Securing business application data
If your business application is accessible from the internet, consider the following security configurations for your application data.
Scoping data
Applications run on the client, where they call actions and other services on the server. When you scope the data that is exposed to the client, remember that all variables that are declared in the application are accessible from the browser whether they are displayed on a page. All variables that are enabled for persistence can be saved regardless of where they are used in the application.
If data is only needed within an action, avoid exposing it to the application. Variables in actions are only visible to the server. However, input variables are received from the caller and output variables are sent back to the caller. Actions that receive data as input from an application should validate the data before they act on it. If the output data needs to be passed from one action to another action, use a third action to call both and exchange the data rather than using the application to act as the intermediary.
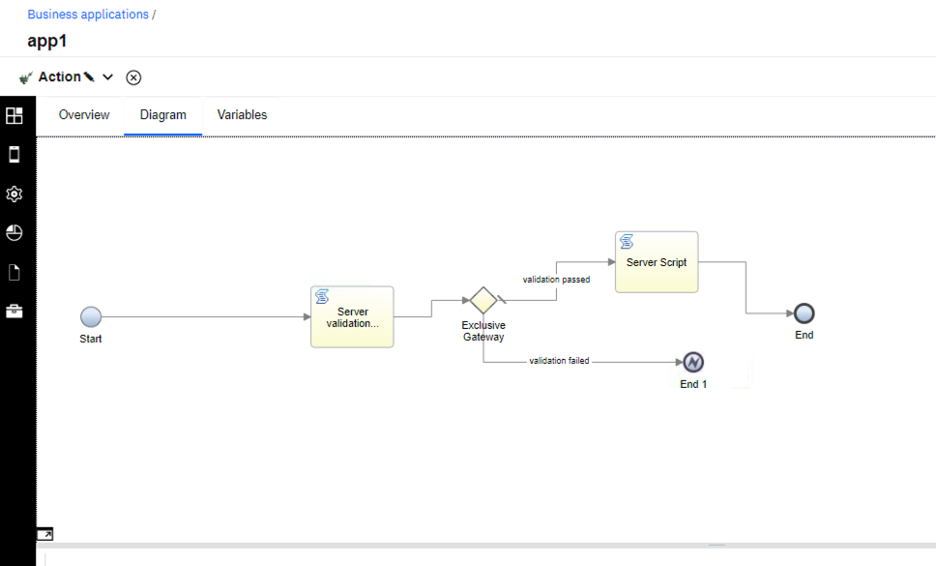
Server-side validation for actions
- Open your business application in the low-code designer, and switch to the Advanced view mode in your user preferences.
- Edit your action in the action editor.
- Add a Server-side script validation immediately after the start of the
action. As illustrated in the following screen capture. In this case, the validation is called
Server validation.
Further considerations
- Don't expose unnecessary REST endpoints of your deployment. You can use a browser debugger to get a network trace of all the network calls that are made when the application is used. Use that trace to determine the endpoints should be available outside the firewall.
- Perform penetration tests on applications before making them available externally.
- Perform static analysis of the files before importing them into application engine.
- Running security scan on your application might highlight the usage of unsafe-inline and unsafe-eval in the CSP header. The directives unsafe-inline and unsafe-eval in the CSP header are required in order to run scripts in the application. The application framework has a mechanism in place to make sure that script execution in the framework is secured. However, it is up to the application author to make sure the JavaScript in the script steps and views follows JavaScript best practices.