10, barley, corn=20, rice };
/* 0 10 11 20 21 */suspend 和 hold 具有相同的整数值。enum status { run, clear=5, suspend, resume, hold=6 };
/* 0 5 6 7 6 */average 和 poor 的第二个声明会导致编译器错误:func()
{
enum score { poor, average, good };
enum rating { below, average, above };
int poor;
} 使用范围枚举可以避免此类错误,因为枚举器仅在枚举的范围内声明,而不是在包含枚举的范围内声明。
使用范围枚举可以避免此类错误,因为枚举器仅在枚举的范围内声明,而不是在包含枚举的范围内声明。
枚举变量声明
必须先声明枚举数据类型,然后才能定义具有该类型的变量。
 枚举变量声明中,关键字 是可选的。
枚举变量声明中,关键字 是可选的。 enum
单个语句中的枚举类型和变量定义
register enum score { poor=1, average, good } rating = good; C++还允许你把存储类放在声明器列表的前面。 例如:
C++还允许你把存储类放在声明器列表的前面。 例如:enum score { poor=1, average, good } register rating = good;
enum score { poor=1, average, good };
register enum score rating = good;这两个示例都定义了枚举数据类型 score 和变量 rating。 rating 具有存储类说明符 register,数据类型 enum
score和初始值 good。
enum { Sunday, Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday,
Saturday } weekday;定义变量 weekday,可以为其分配任何指定的枚举常量。 但是,不能使用这组枚举常量来声明任何其他枚举变量。
