JSOR features and design (Linux only)
JSOR provides support for plain  and NIO
and NIO 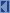 stream socket
applications, IPv6, and an optional method for allowing RDMA-enabled servers to accept TCP clients.
By intercepting socket stream calls, JSOR manages all control operations and data routing for a Java™ application.
stream socket
applications, IPv6, and an optional method for allowing RDMA-enabled servers to accept TCP clients.
By intercepting socket stream calls, JSOR manages all control operations and data routing for a Java™ application.
Note:  The RDMA implementation, which was
previously deprecated is removed from IBM® SDK, Java Technology Edition, Version 8.
The RDMA implementation, which was
previously deprecated is removed from IBM® SDK, Java Technology Edition, Version 8.
 The RDMA implementation, which was
previously deprecated is removed from IBM® SDK, Java Technology Edition, Version 8.
The RDMA implementation, which was
previously deprecated is removed from IBM® SDK, Java Technology Edition, Version 8.
The following JSOR features are available with this release:  and channel
and channel  stream calls are intercepted and routed
through the JSOR native library. The ability to intercept socket stream calls is dependent on rules
that are specified in a runtime configuration file.
stream calls are intercepted and routed
through the JSOR native library. The ability to intercept socket stream calls is dependent on rules
that are specified in a runtime configuration file.
- RMDA-enabled Java plain
 and NIO
stream
and NIO
stream  sockets
sockets - Support for IPv6
- TCP/IP fall back support for RDMA server sockets
- Extensive call tracing at the JSOR native level
 and channel
and channel  stream calls are intercepted and routed
through the JSOR native library. The ability to intercept socket stream calls is dependent on rules
that are specified in a runtime configuration file.
stream calls are intercepted and routed
through the JSOR native library. The ability to intercept socket stream calls is dependent on rules
that are specified in a runtime configuration file.You enable JSOR by specifying a system property when you start your application, which specifies the server or client configuration file. For more information about enabling JSOR, see Enabling Java Sockets over Remote Direct Memory Access (JSOR) (Linux only).
JSOR design
The JSOR library uses two routes to interact with the RDMA network interface adapters, as shown
in the following diagram:


- Fast data path
- The JSOR library uses the OpenFabrics Software (OFS) userspace verbs module to communicate directly with the RDMA network interface adapter. This route is typically used for sending data. For more information about using userspace verbs, see Userspace verbs access.
- Slow control path
- The JSOR library interacts with a device-dependent kernel verbs module for controlling and managing the RDMA resource objects. This path is used mainly for establishing connections.