Refining data with Data Refinery
To refine data, you take it from one location, cleanse and shape it, and then load the result into a different location. You can cleanse and shape tabular data with a graphical flow editor tool called Data Refinery.
Service The Data Refinery service is not available by default. An administrator must install either the Watson Studio service or the IBM Knowledge Catalog service on the IBM Cloud Pak for Data platform. To determine whether the service is installed, open the Services catalog and check whether the Data Refinery service is enabled.
When you cleanse data, you fix or remove data that is incorrect, incomplete, improperly formatted, or duplicated. When you shape data, you customize it by filtering, sorting, combining or removing columns.
You create a Data Refinery flow as a set of ordered operations on data. Data Refinery includes a graphical interface to profile your data to validate it and over 20 customizable charts that give you insights into your data.
- Required service
- Watson Studio or IBM Knowledge Catalog
- Data format
- Avro, CSV, JSON, Microsoft Excel (xls and xlsx formats. First sheet only, except for connections and connected data assets.), Parquet, SAS with the "sas7bdat" extension (read only), TSV (read only), or delimited text data asset
- Tables in relational data sources
- Data size
- Any. Data Refinery operates on a sample subset of rows in the data set. The sample size is 1 MB or 10,000 rows, whichever comes first. However, when you run a job for the Data Refinery flow, the entire data set is processed. If the Data Refinery flow fails with a large data asset, see workarounds in Troubleshooting Data Refinery.
- Prerequisites
- Source file limitations
- Target file limitations
- Data protection rules
- Data set previews
- Refine your data
Prerequisites
Before you can refine data, you need a project. Watch this video to see how to create a project.
Watch this video to see how to create a project
This video provides a visual method to learn the concepts and tasks in this documentation.
If you have data in cloud or on-premises data sources, you'll need to add connections to those sources and you'll need to add data assets from each connection. If you want to be able to save refined data to cloud or on-premises data sources, create connections for this purpose as well. Source connections can be used only to read data; target connections can be used only to load (save) data. When you create a target connection, be sure to use credentials that have Write permission or you won't be able to save your Data Refinery flow output to the target.
Watch this video to see how to create a connection and add connected data to a project.
Watch this video to see how to create a project
This video provides a visual method to learn the concepts and tasks in this documentation.
Source file limitations
CSV files
Be sure that CSV files are correctly formatted and conform to the following rules:
- Two consecutive commas in a row indicate an empty column.
- If a row ends with a comma, an additional column is created.
White-space characters are considered as part of the data
If your data includes columns that contain white space (blank) characters, Data Refinery considers those white-space characters as part of the data, even though you can't see them in the grid. Some database tools might pad character strings with white-space characters to make all the data in a column the same length and this change affects the results of Data Refinery operations that compare data.
Column names
Be sure that column names conform to the following rules:
- Duplicate column names are not allowed. Column names must be unique within the data set. Column names are not case-sensitive. A data set that includes a column name "Sales" and another column name "sales" will not work.
- The column names are not reserved words in the R programming language.
- The column names are not numbers. A workaround is to enclose the column names in double quotation marks ("").
Data sets with columns with the "Other" data type are not supported in Data Refinery flows
If your data set contains columns that have data types that are identified as "Other" in the Watson Studio preview, the columns will show as the String data type in Data Refinery. However, if you try to use the data in a Data Refinery flow, the job for the Data Refinery flow will fail. An example of a data type that shows as "Other" in the preview is the Db2 DECFLOAT data type.
Target file limitations
The following limitation applies if you save Data Refinery flow output (the target data set) to a file:
- You can't change the file format if the file is an existing data asset.
Data protection rules
Data Refinery does not support data protection rules for row filtering. Data Refinery jobs will fail if the asset is governed by row filtering data protection rules. For information, see Data protection rules enforcement.
Data set previews
Data Refinery provides support for large data sets, which can be time-consuming and unwieldy to refine. To enable you to work quickly and efficiently, it operates on a subset of rows in the data set while you interactively refine the data. When you run a job for the Data Refinery flow, it operates on the entire data set.
Refine your data
The following video shows you how to refine data.
This video provides a visual method to learn the concepts and tasks in this documentation.
1. Access Data Refinery from within a project. Click New asset > Data Refinery. Then select the data that you want to work with. Alternatively, from the Assets tab of a project, open a file (supported formats) to preview it, and then click Prepare data.
Note that different asset types can have duplicate names. However, you can't add an asset type with the same name multiple times.
2. Use steps to apply operations that cleanse, shape, and enrich your data. Browse operation categories or search for a specific operation, then let the UI guide you. You can enter R code in the command line and let autocomplete assist you in getting the correct syntax. As you apply operations to a data set, Data Refinery keeps track of them and builds a Data Refinery flow. For each operation that you apply, Data Refinery adds a step.
Data tab
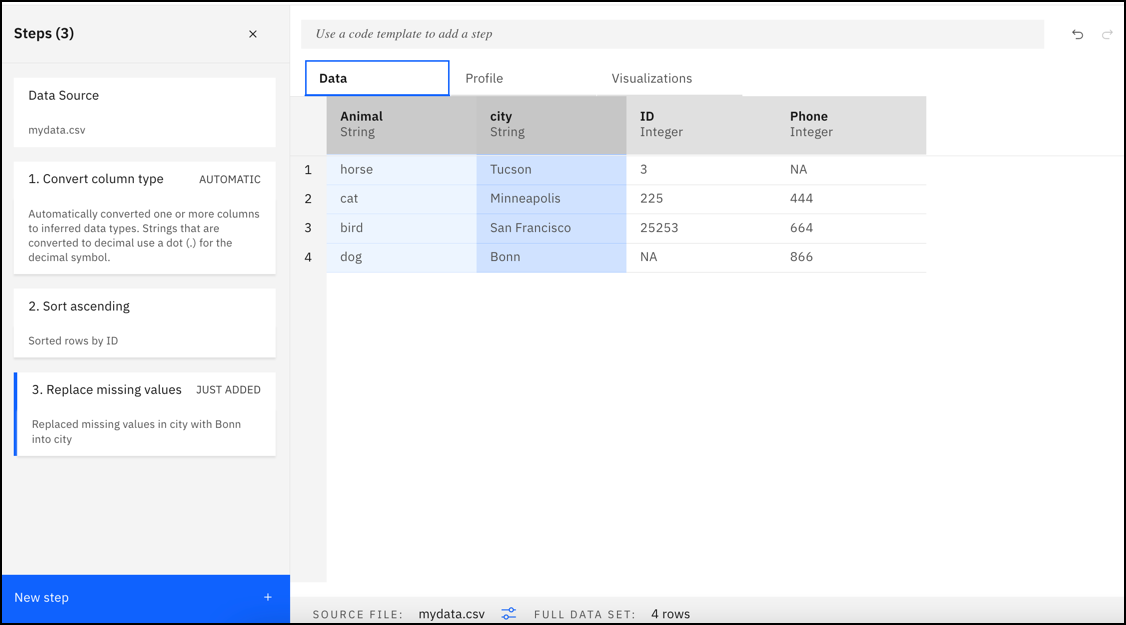
If your data contains non-string data types, the Convert column type GUI operation is automatically applied as the first step in the Data Refinery flow when you open a file in Data Refinery. Data types are automatically converted to inferred data types, such as Integer, Date, or Boolean. You can undo or edit this step.
4. Click the Visualizations tab to visualize the data in charts. Uncover patterns, trends, and correlations within your data.
Visualizations tab
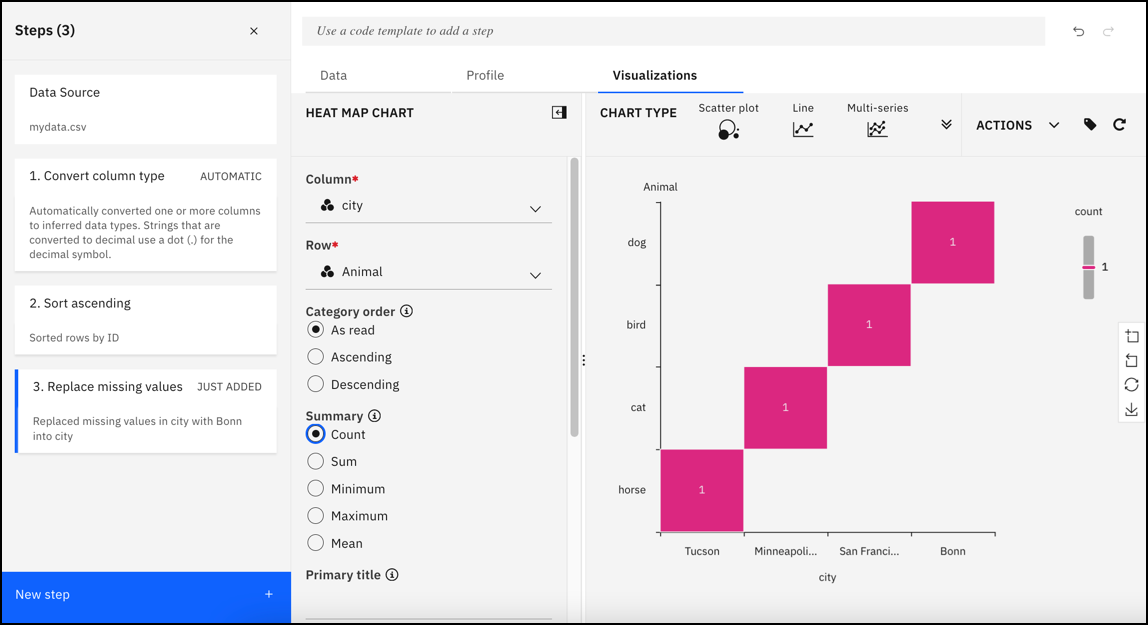
5. Refine the sample data set to suit your needs.
6. Click Save and create a job or Save and view jobs in the toolbar to run the Data Refinery flow on the entire data set. Select the runtime and add a one-time or repeating schedule. For information about jobs, see Creating jobs in Data Refinery.
For the actions that you can do as you refine your data, see Managing Data Refinery flows.
Learn more
Parent topic: Preparing and integrating data