
Export and import binding overview
An export lets you make services in an integration module available to external clients, and an import makes it possible for your SCA components in an integration module to call external services. The binding associated with the export or import specifies the relationship between protocol messages and business objects. It also specifies the way that operations and faults are selected.
Flow of information through an export
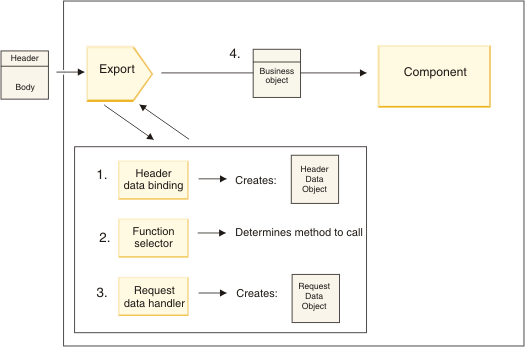
- For WebSphere® MQ bindings only, the header data binding transforms the protocol header into a header data object.
- The function selector determines the native method name from the protocol message. The native method name is mapped by the export configuration to the name of an operation on the interface of the export.
- The request data handler or data binding on the method transforms the request to a request business object.
- The export invokes the component method with the request business
object.
- The HTTP export binding, the web service export binding, and the EJB export binding invoke the SCA component synchronously.
- The JMS, Generic JMS, MQ JMS, and WebSphere MQ export bindings invoke the SCA component asynchronously.
Note that an export can propagate the headers and user properties it receives over the protocol, if context propagation is enabled. Components that are wired to the export can then access these headers and user properties. See the "Propagation" topic in the WebSphere Integration Developer information center for more information.

- If a normal response message is received by the export binding,
the response data handler or data binding on the method transforms
the business object to a response.
If the response is a fault, the fault data handler or data binding on the method transforms the fault to a fault response.
For HTTP export bindings only, if the response is a runtime exception, the runtime exception data handler, if configured, is called.
- For WebSphere MQ bindings only, the header data binding transforms the header data objects into protocol headers.
- The export sends the service response over the transport.
Flow of information through an import

- The HTTP import binding, the web service import binding, and the EJB import binding should be invoked synchronously by the calling component.
- The JMS, Generic JMS, MQ JMS, and WebSphere MQ import binding should be invoked asynchronously.
- The request data handler or data binding on the method transforms the request business object into a protocol request message.
- For WebSphere MQ bindings only, the header data binding on the method sets the header business object in the protocol header.
- The import invokes the service with the service request over the transport.

- For WebSphere MQ bindings only, the header data binding transforms the protocol header into a header data object.
- A determination is made about whether the response is a fault.
- If the response is a fault, the fault selector inspects the fault to determine which WSDL fault it maps to. The fault data handler on the method then transforms the fault to a fault response.
- If the response is a runtime exception, the runtime exception data handler, if configured, is called.
- The response data handler or binding on the method transforms the response to a response business object.
- The import returns the response business object to the component.