Host blocking
A blocked host is no longer available as a resource for that application or service, so that the system does not continuously try to start services on a host that is lacking vital software or hardware requirements. The host blocking feature prevents IBM® Spectrum Symphony from repeatedly trying to run a service on a host that does not have adequate hardware or software resources.
You can configure host blocking to take effect on timeout or exit for each of your services, or when a service throws an exception or sends a specific return code.
About host blocking
When host blocking takes effect, IBM Spectrum Symphony creates a blocked host list for the application with which the service is associated. A host that appears on the blocked host list can no longer be used by the application until you intentionally unblock the host, or the application is re-registered or disabled and enabled again.
| Method | Event types |
|---|---|
| Register |
|
| CreateService |
|
| SessionEnter |
|
| SessionUpdate |
|
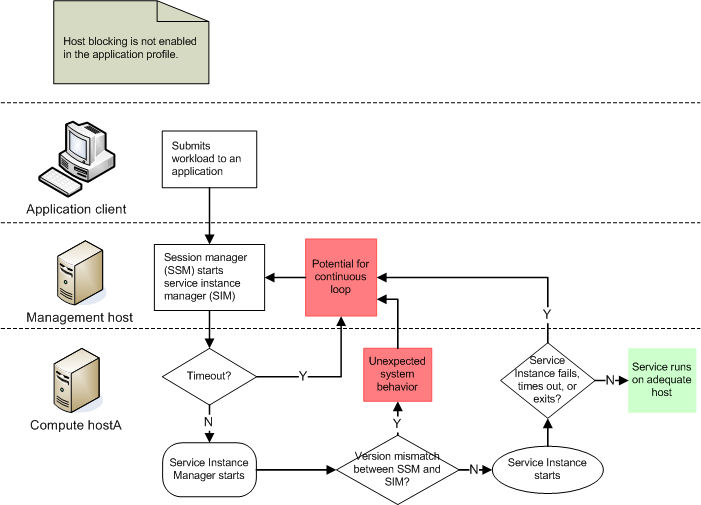
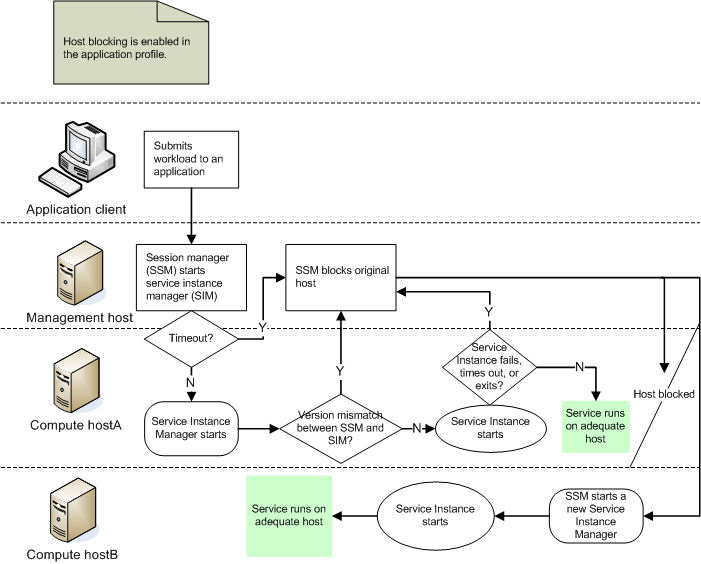
The following illustrations show the benefits of using the host blocking feature.
Without host blocking (feature disabled)
With host blocking enabled
Host blocking triggers
Host blocking triggers automatically when the session manager version on the management host does not match the service instance manager version on the compute host.
- A service method times out, exits or crashes, throws an exception, or returns certain control codes.
- The service instance manager does not communicate with the session manager before the configured timeout period expires (controlled by the startUpTimeout value).
- The service instance does not communicate with the service instance manager before the configured timeout period expires (controlled by the setting for the Register method actionOnSI attribute).
Slot blocking for IBM Spectrum Symphony Developer Edition
IBM Spectrum Symphony Developer Edition blocks slots (not hosts) under the same conditions that trigger host blocking for a production grid. Symptoms of blocked slots include fewer resources than expected or no resources serving your application, more tasks in the PENDING state, a slower rate of workload completion, and clients that hang. You can check for blocked slots by looking in the ssm.hostname.app_name.log file and searching for WARN or ERROR messages about blocked hosts. If you see a blocked host message, one or more slots might be blocked. You can unblock slots by disabling and then enabling the application or by restarting the Developer Edition cluster.Slot blocking for IBM Spectrum Symphony Developer Edition is supported on all host types supported by the product. Note that for IBM Spectrum Symphony Developer Edition, only slots (not hosts) are blocked.
Configuration to enable host blocking
| Section | Attribute name and syntax | Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| blockHostOnTimeout="true" |
|
|
| startUpTimeout="seconds" |
|
|
| actionOnSI=blockHost |
|
|
| actionOnSI=blockHost |
|
|
| actionOnSI=blockHost |
|
|
| actionOnSI=blockHost |
|
Host blocking behavior
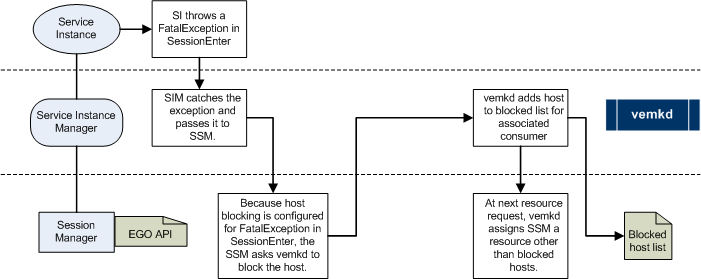
When host blocking is triggered, the system creates a blocked host list for the application. The following example illustrates the host blocking process triggered at the service instance level.
Example of the host blocking process
Configuration to modify host blocking behavior
Not applicable. There are no attributes that change the way that host blocking works other than those attributes configured in the application profile.
Host blocking actions
Actions to monitor
You can monitor host blocking through the cluster management console, the command line, and through the IBM Spectrum Symphony log files located in the logs directory of SOAM_HOME. You can also trap SNMP events to receive notifications when a service triggers the system to block a host.| User | Action | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
From the cluster management console: | Displays a list of blocked hosts for the selected application. |
|
From the command line: egosh alloc view | Displays detailed information about all allocations, including the allocation ID, current users, consumer, resource groups, resource requirements, minimum and maximum slots requested, whether it has exclusive use of the host, names of the allocated hosts, and any blocked hosts. |
- Linux®: $SOAM_HOME/logs
- Windows: %SOAM_HOME%\logs.
Look for the SOA_SERVICE_BLOCKED event, an error level message that indicates that host blocking has occurred.
Actions to control
- Directly from the cluster management console
- Indirectly, by disabling and re-enabling the application associated with the blocked host
| User | Action | Behavior |
|---|---|---|
|
From the cluster management console:, then select , then select the host name, and click Unblock. |
|
|
From the cluster management console:, then select application_name, and click Disable. |
|
|
From the command line: soamcontrol app disable application_name |
|
|
From the cluster management console: |
The system first disables and then re-registers the application, which clears the blocked host list for the modified application. |
| User | Action | Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Developer | From the command line: soamcontrol app disable application_name |
|
| From the command line: soamcontrol app enable application_name | Enables the application, which can start services on any previously blocked slot | |
| Developer | Windows:
Linux:
|
|
Actions to display configuration
| User | Command | Behavior |
|---|---|---|
|
From the cluster management console: |
Displays application profile settings for the selected application. |
|
From the command line: soamview app app_name -p | Displays application profile settings for the selected application. |
You can also view an application profile using an XML editor.